Detection of filoviruses by the innate immune system MDPIOpenAccess StJude Filovirus InateImmuneSystem ImmuneSystem
By Bhavana KunkalikarDec 1 2022Reviewed by Aimee Molineux In a recent study published in Pathogens, researchers examined how the innate immune system detects filoviruses.
Sensing components of the innate immune system The innate immune system has developed the capability to recognize and react to danger- or damage-associated molecular patterns and pathogen-associated molecular patterns to protect against infections and cellular disturbances. Germline-encoded pattern recognition receptors like membrane-bound toll-like receptors , C-type lectin receptors , NOD-like receptors , and cytoplasmic retinoic acid-inducible gene-I -like receptors detect DAMPs and PAMPs.
IFN signaling and RIG-I-like Receptors Some RLRs are observed in the nucleus, although most RLRs are found in the cytoplasm. RIG-I, laboratory of genetics and physiology 2 , and melanoma differentiation-associated factor 5 are the three discovered RLRs in humans. MDA5 and RIG-I possess two N-terminal caspase activation and recruitment domains , a C-terminal domain , and two DExD/H box RNA helicase domains, while LGP2 is devoid of a CARD.
Apoptosis Apoptosis is a crucial cell death process for regulating cell homeostasis. It does not destroy cells or liberate intracellular substances but causes widespread membrane blebbing and contraction. Either the intrinsic or the extrinsic mechanisms can initiate apoptosis. In response to mitochondrial disturbances, intrinsic apoptosis is characterized by the development of an apoptosome, including apoptotic peptidase activating factor 1 , cytochrome c, and caspase-9.
United Kingdom Latest News, United Kingdom Headlines
Similar News:You can also read news stories similar to this one that we have collected from other news sources.
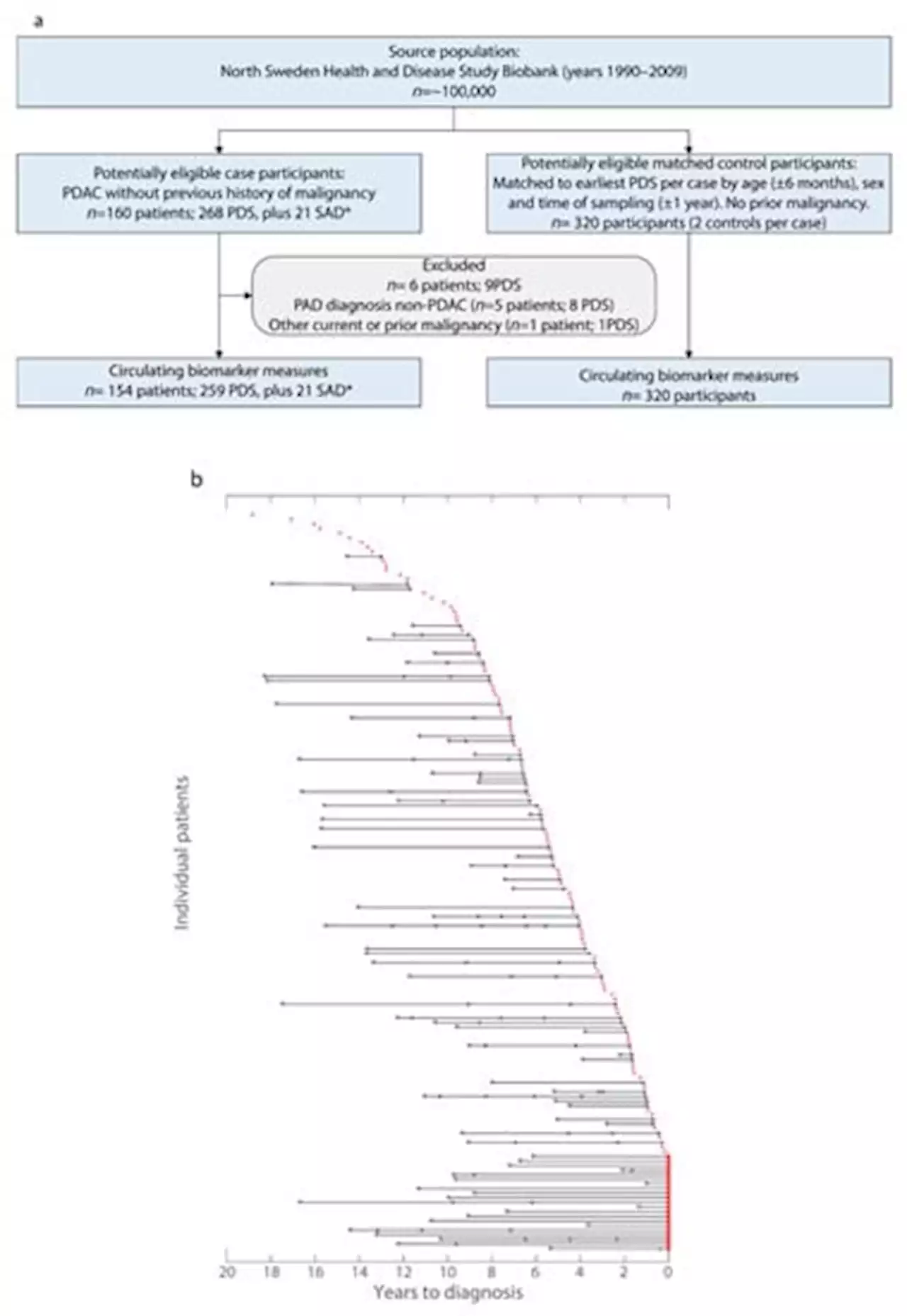 A Cross-Sectional and Longitudinal Analysis of Pre-Diagnostic Blood Plasma Biomarkers for Early Detection of Pancreatic CancerPancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC) is a major cause of cancer death that typically presents at an advanced stage. No reliable markers for early detection presently exist. The prominent tumor stroma represents a source of circulating biomarkers for use together with cancer cell-derived biomarkers for earlier PDAC diagnosis. CA19-9 and CEA (cancer cell-derived biomarkers), together with endostatin and collagen IV (stroma-derived) were examined alone, or together, by multivariable modelling, using pre-diagnostic plasma samples (n=259 samples) from the Northern Sweden Health and Disease Study biobank. Serial samples were available for a subgroup of future patients. Marker efficacy for future PDAC case prediction (n=154 future cases) was examined by both cross-sectional (ROC analysis) and longitudinal analyses. CA19-9 performed well at, and within, six months to diagnosis and multivariable modelling was not superior to CA19-9 alone in cross-sectional analysis. Within six months to diagnosis, CA19-9 (AUC=0.92) outperformed the multivariable model (AUC=0.81) at a cross-sectional level. At diagnosis, CA19-9 (AUC=0.995) and the model (AUC=0.977) performed similarly. Longitudinal analysis revealed increases in CA19-9 up to two years to diagnosis which indicates a window of opportunity for early detection of PDAC.
A Cross-Sectional and Longitudinal Analysis of Pre-Diagnostic Blood Plasma Biomarkers for Early Detection of Pancreatic CancerPancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC) is a major cause of cancer death that typically presents at an advanced stage. No reliable markers for early detection presently exist. The prominent tumor stroma represents a source of circulating biomarkers for use together with cancer cell-derived biomarkers for earlier PDAC diagnosis. CA19-9 and CEA (cancer cell-derived biomarkers), together with endostatin and collagen IV (stroma-derived) were examined alone, or together, by multivariable modelling, using pre-diagnostic plasma samples (n=259 samples) from the Northern Sweden Health and Disease Study biobank. Serial samples were available for a subgroup of future patients. Marker efficacy for future PDAC case prediction (n=154 future cases) was examined by both cross-sectional (ROC analysis) and longitudinal analyses. CA19-9 performed well at, and within, six months to diagnosis and multivariable modelling was not superior to CA19-9 alone in cross-sectional analysis. Within six months to diagnosis, CA19-9 (AUC=0.92) outperformed the multivariable model (AUC=0.81) at a cross-sectional level. At diagnosis, CA19-9 (AUC=0.995) and the model (AUC=0.977) performed similarly. Longitudinal analysis revealed increases in CA19-9 up to two years to diagnosis which indicates a window of opportunity for early detection of PDAC.
Read more »
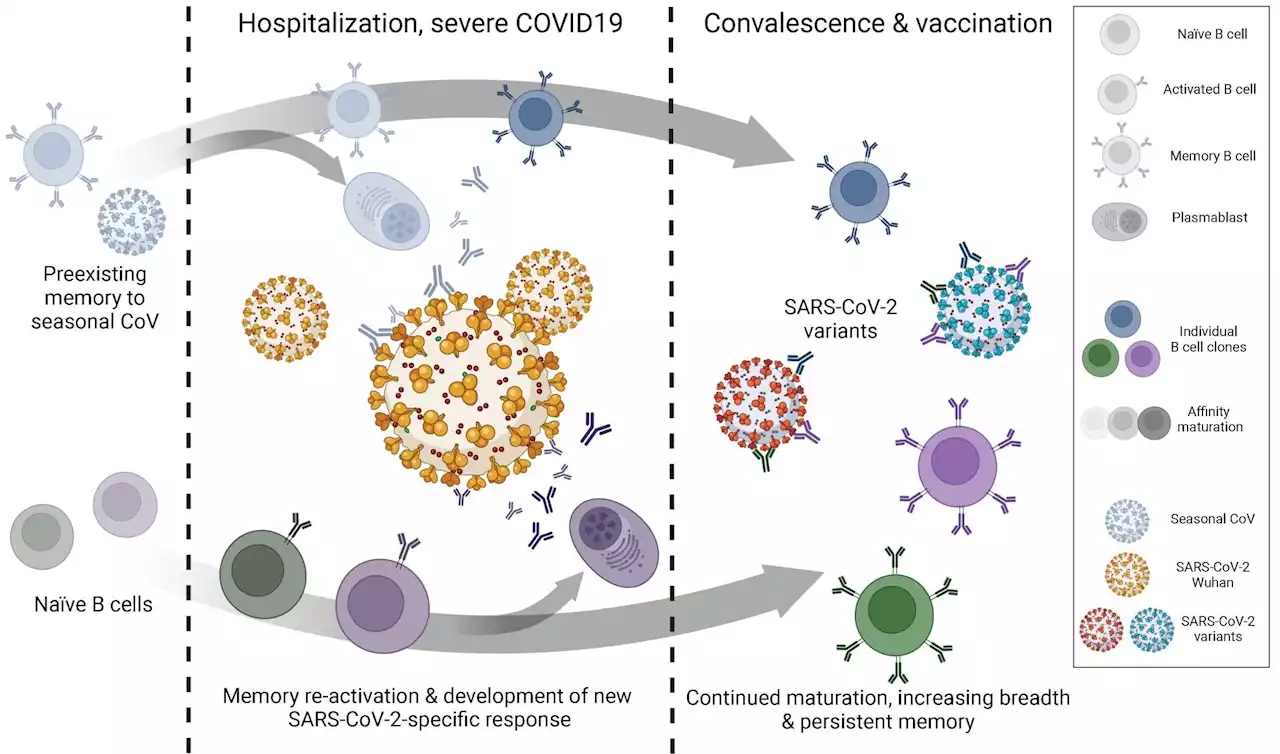 Detection of early-formed, antigen-specific clones in SARS-CoV-2-reactive B cells after longitudinal analysisSevere acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus-2 (SARS-CoV-2), the causal agent of the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic, has globally infected more than 639 million individuals and claimed over 6.6 million lives. Despite the rapid commencement of COVID-19 vaccination programs in most countries across the world, the virus has remained in circulation.
Detection of early-formed, antigen-specific clones in SARS-CoV-2-reactive B cells after longitudinal analysisSevere acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus-2 (SARS-CoV-2), the causal agent of the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic, has globally infected more than 639 million individuals and claimed over 6.6 million lives. Despite the rapid commencement of COVID-19 vaccination programs in most countries across the world, the virus has remained in circulation.
Read more »
 Dualplex lateral flow assay for simultaneous scopolamine and “cannibal drug” detection based on receptor-gated mesoporous nanoparticlesWe report herein the design of a strip-based rapid test utilizing bio-inspired hybrid nanomaterials for the in situ and at site detection of the drug scopolamine (SCP) using a smartphone for readout, allowing SCP identification in diluted saliva down to 40 nM in less than 15 min. For this purpose, we prepare
Dualplex lateral flow assay for simultaneous scopolamine and “cannibal drug” detection based on receptor-gated mesoporous nanoparticlesWe report herein the design of a strip-based rapid test utilizing bio-inspired hybrid nanomaterials for the in situ and at site detection of the drug scopolamine (SCP) using a smartphone for readout, allowing SCP identification in diluted saliva down to 40 nM in less than 15 min. For this purpose, we prepare
Read more »
 Study suggests persistent immune activation and long COVID correlate independently with severe COVID-19Researchers investigated whether severe COVID-19 patients exhibited inflammation and immune activation three months after hospitalization and explored the associations among COVID-19 severity, long COVID, and immune activation.
Study suggests persistent immune activation and long COVID correlate independently with severe COVID-19Researchers investigated whether severe COVID-19 patients exhibited inflammation and immune activation three months after hospitalization and explored the associations among COVID-19 severity, long COVID, and immune activation.
Read more »
