Emerging personalized treatment approaches for chronic urticari.
By Vijay Kumar MalesuReviewed by Lily Ramsey, LLMJul 16 2024 In a recent review published in The Lancet, a group of authors explored emerging personalized treatment approaches for chronic urticaria , emphasizing novel therapies and addressing the limitations of current management guidelines.
Current guidelines recommend second-generation antihistamines, omalizumab, and ciclosporin. However, many patients remain uncontrolled, necessitating further research to develop more effective therapies targeting chronic urticaria's heterogeneous pathophysiology. Approximately 50% of patients experience spontaneous remission within five years, but many require long-term treatment. The disease's chronic nature and impact on daily functioning necessitate effective management strategies.
Unmet needs in chronic urticaria management Despite existing treatments, many patients with chronic urticaria do not achieve adequate disease control. At least a quarter of patients do not respond to second-generation antihistamines, and a substantial number also do not react to omalizumab. Difficult-to-treat CIU CIU's pathogenesis remains unclear and is often linked to specific neoallergen production in the skin. Identifying relevant triggers is crucial for management but can be challenging.
Disease modification There is a critical need for disease-modifying treatments that address the underlying mechanisms of chronic urticaria. Such therapies should aim to induce long-term remission or cure after withdrawal. Bruton's Tyrosine Kinase inhibitors BTK inhibitors such as fenebrutinib, remibrutinib, and rilzabrutinib show promise in treating antihistamine-refractory CSU. These inhibitors target mast cell and basophil activation pathways.
Urticaria Angioedema Antibody Antihistamines Autoantibodies Cell Cold Cytokine Cytokines Drugs Efficacy Heat Histamine Immunoglobulin Inflammation Kinase Mast Cell Pathophysiology Protein Receptor Research Skin Tyrosine
United Kingdom Latest News, United Kingdom Headlines
Similar News:You can also read news stories similar to this one that we have collected from other news sources.
 Tell-tale gene affects success of drug used to treat chronic pain, study findsWomen who carry a particular form of a pain gene are more likely to respond well to a common medication used to treat long-term discomfort, research shows.
Tell-tale gene affects success of drug used to treat chronic pain, study findsWomen who carry a particular form of a pain gene are more likely to respond well to a common medication used to treat long-term discomfort, research shows.
Read more »
 Mike Nesbitt: Addressing inequalities 'central to health reform'Health Minister Mike Nesbitt has announced a series of planned initiatives for the next six months.
Mike Nesbitt: Addressing inequalities 'central to health reform'Health Minister Mike Nesbitt has announced a series of planned initiatives for the next six months.
Read more »
 Researcher details risk factors for chronic kidney disease and barriers for early detectionAbout 90% of people living with a condition that is one of the leading causes of death in the United States are unaware that they have it.
Researcher details risk factors for chronic kidney disease and barriers for early detectionAbout 90% of people living with a condition that is one of the leading causes of death in the United States are unaware that they have it.
Read more »
 I was a chronic people-pleaser living in denial – this is how I stoppedI would drink cow's milk in tea even though I'm allergic and do work I didn't have time to do. So I decided to stop, says Marisa Bate
I was a chronic people-pleaser living in denial – this is how I stoppedI would drink cow's milk in tea even though I'm allergic and do work I didn't have time to do. So I decided to stop, says Marisa Bate
Read more »
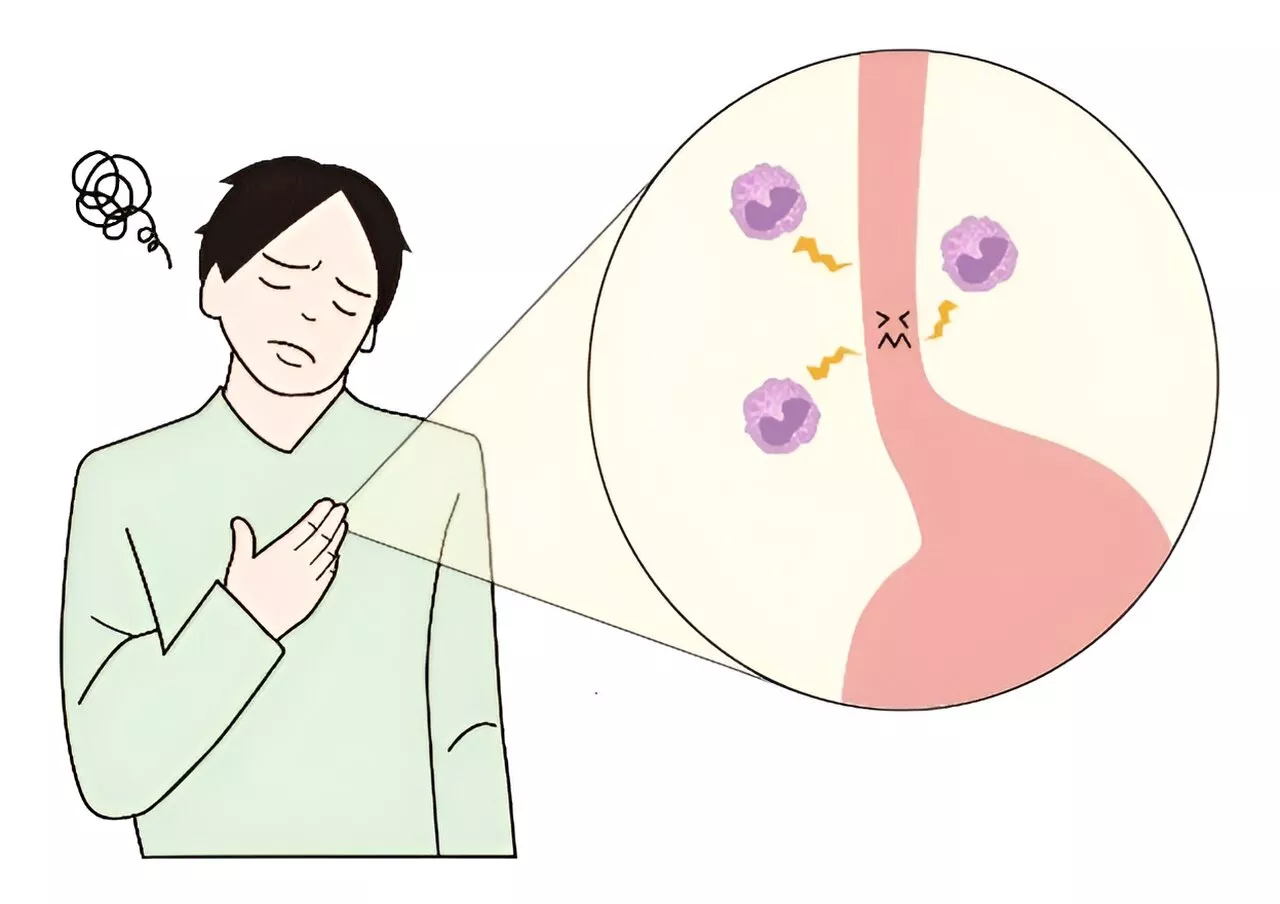 Rising incidence of chronic allergic disorder in Japan confirmed by large-scale data analysisIn one of the first studies of its kind in Japan, Osaka Metropolitan University-led researchers uncovered the incidence and prevalence of the chronic allergic disorder eosinophilic esophagitis, or EoE.
Rising incidence of chronic allergic disorder in Japan confirmed by large-scale data analysisIn one of the first studies of its kind in Japan, Osaka Metropolitan University-led researchers uncovered the incidence and prevalence of the chronic allergic disorder eosinophilic esophagitis, or EoE.
Read more »
 Chronic exposure to air pollutants may increase lupus risk, research showsNew research published in Arthritis & Rheumatology indicates that chronic exposure to air pollutants may increase the risk of developing lupus, an autoimmune disease that affects multiple organs.
Chronic exposure to air pollutants may increase lupus risk, research showsNew research published in Arthritis & Rheumatology indicates that chronic exposure to air pollutants may increase the risk of developing lupus, an autoimmune disease that affects multiple organs.
Read more »