Study demonstrates that dietary interventions such as calorie restriction, intermittent fasting, and ketogenic diet improve mitochondrial function in monocytes and reduce inflammation in obesity by modulating gut microbiota.
By Dr. Sanchari Sinha Dutta, Ph.D.Jul 23 2024 A randomized clinical trial involving obese individuals highlights the significance of dietary interventions in improving mitochondrial functions and the metabolic profile of monocytes, which are key aspects for controlling chronic inflammation in obesity.
Mitochondrial dysfunction in monocytes during obesity is known to contribute to low-grade chronic inflammation, a major hallmark of obesity. Recent evidence indicates that monocytes positively regulate fatty acid oxidation to reduce inflammatory responses in low-glucose environments. This suggests that dietary restrictions may influence monocyte bioenergetics.
Related StoriesThe participants subsequently received rifaximin, a non-absorbable antibiotic, and continued with the assigned diet for another month. Rifaximin was used to evaluate gut microbiota's role in modulating dietary interventions' effects on mitochondrial function in monocytes. This improvement in mitochondrial function was associated with a reduction in monocyte dependence on glycolysis for participants from the intermittent fasting and ketogenic diet groups.
Specifically, significant inverse correlations of serum LPS concentration were observed with the maximal respiration oxygen consumption rate, bioenergetic health index, and the bacterium Phascolarctobacterium faecium . A significant reduction in LPS-mediated intracellular signaling was observed in monocytes isolated from participants in the three dietary intervention groups. A significant reduction in body weight and visceral fat was also observed in these participants.
Obesity Chronic Clinical Trial Diet Fasting Glycolysis Intracellular Ketogenic Diet Mitochondria Monocyte Nutrition Oxygen Weight Loss
United Kingdom Latest News, United Kingdom Headlines
Similar News:You can also read news stories similar to this one that we have collected from other news sources.
 Study links improved dietary fat quality to reduced cardiovascular and diabetes riskThe impact of dietary fat quality on lipid metabolites and its association with reduced cardiometabolic disease risk.
Study links improved dietary fat quality to reduced cardiovascular and diabetes riskThe impact of dietary fat quality on lipid metabolites and its association with reduced cardiometabolic disease risk.
Read more »
 Total dietary quality score improved for U.S. children during 2005 to 2020, study showsTotal dietary scores improved for U.S. children during 2005 to 2020, with increases for all diet adequacy components, apart from dairy, according to a research letter published online July 8 in JAMA Pediatrics.
Total dietary quality score improved for U.S. children during 2005 to 2020, study showsTotal dietary scores improved for U.S. children during 2005 to 2020, with increases for all diet adequacy components, apart from dairy, according to a research letter published online July 8 in JAMA Pediatrics.
Read more »
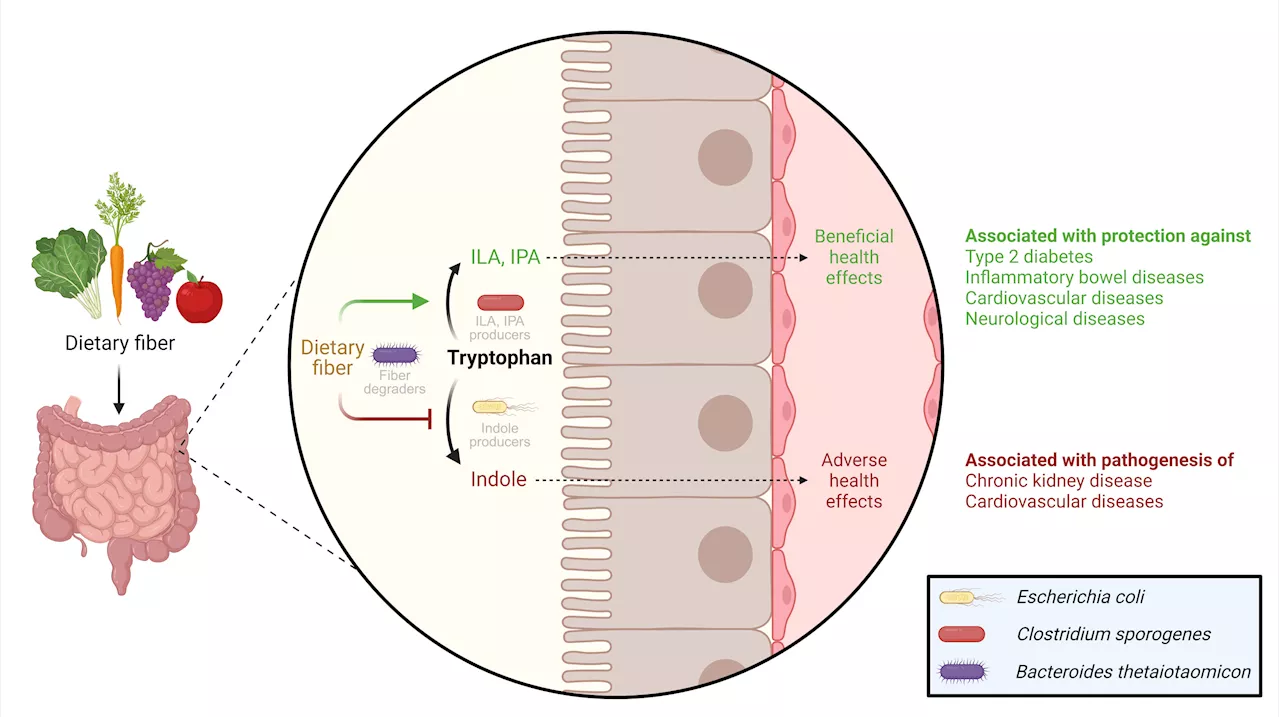 Dietary fiber found to regulate gut bacteria's use of tryptophan, impacting healthWe get healthy dietary fiber from consuming fruits, vegetables, and whole grains. But why is fiber so good for us? A team of researchers has discovered that dietary fiber plays a crucial role in determining the balance between the production of healthy and harmful substances by influencing the behavior of bacteria in the colon.
Dietary fiber found to regulate gut bacteria's use of tryptophan, impacting healthWe get healthy dietary fiber from consuming fruits, vegetables, and whole grains. But why is fiber so good for us? A team of researchers has discovered that dietary fiber plays a crucial role in determining the balance between the production of healthy and harmful substances by influencing the behavior of bacteria in the colon.
Read more »
 Dietary sucrose modulates lithium's regulatory activity in DrosophilaA new research paper was published in Aging (listed by MEDLINE/PubMed as 'Aging (Albany NY)' and 'Aging-US' by Web of Science) Volume 16, Issue 11, entitled, 'Dietary sucrose determines the regulatory activity of lithium on gene expression and lifespan in Drosophila melanogaster.
Dietary sucrose modulates lithium's regulatory activity in DrosophilaA new research paper was published in Aging (listed by MEDLINE/PubMed as 'Aging (Albany NY)' and 'Aging-US' by Web of Science) Volume 16, Issue 11, entitled, 'Dietary sucrose determines the regulatory activity of lithium on gene expression and lifespan in Drosophila melanogaster.
Read more »
 Dietary fiber promotes beneficial conversion of tryptophan by gut bacteriaWe get healthy dietary fibres from consuming fruits, vegetables, and whole grains. But why are the fibres so good for us? A team of researchers has discovered that dietary fibres play a crucial role in determining the balance between the production of healthy and harmful substances by influencing the behavior of bacteria in the colon.
Dietary fiber promotes beneficial conversion of tryptophan by gut bacteriaWe get healthy dietary fibres from consuming fruits, vegetables, and whole grains. But why are the fibres so good for us? A team of researchers has discovered that dietary fibres play a crucial role in determining the balance between the production of healthy and harmful substances by influencing the behavior of bacteria in the colon.
Read more »
 Dietary fiber intake reshapes tryptophan metabolism, promoting gut health and reducing disease risksA recent study in Nature Microbiology reveals that increased dietary fiber intake directs microbial tryptophan metabolism, leading to health benefits such as improved gut mucosa integrity and reduced risk of metabolic disorders.
Dietary fiber intake reshapes tryptophan metabolism, promoting gut health and reducing disease risksA recent study in Nature Microbiology reveals that increased dietary fiber intake directs microbial tryptophan metabolism, leading to health benefits such as improved gut mucosa integrity and reduced risk of metabolic disorders.
Read more »
