Researchers have found that SSRI (Selective Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitors) antidepressants have the potential to improve certain cognitive functions, such as verbal memory.
European College of NeuropsychopharmacologySep 22 2024 Researchers have found that SSRI antidepressants have the potential to improve certain cognitive function s, such as verbal memory. They measured brain function in patients before and after taking the SSRI escitalopram and correlated this to a drop in the level of one of the serotonin receptors in the brain and to cognitive improvements during treatment.
The researchers began by scanning the brains of 90 depressed patients, to measure the quantity of 5HT4 receptor which serotonin binds to. At the same time, patients were given a series of tests to measure mood and cognitive abilities. This is potentially significant. It seems that the SSRI medication contributes to an improvement on cognitive function, at the same time as helping improve mood. Our work ties the improvement in cognitive function to the specific 5HT4 receptor and suggest that direct serotonin 4 receptor stimulation may be in important pro-cognitive target to consider in optimizing outcomes of antidepressant treatment. It also reinforces the idea that serotonin is crucial to mood improvement.
Clinical Depression Cognitive Function Depression Drugs Hospital Psychiatry Receptor Serotonin
United Kingdom Latest News, United Kingdom Headlines
Similar News:You can also read news stories similar to this one that we have collected from other news sources.
 Researchers develop affordable, rapid blood test for brain cancerResearchers at the University of Notre Dame have developed a novel, automated device capable of diagnosing glioblastoma, a fast-growing and incurable brain cancer, in less than an hour. The average glioblastoma patient survives 12–18 months after diagnosis.
Researchers develop affordable, rapid blood test for brain cancerResearchers at the University of Notre Dame have developed a novel, automated device capable of diagnosing glioblastoma, a fast-growing and incurable brain cancer, in less than an hour. The average glioblastoma patient survives 12–18 months after diagnosis.
Read more »
 Researchers pinpoint key gene mutations, new mechanisms that cause brain bleeding and dementiaScientists have revealed new insights into the mechanisms behind cerebral small vessel disease, a condition that affects the smaller blood vessels in the brain and causes approximately half of all dementia cases.
Researchers pinpoint key gene mutations, new mechanisms that cause brain bleeding and dementiaScientists have revealed new insights into the mechanisms behind cerebral small vessel disease, a condition that affects the smaller blood vessels in the brain and causes approximately half of all dementia cases.
Read more »
 Human brain cancers fire electrical impulses: Researchers reveal unexpected hybrid cell spiking the signalsResearchers at Baylor College of Medicine and the Jan and Dan Duncan Neurological Research Institute at Texas Children's Hospital have uncovered a new cell type in the human brain.
Human brain cancers fire electrical impulses: Researchers reveal unexpected hybrid cell spiking the signalsResearchers at Baylor College of Medicine and the Jan and Dan Duncan Neurological Research Institute at Texas Children's Hospital have uncovered a new cell type in the human brain.
Read more »
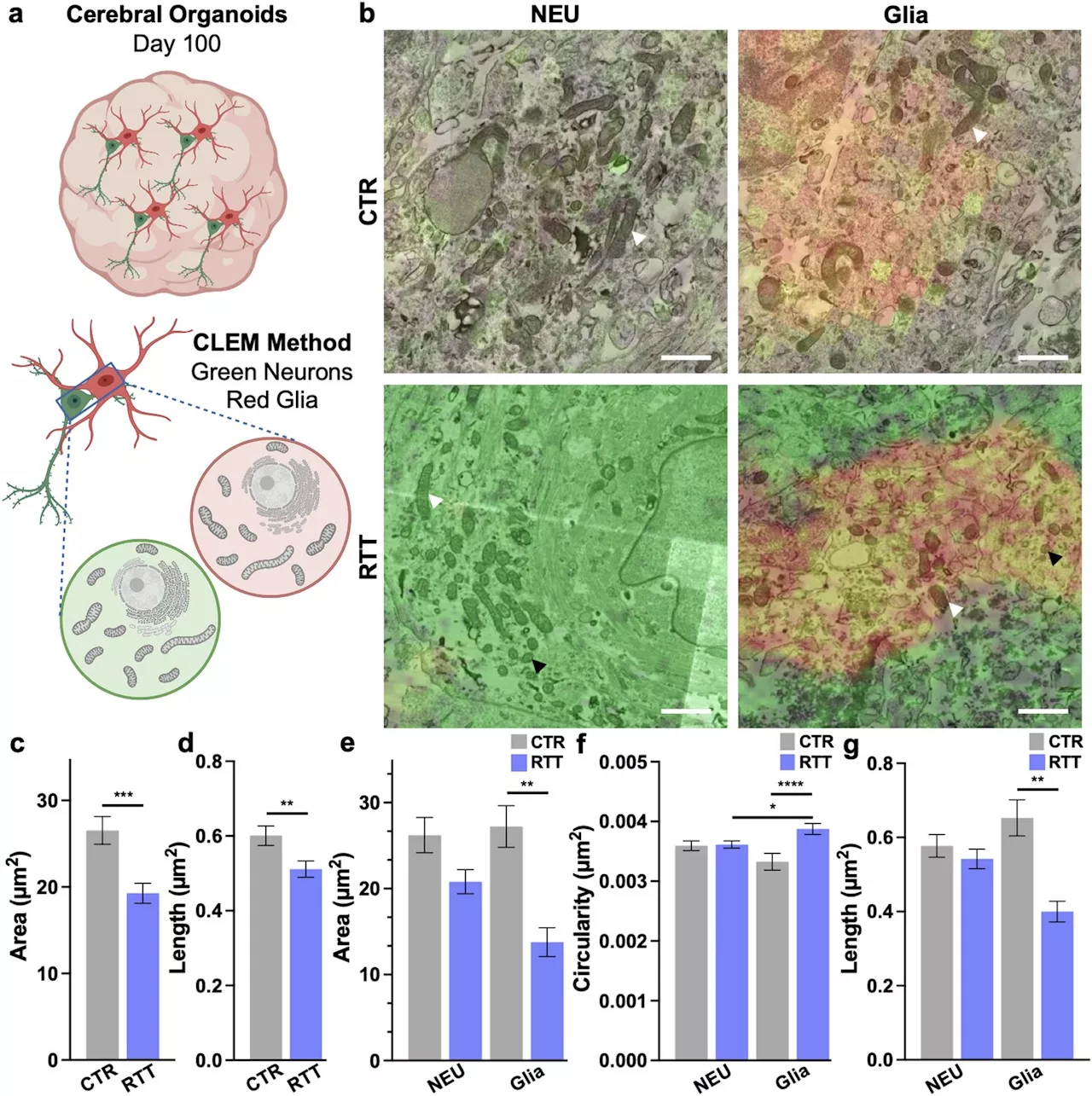 Brain cell types are affected differently by Rett syndrome mutation, researchers discoverRett syndrome is a X-chromosome-linked neurodevelopmental disorder; it can lead to loss of coordination, mobility, ability to speak, and use of the hands, among other symptoms. The syndrome is typically caused by mutations within the gene MECP2.
Brain cell types are affected differently by Rett syndrome mutation, researchers discoverRett syndrome is a X-chromosome-linked neurodevelopmental disorder; it can lead to loss of coordination, mobility, ability to speak, and use of the hands, among other symptoms. The syndrome is typically caused by mutations within the gene MECP2.
Read more »
COVID-19 lockdowns accelerated brain aging in adolescent girls, researchers findResearchers discovered that COVID-19 lockdowns accelerated cortical thinning in adolescent brains, with females experiencing more significant and widespread changes than males, indicating a higher developmental impact on female brains.
Read more »
 Breakthrough miniaturized brain-machine interface enables brain-to-text communicationResearchers from EPFL have developed a next-generation miniaturized brain-machine interface capable of direct brain-to-text communication on tiny silicon chips.
Breakthrough miniaturized brain-machine interface enables brain-to-text communicationResearchers from EPFL have developed a next-generation miniaturized brain-machine interface capable of direct brain-to-text communication on tiny silicon chips.
Read more »