The deoxyribonucleic acid or DNA, the molecular system that carries the genetic information of living organisms, can transcribe and amplify information using its two helical strands.
Tokyo University of ScienceAug 9 2024 Creating such artificial molecular systems that match or surpass DNA in functionality is of great interest to scientists. Double-helical foldamers are one such molecular system.
In a breakthrough, a team of researchers from Tokyo University of Science, Japan, led by Professor Hidetoshi Kawai from the Department of Chemistry, Faculty of Science, and including Mr. Kotaro Matsumura from the Department of Chemistry, developed a novel mechanical motif, called double-helical monometallofoldamers with controllable chiral switching. Prof.
Interestingly, the helicity of the double-helical monometallofoldamer with chiral chains can be controlled in response to achiral solvents. For example, in non-polar solvents , it becomes left-handed or M-form, and in Lewis basic solvents , it becomes right-handed or the P-form. The conformation of chiral chains introduced into the helix strands was found to be important for this M/P switching.
Cation DNA Genetic Genetic Information Research Transcription
United Kingdom Latest News, United Kingdom Headlines
Similar News:You can also read news stories similar to this one that we have collected from other news sources.
 Charting an equitable future for DNA and ancient DNA research in AfricaToday, the American Journal of Human Geneticspublished a perspective piece on the need for an equitable and inclusive future for DNA and ancient DNA (aDNA) research in Africa. The paper, coauthored by an international team of 36 scientists from Africa, North America, Asia, Australia, and Europe, was led by Dr.
Charting an equitable future for DNA and ancient DNA research in AfricaToday, the American Journal of Human Geneticspublished a perspective piece on the need for an equitable and inclusive future for DNA and ancient DNA (aDNA) research in Africa. The paper, coauthored by an international team of 36 scientists from Africa, North America, Asia, Australia, and Europe, was led by Dr.
Read more »
 Epigenetic change to DNA associated with cancer risk in 'multi-omics' studyA research team co-led by investigators at Vanderbilt University Medical Center and the University of Virginia has identified associations between DNA methylation and cancer risk. DNA methylation is an epigenetic change—the addition of 'methyl groups' to DNA—that can affect gene expression without changing the DNA sequence.
Epigenetic change to DNA associated with cancer risk in 'multi-omics' studyA research team co-led by investigators at Vanderbilt University Medical Center and the University of Virginia has identified associations between DNA methylation and cancer risk. DNA methylation is an epigenetic change—the addition of 'methyl groups' to DNA—that can affect gene expression without changing the DNA sequence.
Read more »
 Hope for woolly mammoth ‘de-extinction’ after DNA from frozen 52,000-year-old remains foundHope for woolly mammoth ‘de-extinction’ after giant frozen 72,000-year-old foot found perfectly preserved in permafrost
Hope for woolly mammoth ‘de-extinction’ after DNA from frozen 52,000-year-old remains foundHope for woolly mammoth ‘de-extinction’ after giant frozen 72,000-year-old foot found perfectly preserved in permafrost
Read more »
 Jorge Martin issued warning about ‘DNA’ of ApriliaJorge Martin tipped off about the 'weak point' of the Aprilia
Jorge Martin issued warning about ‘DNA’ of ApriliaJorge Martin tipped off about the 'weak point' of the Aprilia
Read more »
 Lifting people out of poverty is in Labour's DNA and we’ll do it againWriting in the Daily Record, Scotland Secretary Ian Murray says the new Government will give people more security at work and put more money in their wage packets.
Lifting people out of poverty is in Labour's DNA and we’ll do it againWriting in the Daily Record, Scotland Secretary Ian Murray says the new Government will give people more security at work and put more money in their wage packets.
Read more »
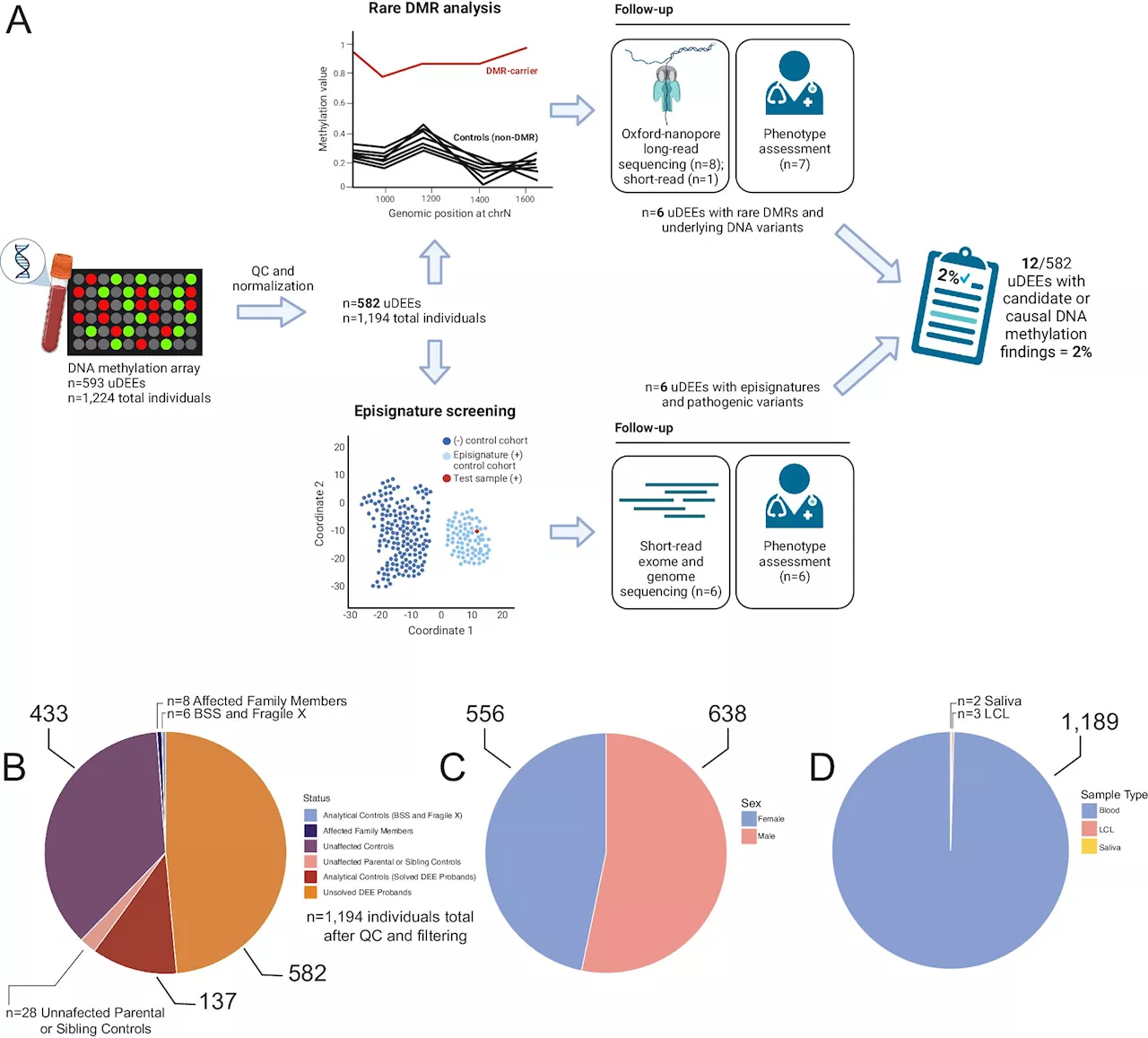 Scientists use DNA methylation patterns as roadmap for identifying causes of severe epilepsies in childrenTo effectively treat a disease or disorder, doctors must first know the root cause. Such is the case for developmental and epileptic encephalopathies (DEEs), whose root causes can be hugely complex and heterogeneous.
Scientists use DNA methylation patterns as roadmap for identifying causes of severe epilepsies in childrenTo effectively treat a disease or disorder, doctors must first know the root cause. Such is the case for developmental and epileptic encephalopathies (DEEs), whose root causes can be hugely complex and heterogeneous.
Read more »
