A new study explores ketamine's impact on the brain and provides hope for those suffering from treatment-resistant depression.
Ketamine shows complex neural patterns, affecting inhibitory and excitatory brain circuits.led by Flora Moujaes at Yale University investigates ketamine's effects on brain activity and behavior in healthy individuals, revealing complexpatterns. Understanding these nuances could lead to more targeted treatments for depression, offering hope for those who have not responded to conventional
Ketamine was developed in the 1960s to be used as a battlefield anesthetic in the Vietnam War as well as in health care settings. It was historically used in highly regulated and supervised health care facilities but its usage has changed significantly since then.Ketamine is approved by the United States Food and Drug Administration as an anesthetic and is widely used for short, painful procedures that require immobilization.
This may be due to the influence it has between different parts of the brain; for example, the connection between two excitatory parts of the brain or between an excitatory part and an inhibitory part. It may also target specific types of cells in the brain more strongly based on their receptor makeup. Or it could be affecting various smaller circuits within the brain.
United Kingdom Latest News, United Kingdom Headlines
Similar News:You can also read news stories similar to this one that we have collected from other news sources.
 Work That Challenges Your Brain Helps You Stay Sharp With AgeJobs that challenge your mind could help your brain age more gracefully, a new study suggests.
Work That Challenges Your Brain Helps You Stay Sharp With AgeJobs that challenge your mind could help your brain age more gracefully, a new study suggests.
Read more »
 Our brains are growing. Will that help prevent dementia?UC Davis study finds brain size has steadily increased for people born after the 1930s.
Our brains are growing. Will that help prevent dementia?UC Davis study finds brain size has steadily increased for people born after the 1930s.
Read more »
 Brain imaging study reveals connections critical to human consciousnessA new study involved high-resolution scans that enabled the researchers to visualize brain connections at submillimeter spatial resolution. Together, these pathways form a 'default ascending arousal network' that sustains wakefulness in the resting, conscious human brain.
Brain imaging study reveals connections critical to human consciousnessA new study involved high-resolution scans that enabled the researchers to visualize brain connections at submillimeter spatial resolution. Together, these pathways form a 'default ascending arousal network' that sustains wakefulness in the resting, conscious human brain.
Read more »
 San Antonio facility wins $17 million military contract to study traumatic brain injuryA consortium based at the University of Texas Health Science Center (UTHSC) at San Antonio has landed a $17 million Defense Department contract to launch eight new research projects dealing with traumatic brain injury and psychological health, according to officials with the school.
San Antonio facility wins $17 million military contract to study traumatic brain injuryA consortium based at the University of Texas Health Science Center (UTHSC) at San Antonio has landed a $17 million Defense Department contract to launch eight new research projects dealing with traumatic brain injury and psychological health, according to officials with the school.
Read more »
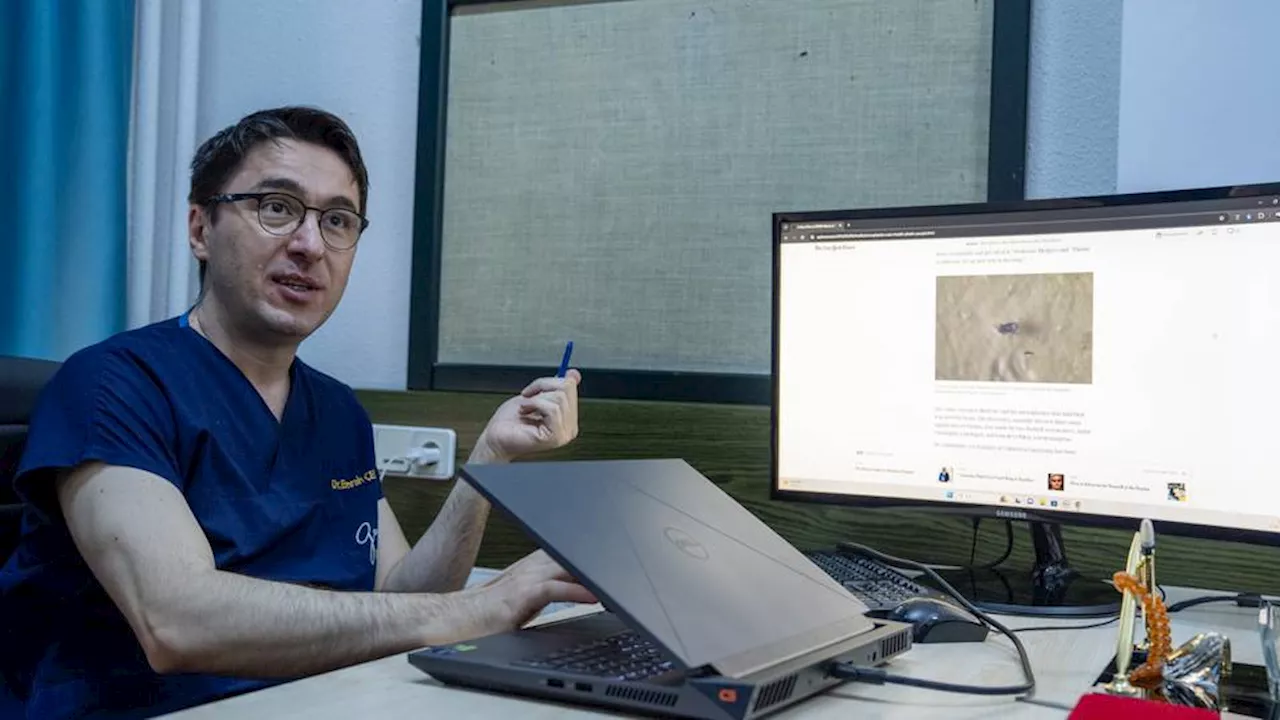 Turkish study finds microplastics in brain cellsThe study conducted by Turkish scientists quickly gains global recognition and receives offers from countries, particularly the US and Canada.
Turkish study finds microplastics in brain cellsThe study conducted by Turkish scientists quickly gains global recognition and receives offers from countries, particularly the US and Canada.
Read more »
 Groundbreaking Study Links Tiny Brain Bubbles to Alzheimer’s ProgressionScience, Space and Technology News 2024
Groundbreaking Study Links Tiny Brain Bubbles to Alzheimer’s ProgressionScience, Space and Technology News 2024
Read more »
