AI model NYUTron shows remarkable accuracy in clinical tasks using handwritten physician notes Clinical Healthcare AI LanguageModels HealthTech PatientCare HealthData NaturalLanguage HealthInformatics Nature
Study: Health system-scale language models are all-purpose prediction engines. Image Credit: Elnur / Shutterstock
On the other hand, artificial intelligence -based large language models rely on reading and interpreting human language. Thus, the researchers theorized that LLMs could read handwritten physician notes to solve the last-mile problem. In this way, these LLMs could facilitate medical decision-making at the point of care for a broad range of clinical and operational tasks.
In retrospective evaluations, they head-to-head compared six physicians at different levels of seniority against NYUTron. In prospective evaluations running between January and April 2022, the team tested NYUTron in an accelerated format. They loaded it into an inference engine which interfaced with the EHR and read discharge notes duly signed by treating physicians.
Related StoriesReadmission prediction is a well-studied task in the published literature on medical informatics. In its retrospective evaluation, NYUTron performed better than a physician, with a median false positive rate of 11.11% for both NYUTron and the physician. However, the median true positive rate was higher for NYUTron than physicians, 81.72% vs. 50%.
The researchers used 24 NVIDIA A100 GPUs with 40 GB of VRAM for three weeks for pretraining NYUTron, and eight A100 GPUs for six hours per run for fine-tuning. Generally, this amount of computation is inaccessible to researchers. However, the study data demonstrated that high-quality datasets for fine-tuning were more valuable than pretraining. Based on their experimental results, the authors recommended that users use local fine-tuning when their computational ability is limited.
United Kingdom Latest News, United Kingdom Headlines
Similar News:You can also read news stories similar to this one that we have collected from other news sources.
 Birthweight is associated with clinical characteristics in people with recently diagnosed type 2 diabetes - DiabetologiaAims/hypothesis Low birthweight is a risk factor for type 2 diabetes but it is unknown whether low birthweight is associated with distinct clinical characteristics at disease onset. We examined whether a lower or higher birthweight in type 2 diabetes is associated with clinically relevant characteristics at disease onset. Methods Midwife records were traced for 6866 individuals with type 2 diabetes in the Danish Centre for Strategic Research in Type 2 Diabetes (DD2) cohort. Using a cross-sectional design, we assessed age at diagnosis, anthropomorphic measures, comorbidities, medications, metabolic variables and family history of type 2 diabetes in individuals with the lowest 25% of birthweight (3700 g), compared with a birthweight of 3000–3700 g as reference, using log-binomial and Poisson regression. Continuous relationships across the entire birthweight spectrum were assessed with linear and restricted cubic spline regression. Weighted polygenic scores (PS) for type 2 diabetes and birthweight were calculated to assess the impact of genetic predispositions. Results Each 1000 g decrease in birthweight was associated with a 3.3 year (95% CI 2.9, 3.8) younger age of diabetes onset, 1.5 kg/m2 (95% CI 1.2, 1.7) lower BMI and 3.9 cm (95% CI 3.3, 4.5) smaller waist circumference. Compared with the reference birthweight, a birthweight of |3000 g was associated with more overall comorbidity (prevalence ratio [PR] for Charlson Comorbidity Index Score ≥3 was 1.36 [95% CI 1.07, 1.73]), having a systolic BP ≥155 mmHg (PR 1.26 [95% CI 0.99, 1.59]), lower prevalence of diabetes-associated neurological disease, less likelihood of family history of type 2 diabetes, use of three or more glucose-lowering drugs (PR 1.33 [95% CI 1.06, 1.65]) and use of three or more antihypertensive drugs (PR 1.09 [95% CI 0.99, 1.20]). Clinically defined low birthweight (|2500 g) yielded stronger associations. Most associations between birthweight and clinical characteristics appeared linear, and a hig
Birthweight is associated with clinical characteristics in people with recently diagnosed type 2 diabetes - DiabetologiaAims/hypothesis Low birthweight is a risk factor for type 2 diabetes but it is unknown whether low birthweight is associated with distinct clinical characteristics at disease onset. We examined whether a lower or higher birthweight in type 2 diabetes is associated with clinically relevant characteristics at disease onset. Methods Midwife records were traced for 6866 individuals with type 2 diabetes in the Danish Centre for Strategic Research in Type 2 Diabetes (DD2) cohort. Using a cross-sectional design, we assessed age at diagnosis, anthropomorphic measures, comorbidities, medications, metabolic variables and family history of type 2 diabetes in individuals with the lowest 25% of birthweight (3700 g), compared with a birthweight of 3000–3700 g as reference, using log-binomial and Poisson regression. Continuous relationships across the entire birthweight spectrum were assessed with linear and restricted cubic spline regression. Weighted polygenic scores (PS) for type 2 diabetes and birthweight were calculated to assess the impact of genetic predispositions. Results Each 1000 g decrease in birthweight was associated with a 3.3 year (95% CI 2.9, 3.8) younger age of diabetes onset, 1.5 kg/m2 (95% CI 1.2, 1.7) lower BMI and 3.9 cm (95% CI 3.3, 4.5) smaller waist circumference. Compared with the reference birthweight, a birthweight of |3000 g was associated with more overall comorbidity (prevalence ratio [PR] for Charlson Comorbidity Index Score ≥3 was 1.36 [95% CI 1.07, 1.73]), having a systolic BP ≥155 mmHg (PR 1.26 [95% CI 0.99, 1.59]), lower prevalence of diabetes-associated neurological disease, less likelihood of family history of type 2 diabetes, use of three or more glucose-lowering drugs (PR 1.33 [95% CI 1.06, 1.65]) and use of three or more antihypertensive drugs (PR 1.09 [95% CI 0.99, 1.20]). Clinically defined low birthweight (|2500 g) yielded stronger associations. Most associations between birthweight and clinical characteristics appeared linear, and a hig
Read more »
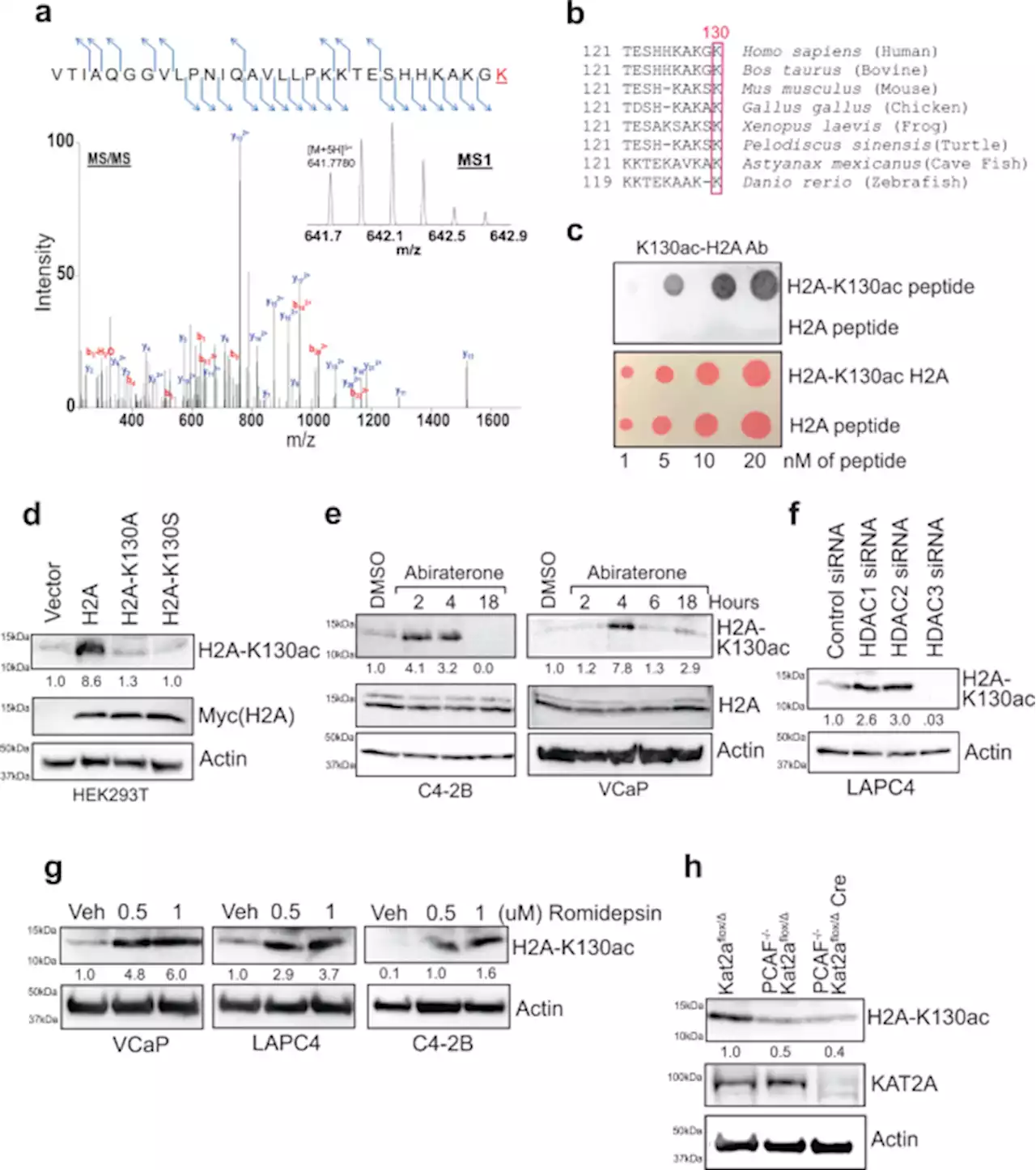 Histone H2A Lys130 acetylation epigenetically regulates androgen production in prostate cancer - Nature CommunicationsThe molecular mechanisms underlying androgen production in prostate cancer remain to be explored. Here, the authors reveal an epigenetic mark, K130Ac on H2A, following dual-phosphorylation on SREBP1 promoting de novo androgen synthesis to overcome the pharmacological inhibition of androgen synthesis.
Histone H2A Lys130 acetylation epigenetically regulates androgen production in prostate cancer - Nature CommunicationsThe molecular mechanisms underlying androgen production in prostate cancer remain to be explored. Here, the authors reveal an epigenetic mark, K130Ac on H2A, following dual-phosphorylation on SREBP1 promoting de novo androgen synthesis to overcome the pharmacological inhibition of androgen synthesis.
Read more »
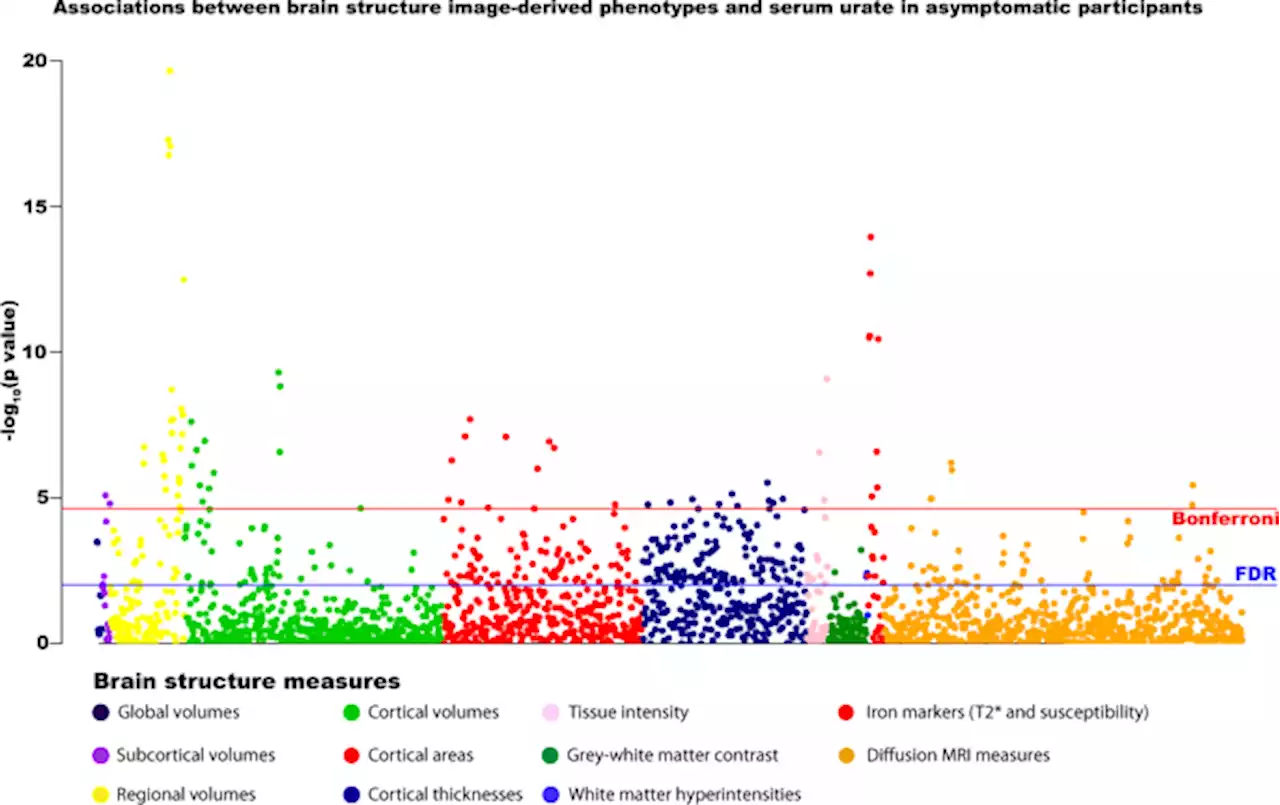 Association of gout with brain reserve and vulnerability to neurodegenerative disease - Nature CommunicationsThe potential association between neurodegenerative disease risk and gout is not fully understood. Here the authors showed that gout is causally related to several measures of brain structure which may explain their higher vulnerability to dementia.
Association of gout with brain reserve and vulnerability to neurodegenerative disease - Nature CommunicationsThe potential association between neurodegenerative disease risk and gout is not fully understood. Here the authors showed that gout is causally related to several measures of brain structure which may explain their higher vulnerability to dementia.
Read more »
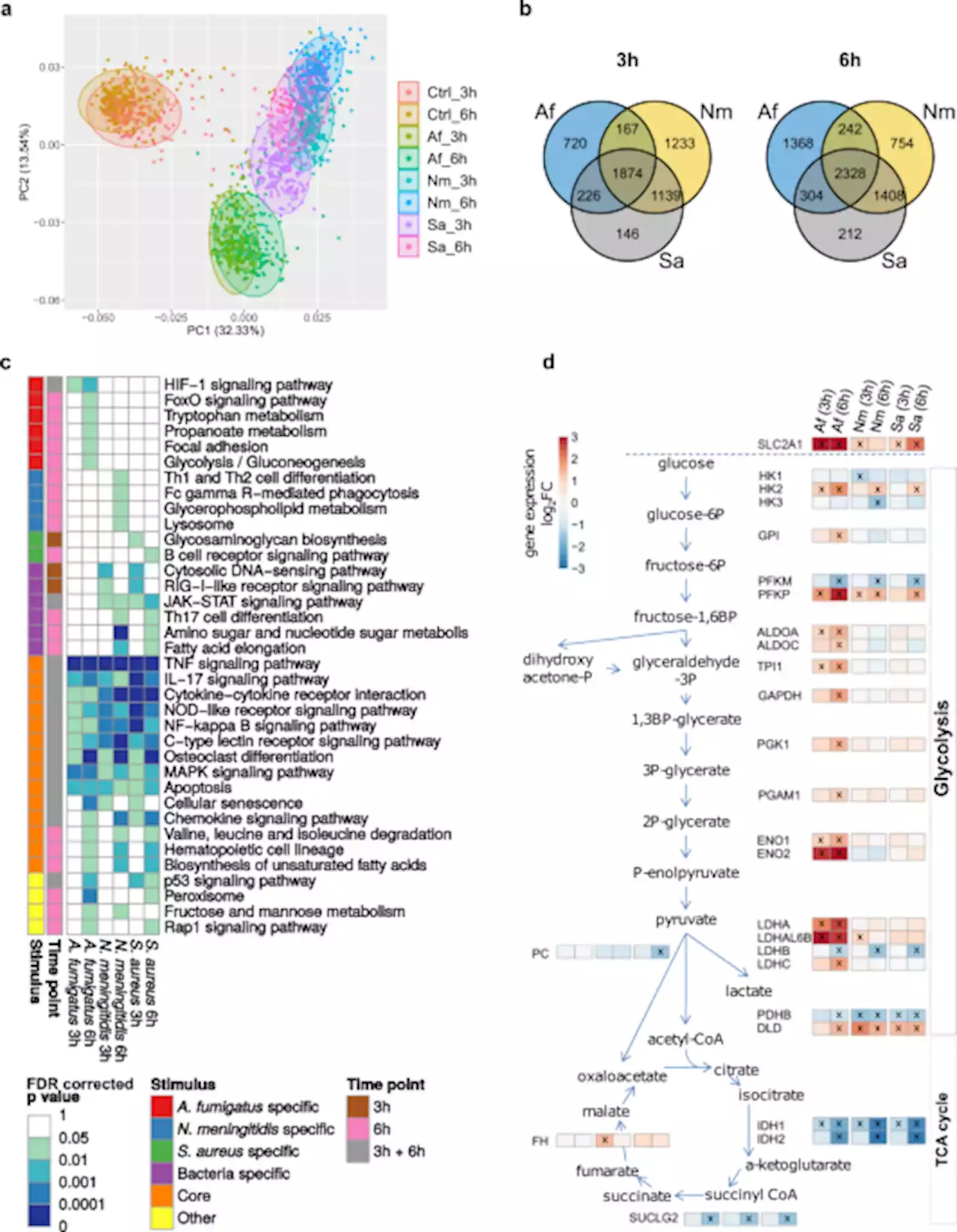 Pathogen-specific innate immune response patterns are distinctly affected by genetic diversity - Nature CommunicationsLooking at genes that are differentially responsive to pathogens depending on the genetic background may help in the identification of therapeutic targets in personalized medicine. Here, using challenge of monocytes with three pathogens the authors identified eQTL that are shared between pathogens and loci that are pathogen specific.
Pathogen-specific innate immune response patterns are distinctly affected by genetic diversity - Nature CommunicationsLooking at genes that are differentially responsive to pathogens depending on the genetic background may help in the identification of therapeutic targets in personalized medicine. Here, using challenge of monocytes with three pathogens the authors identified eQTL that are shared between pathogens and loci that are pathogen specific.
Read more »
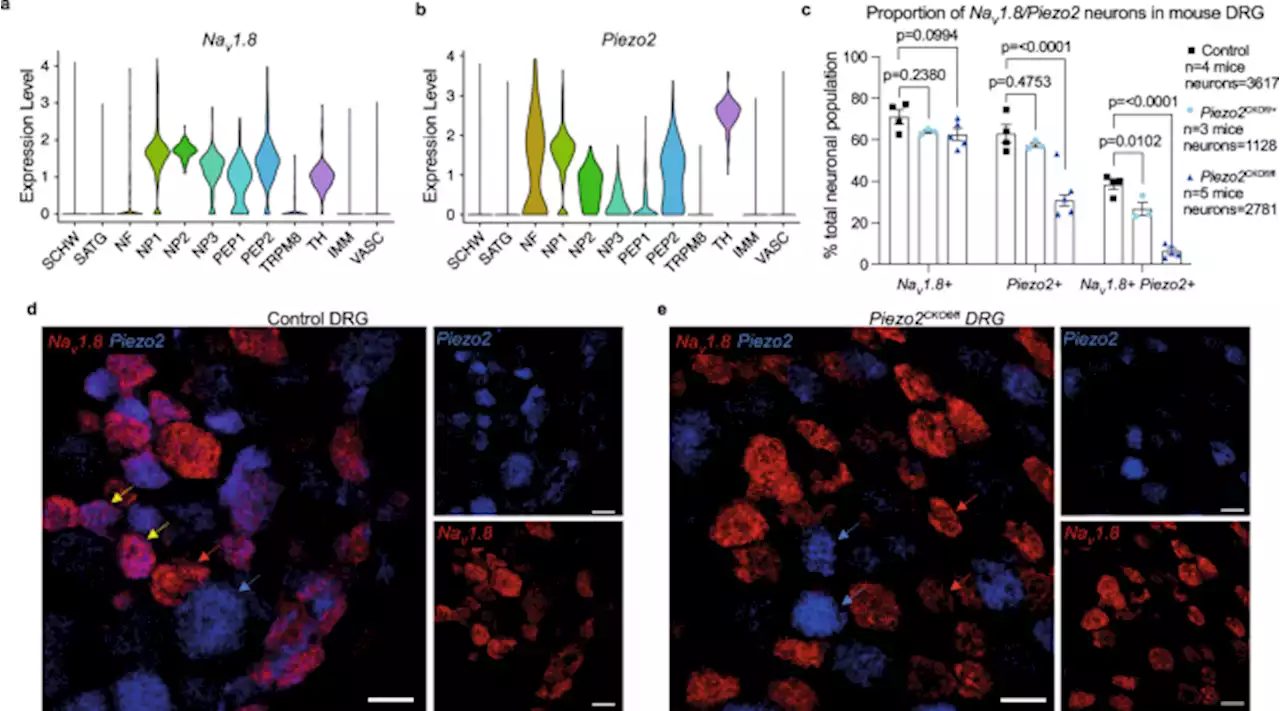 Piezo2 expressing nociceptors mediate mechanical sensitization in experimental osteoarthritis - Nature CommunicationsOsteoarthritis is characterized by mechanically driven pain but lacks adequate treatments. Here, the authors show that inhibiting a mechanically-sensitive ion channel expressed by nociceptors reduces pain behaviors in mouse models of joint pain.
Piezo2 expressing nociceptors mediate mechanical sensitization in experimental osteoarthritis - Nature CommunicationsOsteoarthritis is characterized by mechanically driven pain but lacks adequate treatments. Here, the authors show that inhibiting a mechanically-sensitive ion channel expressed by nociceptors reduces pain behaviors in mouse models of joint pain.
Read more »
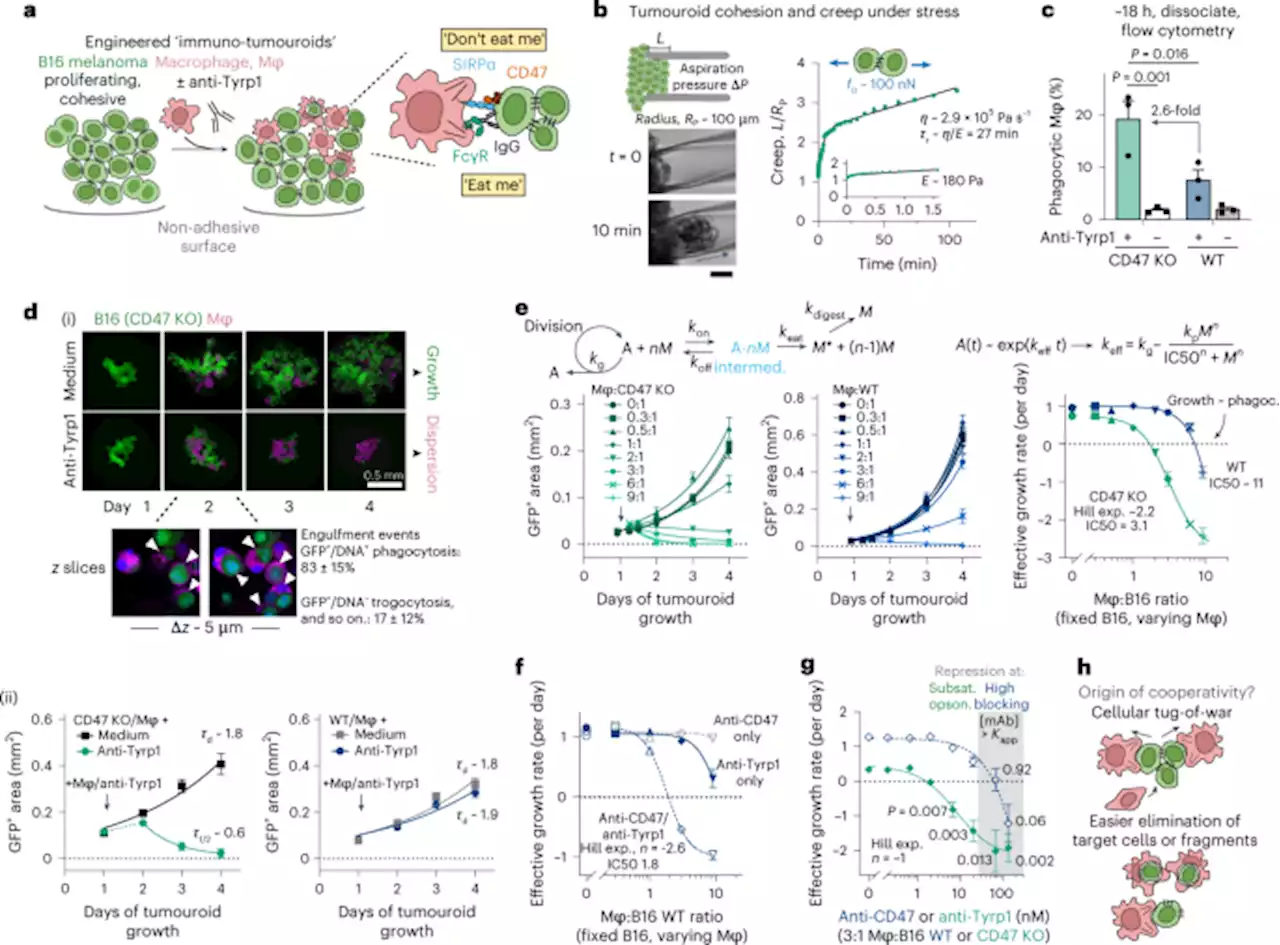 Cooperative phagocytosis of solid tumours by macrophages triggers durable anti-tumour responses - Nature Biomedical EngineeringDurable anti-tumour responses can be triggered by maximizing the cooperative phagocytic potency of macrophages through the disruption of the CD47–SIRPα macrophage checkpoint and by delivering a tumour-opsonizing monoclonal antibody.
Cooperative phagocytosis of solid tumours by macrophages triggers durable anti-tumour responses - Nature Biomedical EngineeringDurable anti-tumour responses can be triggered by maximizing the cooperative phagocytic potency of macrophages through the disruption of the CD47–SIRPα macrophage checkpoint and by delivering a tumour-opsonizing monoclonal antibody.
Read more »
