Science, Space and Technology News 2024
Researchers at Baylor College of Medicine have developed a new technology, tARC-seq, which improves the detection of mutations in SARS-CoV-2, helping explain the rapid emergence of variants by identifying hotspots and mechanisms like template switching that contribute to the virus’s evolution. Credit: SciTechDaily.comSARS-CoV-2The SARS-CoV-2 virus that causes COVID has the unsettling ability of often generating variants of itself.
The researchers wanted to follow RNA replication errors because they are crucial for understanding how the virus evolves, how it changes and adapts as it spreads in the human population, but current methods lacked the precision to detect rare new SARS-CoV-2 mutations, particularly in samples with a low number of viruses, such as those from patients.
“This idea contrasted with the fact that during the pandemic new COVID variants emerged often around the world,” Herman said. “Since the pandemic began, we’ve seen a number of prominent variants, including Alpha, Beta, Delta and Omicron, as well as variants within these groups.” They also discovered that there are hotspots in SARS-CoV-2 RNA, locations that are more prone to mutation than others. “For example, we identified a hotspot on the RNA region corresponding to the spike protein, the protein that allows the virus to invade cells. Also, RNA of the spike protein makes up many vaccines,” Herman said.
United Kingdom Latest News, United Kingdom Headlines
Similar News:You can also read news stories similar to this one that we have collected from other news sources.
 High-throughput RNA isoform sequencing using programmed cDNA concatenationFull-length RNA-sequencing methods using long-read technologies can capture complete transcript isoforms, but their throughput is limited.
High-throughput RNA isoform sequencing using programmed cDNA concatenationFull-length RNA-sequencing methods using long-read technologies can capture complete transcript isoforms, but their throughput is limited.
Read more »
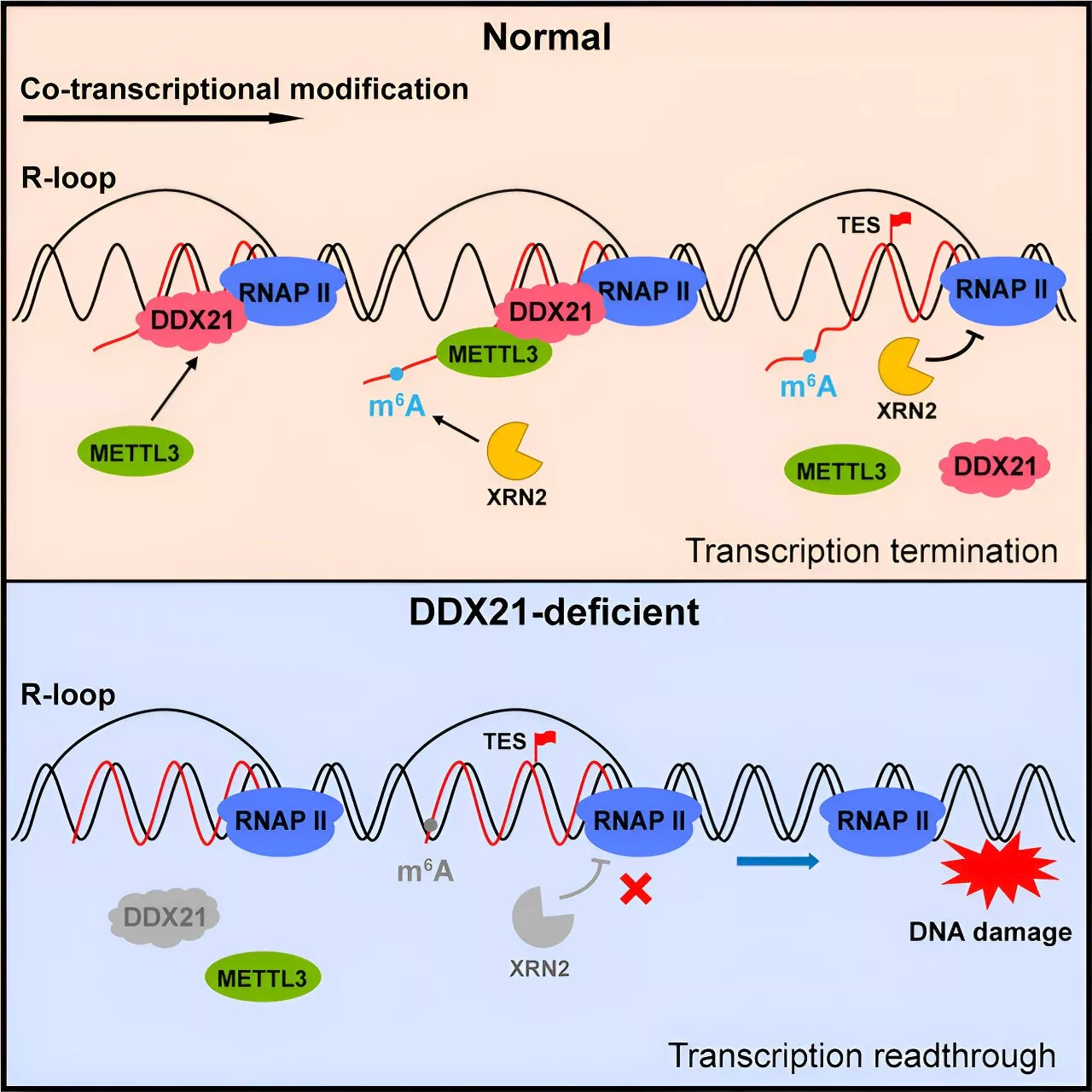 Researchers reveal mechanism behind most common mammalian mRNA modificationRNA—in the form of messenger RNA (mRNA), ribosomal RNA (rRNA), and transfer RNA (tRNA)—transforms the genome coded by DNA into proteins that form the backbone of all cellular functions. However, biochemical modifications to RNA frequently occur, with a subsequent influence on gene expression and the potential to cause disease.
Researchers reveal mechanism behind most common mammalian mRNA modificationRNA—in the form of messenger RNA (mRNA), ribosomal RNA (rRNA), and transfer RNA (tRNA)—transforms the genome coded by DNA into proteins that form the backbone of all cellular functions. However, biochemical modifications to RNA frequently occur, with a subsequent influence on gene expression and the potential to cause disease.
Read more »
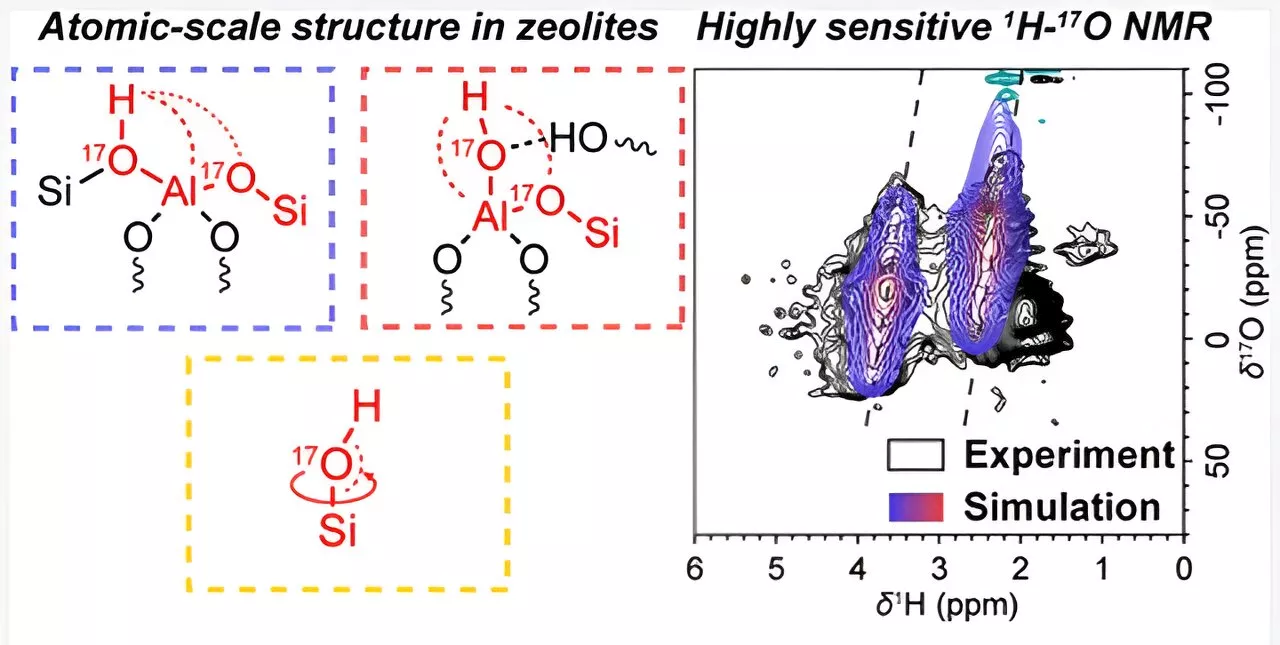 Advanced nuclear magnetic resonance technique reveals precise structural, dynamical details in zeolitesZeolites are widely used in many industries, yet their intrinsic catalytic nature is not completely understood, due to the complexity of the hydroxyl-aluminum moieties.
Advanced nuclear magnetic resonance technique reveals precise structural, dynamical details in zeolitesZeolites are widely used in many industries, yet their intrinsic catalytic nature is not completely understood, due to the complexity of the hydroxyl-aluminum moieties.
Read more »
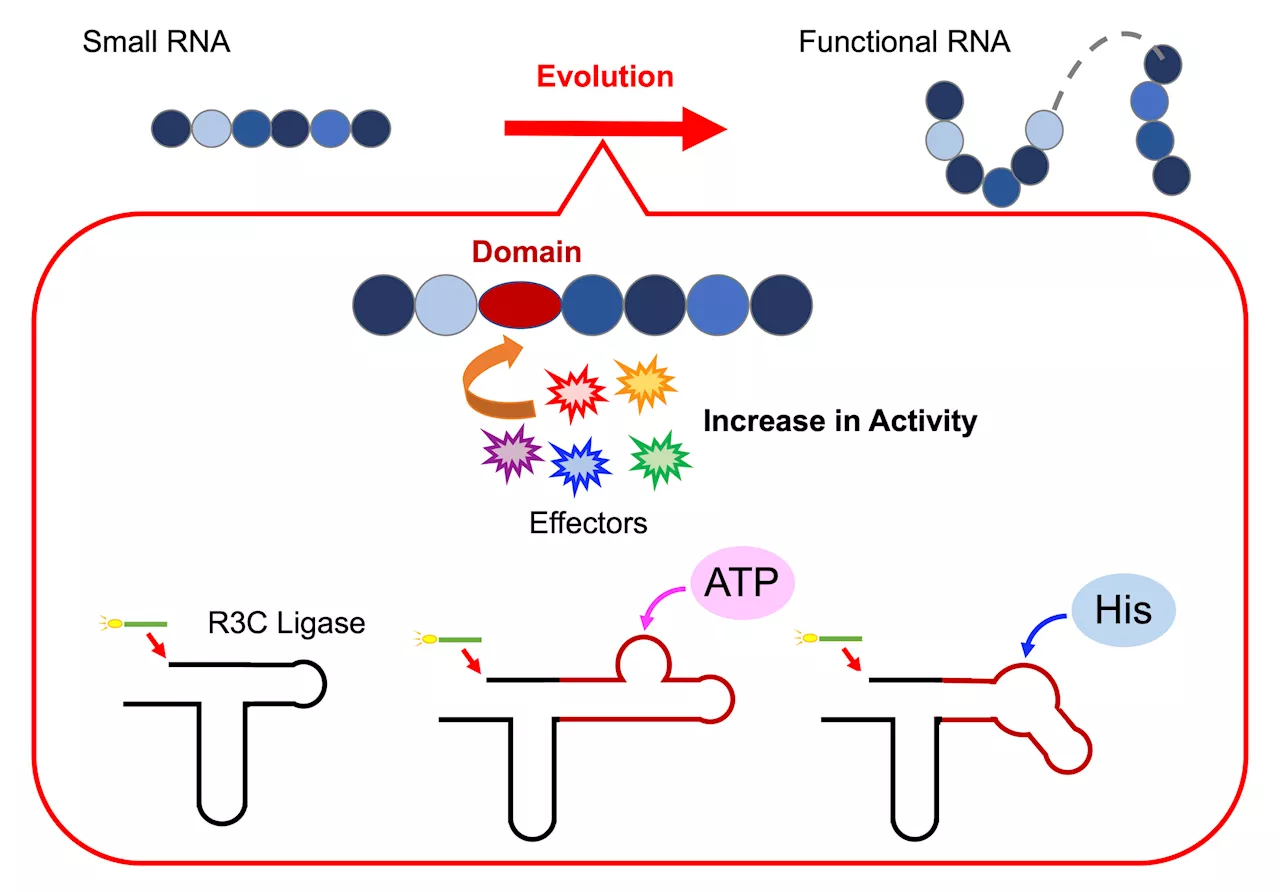 RNA's hidden potential: New study unveils its role in early life and future bioengineeringThe beginning of life on Earth and its evolution over billions of years continue to intrigue researchers worldwide.
RNA's hidden potential: New study unveils its role in early life and future bioengineeringThe beginning of life on Earth and its evolution over billions of years continue to intrigue researchers worldwide.
Read more »
 RNA's hidden potential: New study unveils its role in early life and future bioengineeringThe origin of life continues to remain a matter of debate. The ribonucleic acid (RNA) world hypothesis proposes that 'ribozymes' which store genetic information and possess catalytic functions may have supported the activities of early life forms.
RNA's hidden potential: New study unveils its role in early life and future bioengineeringThe origin of life continues to remain a matter of debate. The ribonucleic acid (RNA) world hypothesis proposes that 'ribozymes' which store genetic information and possess catalytic functions may have supported the activities of early life forms.
Read more »
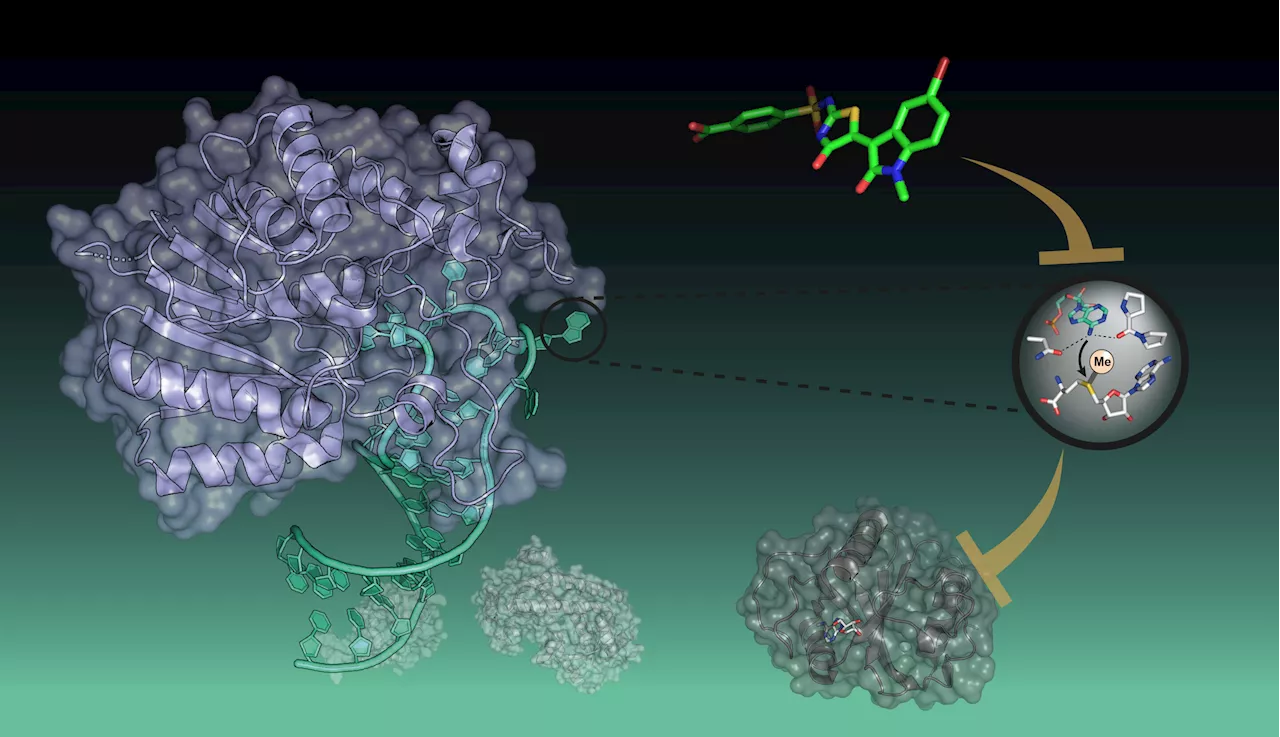 A promising target for new RNA therapeutics now accessibleOnly recently, a new era in medicine began with the first RNA vaccines. These active substances are modified RNAs that trigger immune responses of the human immune system. Another approach in RNA medicine targets the body's own RNA and its protein modulators by specifically tailored active substances.
A promising target for new RNA therapeutics now accessibleOnly recently, a new era in medicine began with the first RNA vaccines. These active substances are modified RNAs that trigger immune responses of the human immune system. Another approach in RNA medicine targets the body's own RNA and its protein modulators by specifically tailored active substances.
Read more »
