Researchers develop an AI model to accurately predict prognosis for patients with non-small cell lung cancer after surgery. The model, which utilized a range of preoperative and postoperative blood test results, achieved high prediction accuracy, offering a promising approach for personalized treatment plans.
By Dr. Priyom Bose, Ph.D.Sep 25 2023Reviewed by Benedette Cuffari, M.Sc. A recent Scientific Reports study discusses the development of an artificial intelligence prognostic model for surgically resected non-small cell lung cancer .
Multiple prognostic factors for postoperative prognosis associated with NSCLC have been identified, including geriatric nutritional risk index, Glasgow prognostic score, neutrophil/lymphocyte ratio, C-reactive protein /albumin ratio, prognostic nutritional index, platelet/lymphocyte ratio, and monocyte/lymphocyte ratio. To date, few studies have described the importance of blood test results in NSCLC prognosis.
A total of 1,049 patients with pathological stage I-IIIA NSCLC who underwent surgery between January 2003 and December 2016 were recruited for the study. The median age of the participants at surgery was 69 years, about 58% of whom were male. XGBoost, a decision-free model, was selected as the algorithm for this AI prognostic model. XGBoost is advantageous as compared to other AI tools due to its ability to use missing values directly as information.
The newly developed AI prognostic model used time-dependent receiver operating characteristic curves and area under the curve values to predict DFS, OS, and CSS, all of which were associated with good prediction accuracy. Notably, the predicted probability of outcome events at five years following surgery was highly accurate.
Histological type was found to be one of the most important factors of prognosis in this AI model. The prognoses of adenosquamous, pleomorphic, and large-cell neuroendocrine carcinoma were worst compared to other histological types. Thus, a more detailed analysis of histological type would improve the prognostic accuracy.
United Kingdom Latest News, United Kingdom Headlines
Similar News:You can also read news stories similar to this one that we have collected from other news sources.
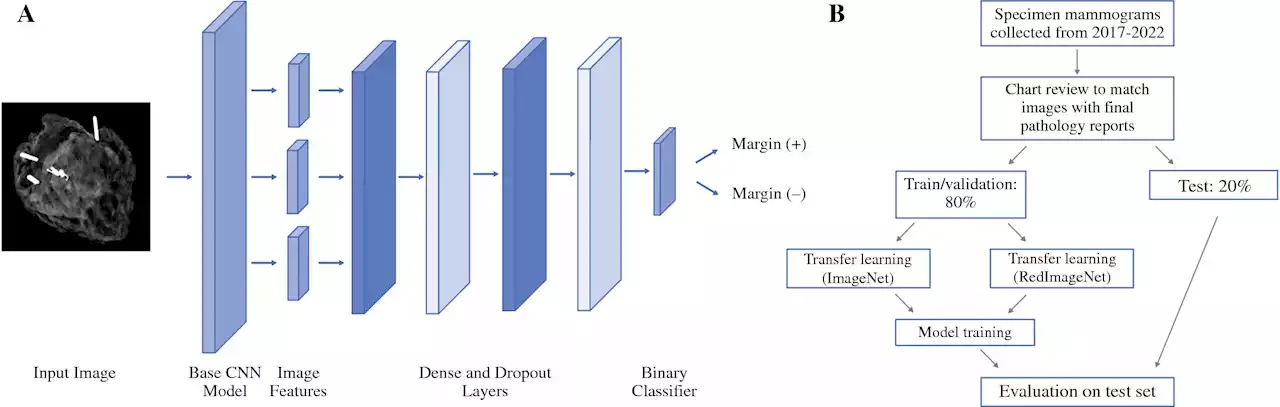 Researchers develop AI model to improve tumor removal accuracy during breast cancer surgeryArtificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning tools have received a lot of attention recently, with the majority of discussions focusing on proper use. However, this technology has a wide range of practical applications, from predicting natural disasters to addressing racial inequalities and now, assisting in cancer surgery.
Researchers develop AI model to improve tumor removal accuracy during breast cancer surgeryArtificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning tools have received a lot of attention recently, with the majority of discussions focusing on proper use. However, this technology has a wide range of practical applications, from predicting natural disasters to addressing racial inequalities and now, assisting in cancer surgery.
Read more »
 Medical researchers tackle immune rejection of biomedical implantsTo learn more about what causes the body to reject biomedical implants, a team at the University of Arizona College of Medicine-Tucson identified a protein that appears to help drive this response, and hopes their discoveries will improve the design and safety of biomedical implants. The findings were published today in Nature Biomedical Engineering.
Medical researchers tackle immune rejection of biomedical implantsTo learn more about what causes the body to reject biomedical implants, a team at the University of Arizona College of Medicine-Tucson identified a protein that appears to help drive this response, and hopes their discoveries will improve the design and safety of biomedical implants. The findings were published today in Nature Biomedical Engineering.
Read more »
 Researchers find contaminated water in fast-food soda fountainsLoma Linda University (LLU) researchers found microbial contamination in common sources of drinking water in the Eastern Coachella Valley, including soda fountains at fast-food restaurants. Their findings revealed that 41% of the water samples researchers collected from these soda fountains contained total coliforms, an indicator of water contamination.
Researchers find contaminated water in fast-food soda fountainsLoma Linda University (LLU) researchers found microbial contamination in common sources of drinking water in the Eastern Coachella Valley, including soda fountains at fast-food restaurants. Their findings revealed that 41% of the water samples researchers collected from these soda fountains contained total coliforms, an indicator of water contamination.
Read more »
 Researchers describe clinical experiences of transgender people, recommend new strategiesMany transgender people experience mistreatment in health care encounters, which can include harassment, assault and denial of care. A new paper published in the September/October 2023 issue of Annals of Family Medicine describes the clinical experiences of transgender people. Study authors also present short-term and long-term strategies towards reducing oppression and its health consequences among this patient population.
Researchers describe clinical experiences of transgender people, recommend new strategiesMany transgender people experience mistreatment in health care encounters, which can include harassment, assault and denial of care. A new paper published in the September/October 2023 issue of Annals of Family Medicine describes the clinical experiences of transgender people. Study authors also present short-term and long-term strategies towards reducing oppression and its health consequences among this patient population.
Read more »
 Researchers identify important strategies for diabetes care and quality improvements in the primary care settingA qualitative study published in the Annals of Family Medicine considers how the strategies used by high-performing primary care practices to improve diabetes care might play a role in successfully managing practice change.
Researchers identify important strategies for diabetes care and quality improvements in the primary care settingA qualitative study published in the Annals of Family Medicine considers how the strategies used by high-performing primary care practices to improve diabetes care might play a role in successfully managing practice change.
Read more »
 Researchers develop new method to deliver strong antibiotic drugs more safelyAntibiotic resistant bacteria are a threat to human lives, and yet the development of new drugs to treat bacterial infections is slow.
Researchers develop new method to deliver strong antibiotic drugs more safelyAntibiotic resistant bacteria are a threat to human lives, and yet the development of new drugs to treat bacterial infections is slow.
Read more »
