In a first for the condensate field, researchers have figured out how nucleolar sub-structures are assembled. This organization gives rise to unique pH profiles within nucleoli, which they measured and compared with the pH of nearby non-nucleolar condensates including nuclear speckles and Cajal bodies.
Scientists trying to understand the physical and chemical properties that govern biomolecular condensates now have a crucial way to measure pH and other emergent properties of these enigmatic, albeit important cellular compartments.
In a first for the condensate field, researchers from the lab of Rohit Pappu, the Gene K. Beare Distinguished Professor of biomedical engineering, and colleagues in the Center for Biomolecular Condensates in the McKelvey School of Engineering at Washington University in St. Louis, figured out how nucleolar sub-structures are assembled.
Condensates form via a process that the team now refers to as condensation. This combines phase separation -- think demixing of oil and water -- and sticky interactions among molecules that like to bind with one another. Differentials in pH between condensates and the surrounding nucleoplasm generate gradients and"a pH gradient generates what is known as a proton motive force," King said.
According to Pappu, this work"provides an elegant solution to the challenge that many biochemists see for the condensate concept."
United Kingdom Latest News, United Kingdom Headlines
Similar News:You can also read news stories similar to this one that we have collected from other news sources.
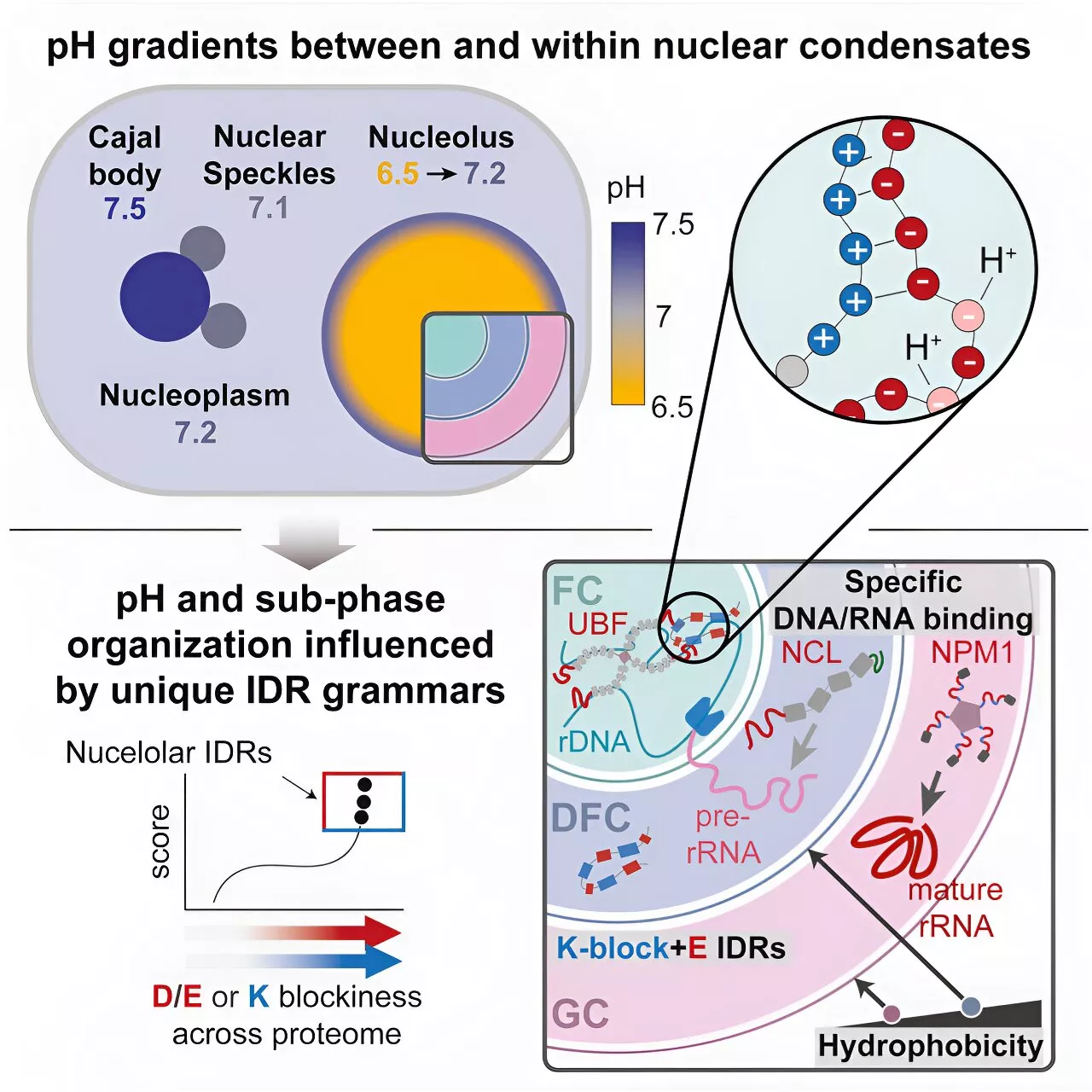 Engineers manage a first: Measuring pH in cell condensatesScientists trying to understand the physical and chemical properties that govern biomolecular condensates now have a crucial way to measure pH and other emergent properties of these enigmatic, albeit important, cellular compartments.
Engineers manage a first: Measuring pH in cell condensatesScientists trying to understand the physical and chemical properties that govern biomolecular condensates now have a crucial way to measure pH and other emergent properties of these enigmatic, albeit important, cellular compartments.
Read more »
 Columbia Engineers Develop Light-Controlled Molecular DevicesScience, Space and Technology News 2024
Columbia Engineers Develop Light-Controlled Molecular DevicesScience, Space and Technology News 2024
Read more »
 Engineers Devise Plan to De-Ice 'Dark Universe' Telescope from a Million Miles AwayEuclid's mission team is testing a new way to de-ice the telescope's optics and restore its ability to explore the dark universe.
Engineers Devise Plan to De-Ice 'Dark Universe' Telescope from a Million Miles AwayEuclid's mission team is testing a new way to de-ice the telescope's optics and restore its ability to explore the dark universe.
Read more »
 Google's woke AI wasn't a mistake, former engineers sayUsers and observers were left stunned by the search results produced by Google's latest AI tool.
Google's woke AI wasn't a mistake, former engineers sayUsers and observers were left stunned by the search results produced by Google's latest AI tool.
Read more »
 Engineers in Nepal Use Eco-Bricks to Rebuild with Less Air PollutionEngineers and entrepreneurs in Nepal are using a different kind of brick to rebuild the country using a process that produces less carbon and other air pollution. The technology, called 'compressed stabilized earth bricks,' has a proven record for its strength and also reduces air pollution compared to conventional brick kilns. This alternative is gaining popularity as people recognize the benefits of eco-bricks, especially in disaster-prone or rural areas where building costs are high. Construction costs can be reduced by up to 25 percent with this technology.
Engineers in Nepal Use Eco-Bricks to Rebuild with Less Air PollutionEngineers and entrepreneurs in Nepal are using a different kind of brick to rebuild the country using a process that produces less carbon and other air pollution. The technology, called 'compressed stabilized earth bricks,' has a proven record for its strength and also reduces air pollution compared to conventional brick kilns. This alternative is gaining popularity as people recognize the benefits of eco-bricks, especially in disaster-prone or rural areas where building costs are high. Construction costs can be reduced by up to 25 percent with this technology.
Read more »
 NASA engineers have renewed hope to fix hobbled Voyager 1 after interstellar space data outageThe process of troubleshooting an issue with Voyager 1 traveling through interstellar space is complicated. It takes about 45 hours for commands to be sent and a response to come back, but NASA engineers recently got a new clue to solving the spacecraft computer issue.
NASA engineers have renewed hope to fix hobbled Voyager 1 after interstellar space data outageThe process of troubleshooting an issue with Voyager 1 traveling through interstellar space is complicated. It takes about 45 hours for commands to be sent and a response to come back, but NASA engineers recently got a new clue to solving the spacecraft computer issue.
Read more »
