Mesothelioma is an aggressive tumor with a poor prognosis. Histological diagnosis of mesothelioma using limited tissue samples can be challenging.
Xia & He Publishing Inc.Oct 27 2024 Background and objectives Carbonic anhydrase IX is a transmembrane protein that is overexpressed in a variety of solid tumors. This study aimed to investigate the clinical utility of CAIX expression in the differential diagnosis of pleural mesothelioma from non-small cell lung carcinoma .
Methods Unstained tissue microarray slides composed of 56 cases of pleural mesothelioma and 82 cases of NSCLC were subjected to immunohistochemical staining using a mouse anti-human antibody against CAIX. Results Of the 38 epithelioid mesothelioma cases, 34 displayed diffuse and strong cytoplasmic membrane reactivity, while the remaining four cases showed weak to moderate staining in tumor cells. Five out of sixteen sarcomatoid mesothelioma cases were negative. Among the non-small cell lung carcinoma cases, 76% of adenocarcinomas and 57% of squamous cell carcinomas were completely negative, whereas the remaining cases showed focal weak expression of CAIX.
Conclusions Our study demonstrates that CAIX expression has a high sensitivity in detecting pleural epithelioid mesothelioma, which is comparable to or better than currently used mesothelial markers. The specificity of CAIX is within a comparable range to that of commonly used mesothelial markers for differentiating epithelioid mesothelioma from NSCLC.
Cell Diagnostic Mesothelioma Biopsy Pathology Research Tumor
United Kingdom Latest News, United Kingdom Headlines
Similar News:You can also read news stories similar to this one that we have collected from other news sources.
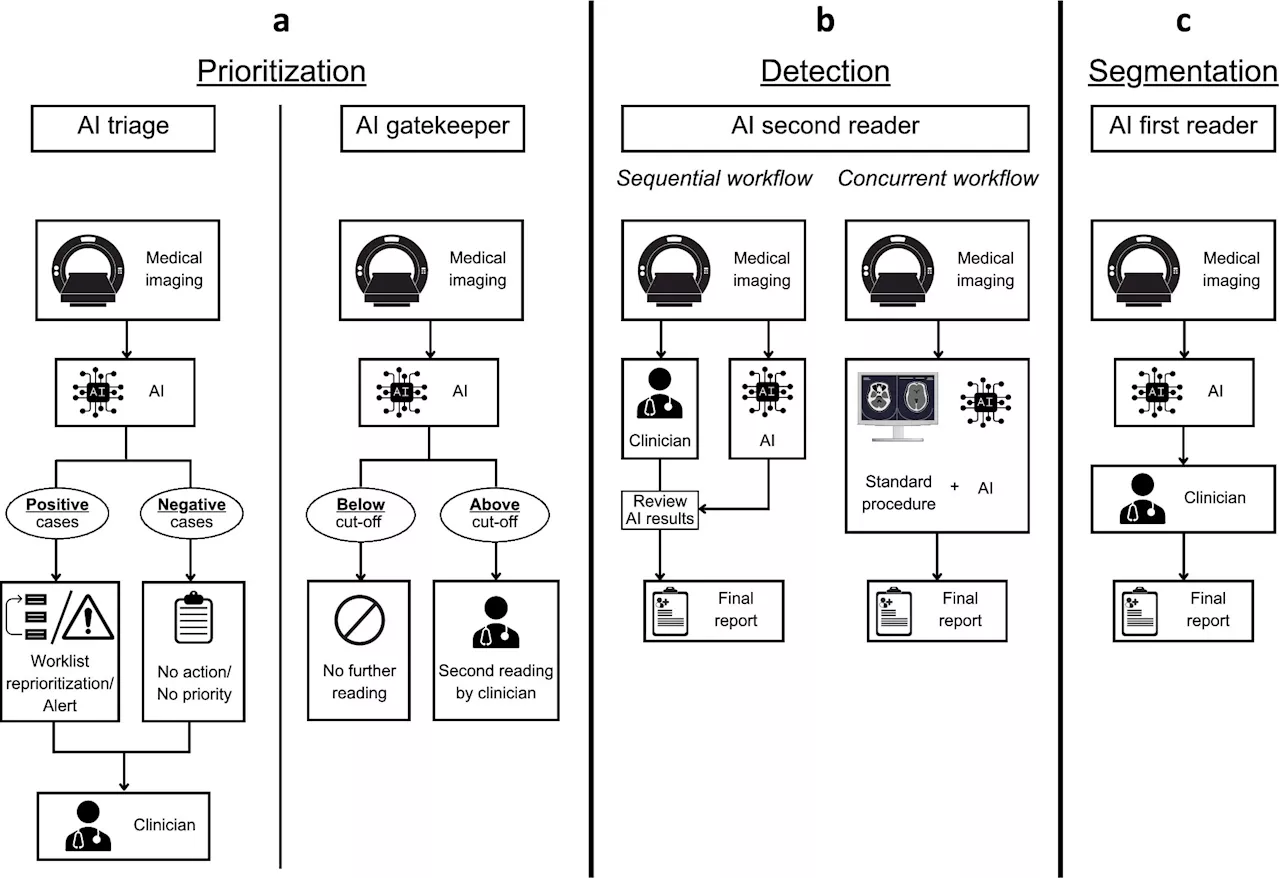 AI does not necessarily lead to more efficiency in clinical practice, research showsThe use of artificial intelligence (AI) in hospitals and patient care is steadily increasing. Especially in specialist areas with a high proportion of imaging, such as radiology, AI has long been part of everyday clinical practice.
AI does not necessarily lead to more efficiency in clinical practice, research showsThe use of artificial intelligence (AI) in hospitals and patient care is steadily increasing. Especially in specialist areas with a high proportion of imaging, such as radiology, AI has long been part of everyday clinical practice.
Read more »
 Clinical trial finds multidisciplinary approach improves quality of life for movement disorder patientsA research team has published a randomized clinical trial demonstrating for the first time that a multidisciplinary approach integrating specific physiotherapy and cognitive-behavioral therapy is effective in improving the symptoms and physical aspects of the quality of life of patients with functional movement disorders.
Clinical trial finds multidisciplinary approach improves quality of life for movement disorder patientsA research team has published a randomized clinical trial demonstrating for the first time that a multidisciplinary approach integrating specific physiotherapy and cognitive-behavioral therapy is effective in improving the symptoms and physical aspects of the quality of life of patients with functional movement disorders.
Read more »
 The explainability challenge: Exploring AI's role in clinical decision-makingAs the impact of artificial intelligence (AI) grows in our world, the University of Adelaide is exploring the role that technology can play in the health sphere, particularly in clinical decision-making and explanations.
The explainability challenge: Exploring AI's role in clinical decision-makingAs the impact of artificial intelligence (AI) grows in our world, the University of Adelaide is exploring the role that technology can play in the health sphere, particularly in clinical decision-making and explanations.
Read more »
 New clinical model can accurately predict hip fracture risk in the elderlyResearchers at Uppsala University have developed a clinical model that can accurately predict the risk of hip fractures in the elderly.
New clinical model can accurately predict hip fracture risk in the elderlyResearchers at Uppsala University have developed a clinical model that can accurately predict the risk of hip fractures in the elderly.
Read more »
 Tissue chips help translate respiratory disease research into clinical applicationsScientists are developing advanced tools to understand and treat neurological symptoms such as brain fog associated with respiratory diseases like influenza.
Tissue chips help translate respiratory disease research into clinical applicationsScientists are developing advanced tools to understand and treat neurological symptoms such as brain fog associated with respiratory diseases like influenza.
Read more »
 A review of clinical features, diagnosis, and management of MpoxA comprehensive review in JAMA outlines monkeypox's clinical presentation and management, stressing the need for increased surveillance and vaccination efforts.
A review of clinical features, diagnosis, and management of MpoxA comprehensive review in JAMA outlines monkeypox's clinical presentation and management, stressing the need for increased surveillance and vaccination efforts.
Read more »