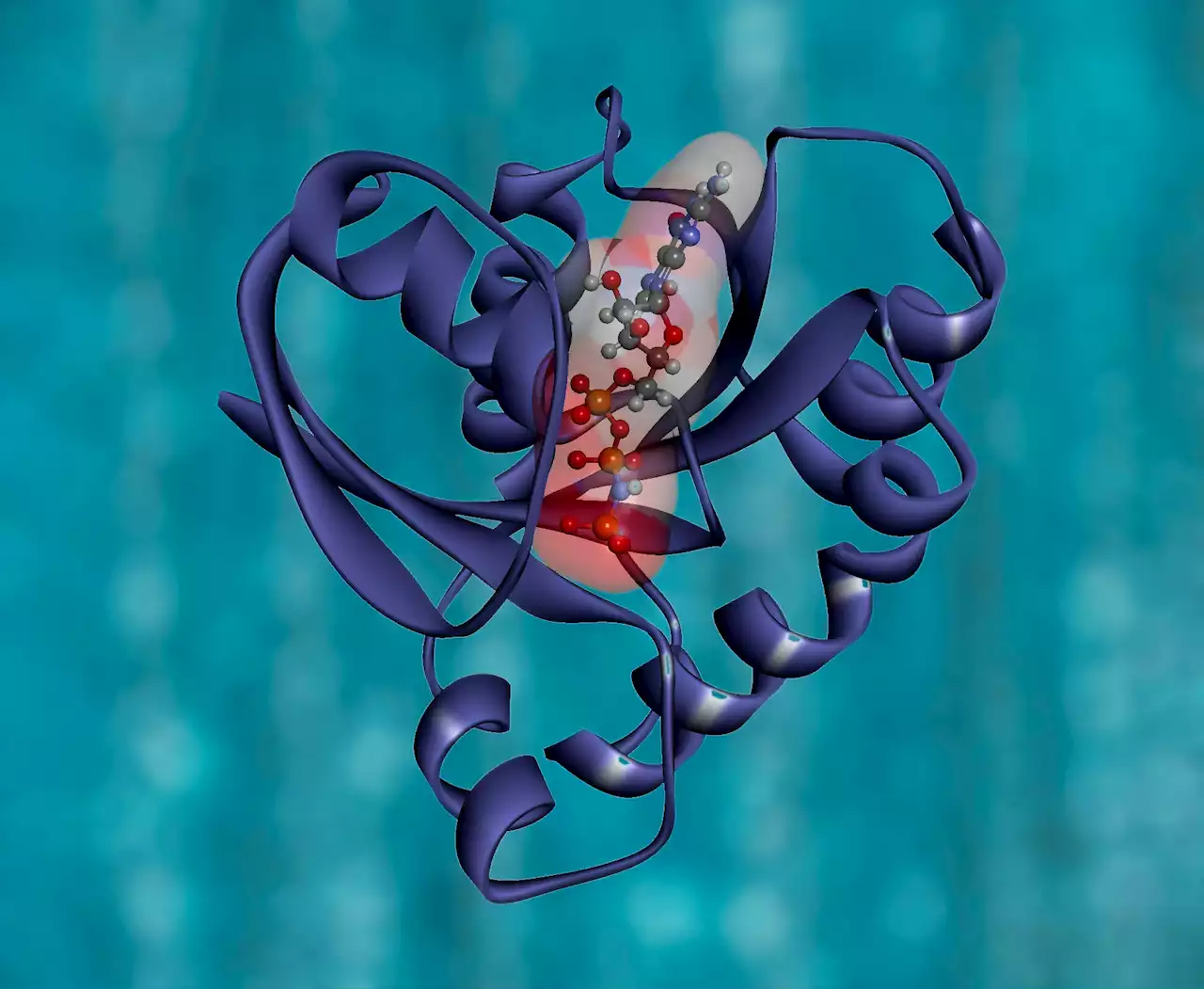
Autoimmune diseases are complex illnesses, the causes of which are diverse and have not yet been fully explained. A research team at MedUni Vienna has now discovered an immunoregulatory protein that could be linked to the development of autoimmune diseases such as rheumatoid arthritis. The identified component of the immune system is called 'Rinl,' which could provide a new target for the development of immunomodulatory therapies. The study results were recently published in the Journal of Experimental Medicine.
Autoimmune diseases are complex illnesses, the causes of which are diverse and have not yet been fully explained. A research team at MedUni Vienna has now discovered an immunoregulatory protein that could be linked to the development of autoimmune diseases such as rheumatoid arthritis. The identified component of the immune system is called"Rinl," which could provide a new target for the development of immunomodulatory therapies.
While a deficiency or excess of Rin 1-3 proteins has already been linked in recent years in international studies, for example, to cancer, Alzheimer's disease or the spinal disease scoliosis, Rinl has so far been little researched.has been clarified by the scientific team as part of the current study.
Tfh are a subset of T cells and support the maturation of other essential components of the immune system, the B cells. Mature B cells, in turn, produce highly effective antibodies and thus play a major role in the body's immune response: in vaccinations, a large amount of such antibodies is desired, but in
United Kingdom Latest News, United Kingdom Headlines
Similar News:You can also read news stories similar to this one that we have collected from other news sources.
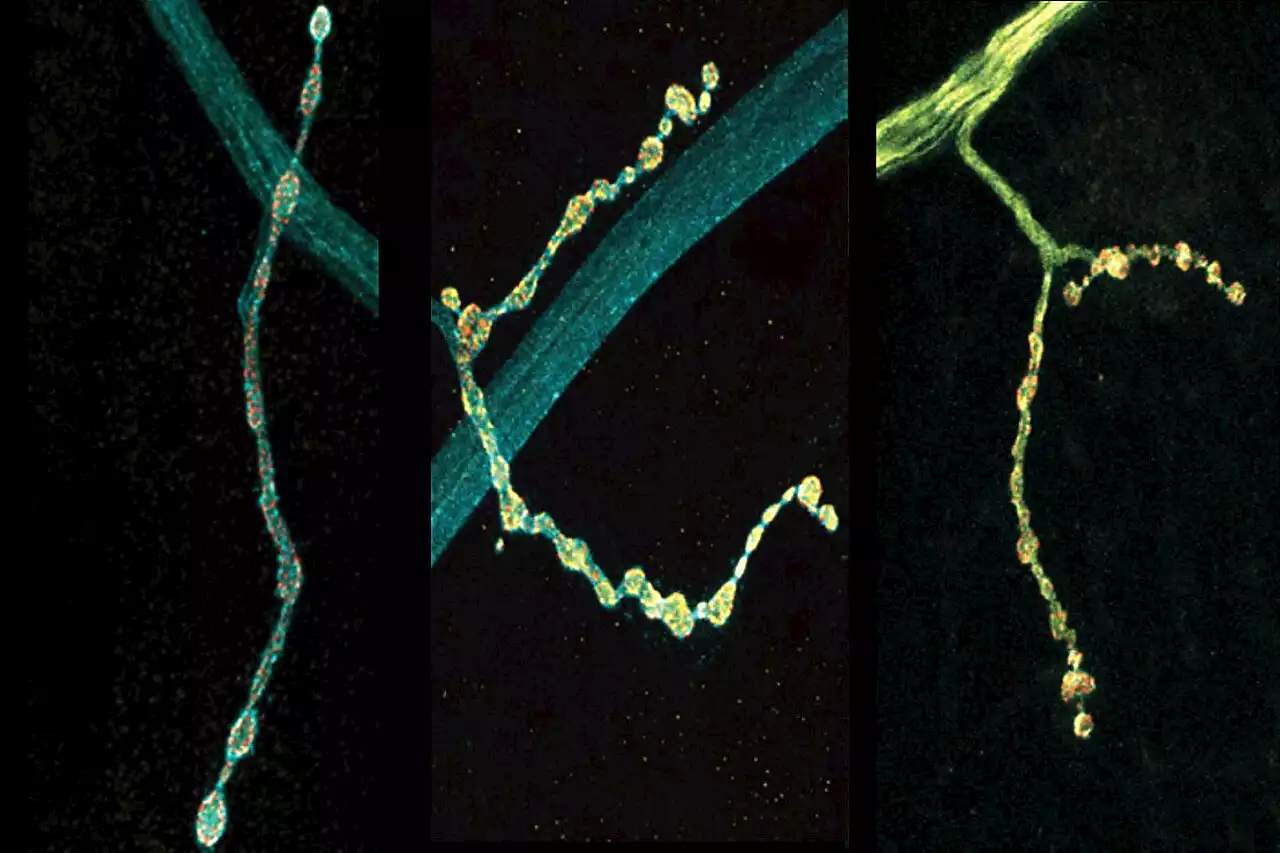 Individual neurons mix multiple RNA edits of key synapse protein, fly study findsNeurons are talkers. They each communicate with fellow neurons, muscles or other cells by releasing neurotransmitter chemicals at 'synapse' junctions, ultimately producing functions ranging from emotions to motions. But even neurons of the exact same type can vary in their conversational style. A new study in Cell Reports by neurobiologists at The Picower Institute for Learning and Memory highlights a molecular mechanism that might help account for the nuanced diversity of neural discourse.
Individual neurons mix multiple RNA edits of key synapse protein, fly study findsNeurons are talkers. They each communicate with fellow neurons, muscles or other cells by releasing neurotransmitter chemicals at 'synapse' junctions, ultimately producing functions ranging from emotions to motions. But even neurons of the exact same type can vary in their conversational style. A new study in Cell Reports by neurobiologists at The Picower Institute for Learning and Memory highlights a molecular mechanism that might help account for the nuanced diversity of neural discourse.
Read more »
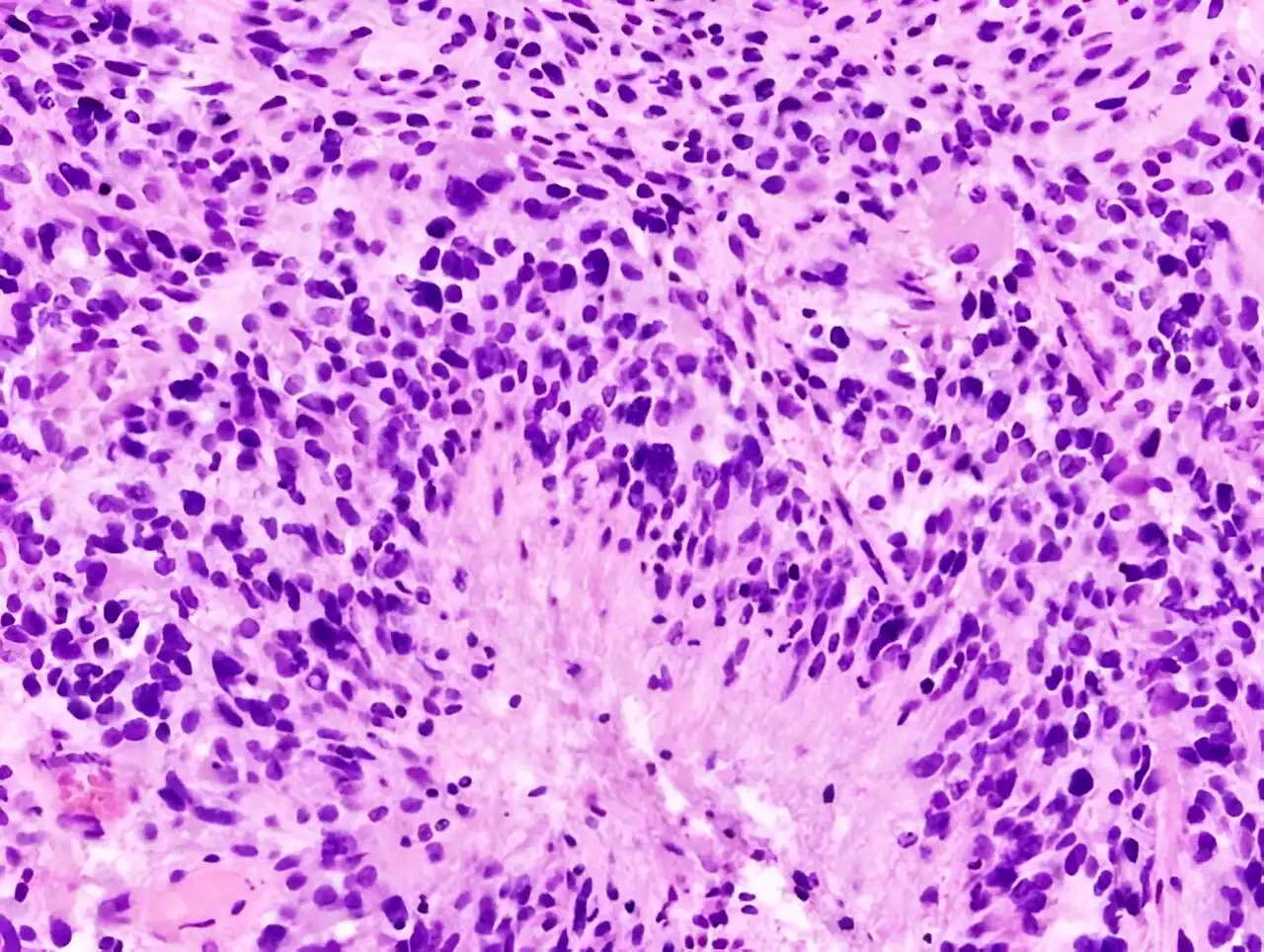 Research team leads adaptive, efficient multi-arm phase 2 clinical trial for glioblastomaAn innovative phase 2 clinical trial led by Dana-Farber Cancer Institute, in collaboration with 10 major brain tumor centers around the country and designed to find new potential treatments for glioblastoma, has reported initial results in the Journal of Clinical Oncology. While none of the three therapeutics tested so far improved overall survival of patients, this adaptive platform trial, the first of its kind in neuro-oncology, has the potential to rapidly and efficiently identify therapies that benefit patients.
Research team leads adaptive, efficient multi-arm phase 2 clinical trial for glioblastomaAn innovative phase 2 clinical trial led by Dana-Farber Cancer Institute, in collaboration with 10 major brain tumor centers around the country and designed to find new potential treatments for glioblastoma, has reported initial results in the Journal of Clinical Oncology. While none of the three therapeutics tested so far improved overall survival of patients, this adaptive platform trial, the first of its kind in neuro-oncology, has the potential to rapidly and efficiently identify therapies that benefit patients.
Read more »
 Researchers say chemo drug may prevent heart failureA chemotherapy drug used to fight bone-marrow cancer has the potential to treat and prevent potentially deadly heart failure, a powerful new drug-screening tool developed at UVA Health suggests.
Researchers say chemo drug may prevent heart failureA chemotherapy drug used to fight bone-marrow cancer has the potential to treat and prevent potentially deadly heart failure, a powerful new drug-screening tool developed at UVA Health suggests.
Read more »
