This article explores the importance of orthogonal and complementary analytical techniques in ensuring the safety, efficacy, and quality of biotherapeutic drug products throughout research, development, and manufacturing.
Sponsored Content by Yokogawa Fluid Imaging Technologies, Inc.Reviewed by Andrea SalazarJul 18 2024 One of the fundamental purposes of biotherapeutic research, development, and production is to assure the safety and efficacy of medicinal products in clinical settings.
Understanding these correlations can assist scientists in choosing effective ways to acquire sufficiently precise data on the relevant CQAs for an application. Analytical technique A technique for gathering information on at least one CQA for a medicinal product. Analytical approaches differ in terms of the sample properties they monitor, the dynamic range or species in a sample they evaluate , and the measurement principle, or how the methodology gathers data and what bias or error is introduced.
Orthogonal techniques An orthogonal methodology to a given method assesses at least one common application-relevant CQA while employing a distinct measurement technique. If applicable, the feature should be described throughout a comparable dynamic range . Because of limitations in the measuring method used, each analytical approach is susceptible to bias or systematic inaccuracies in the data it produces. Bias can lead to orthogonal procedures providing different values for the same parameter.5
While this might suggest a problem with data collection, it could also mean that something else in the sample has changed , which only affected one technique due to bias. Complementary but not orthogonal techniques offer information on brand-new qualities that the other does not monitor, and most applications require all relevant sample attributes to be monitored.
In the above example, the researcher might employ one way to analyze nanoparticle size distributions and another to characterize subvisible particle size distributions as complimentary methodologies, even though both approaches characterize the "same" metric. Light obscuration Light obscuration, perhaps the most used subvisible particle analysis technique, captures subvisible particle counts and size distributions by passing a sample through a light source and counting and measuring the particles' shadows on the detector.
Table 1 compares FIM and LO instrument design and performance. Flow imaging particle data provides more accurate transparent particle counts and sizing5,9 and has a greater upper concentration limit than LO. FlowCam LO greatly simplifies the process of collecting FIM and LO data for samples.14 This instrument combines an FIM module configured for subvisible particle analysis and a light obscuration module, allowing researchers to collect results from both approaches on a single instrument using a single aliquot of sample.
Figure 4. FlowCam LO-measured particle size distributions and FIM images for stressed samples containing protein , surfactant , or both. Dark histogram bars indicate FIM data, light bars indicate LO data. Image Credit: Yokogawa Fluid Imaging Technologies, Inc. The LO results for these samples consistently showed lower particle concentrations than those obtained with FIM.
The elimination of the background fluid is the primary strength and weakness of this method and its current variants. Removing the fluid allows the user to detect particles with the same refractive index as the background material. While particle changes with filtering and other constraints are troublesome, membrane microscopy and its derivatives give extra visible particle information when employed as an orthogonal assessment of particle count, size, and morphology in conjunction with FIM.Laser diffraction This approach employs light scattering as particles travel through a laser beam to calculate particle size using a scattering model.
Electrical sensing zone The electrical sensing zone, often known as the Coulter principle, counts and sizes particles in samples by passing them between two electrodes and monitoring the electrical field disturbance that results. The primary disadvantage of this higher resolution is that it necessitates more involved sample preparation and a longer total analysis time, resulting in poorer throughput and perhaps altered particle shape.
Complementary techniques with flow imaging microscopy Complementary strategies to explore alongside FIM will frequently be determined by the treatment being used and the questions being asked. Dynamic light scattering DLS, one of the most widely used analytical methods, is an effective method for monitoring nanoparticles, submicron particles, and tiny subvisible particles near and below the lower size range of optical techniques such as FIM.
FlowCam systems typically employ 10X and 20X objective lenses to detect particles as small as 2-100 µm.
Research Orthogonal Complementary Analytical Techniques
United Kingdom Latest News, United Kingdom Headlines
Similar News:You can also read news stories similar to this one that we have collected from other news sources.
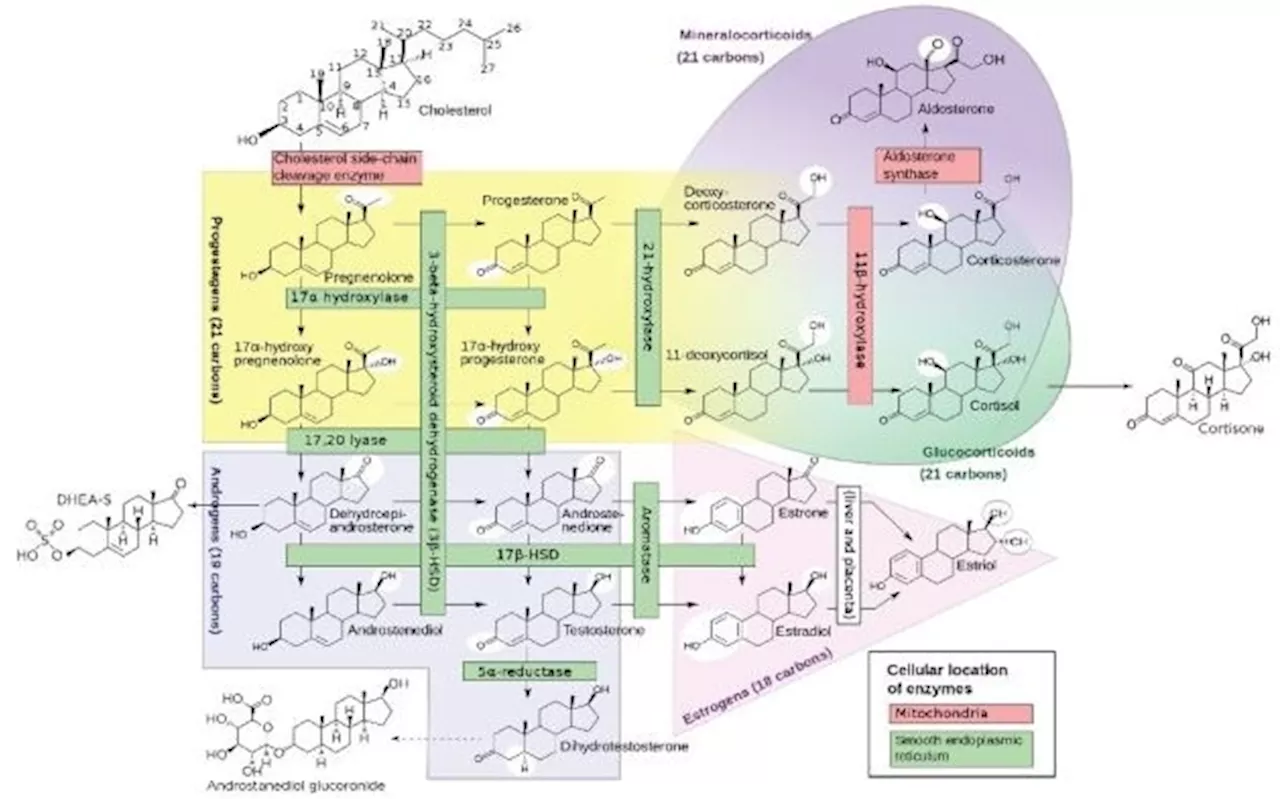 Enhancing LC-MS laboratories with expert endocrinology insightsEnhancing LC-MS laboratories with expert endocrinology insights enables precise and reliable hormone analysis, ensuring superior diagnostic outcomes.
Enhancing LC-MS laboratories with expert endocrinology insightsEnhancing LC-MS laboratories with expert endocrinology insights enables precise and reliable hormone analysis, ensuring superior diagnostic outcomes.
Read more »
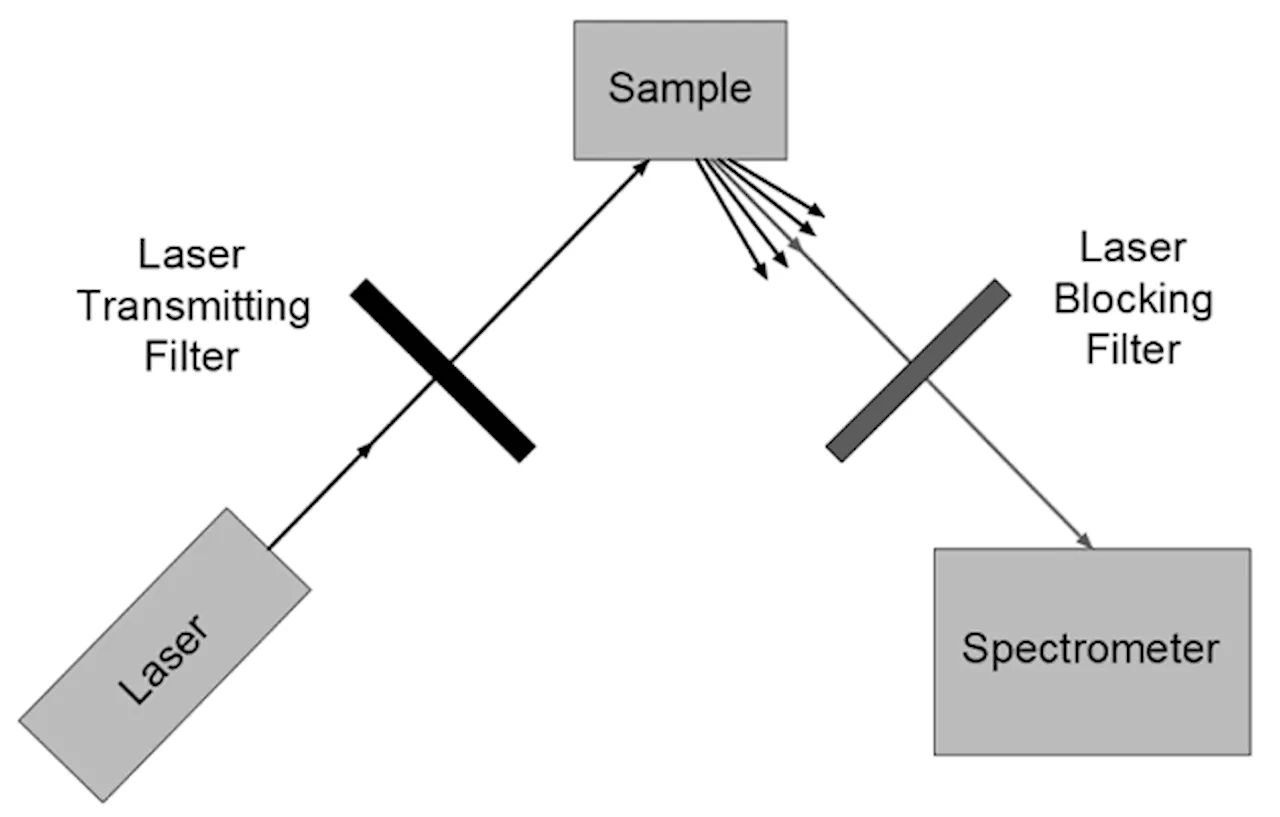 Enhancing biomedical applications: The role of advanced Raman filters in spectroscopyThis article discusses how advanced Raman filters enhance Raman spectroscopy by providing real-time data on biological tissues, highlighting their potential in medicine, research, and biomedical engineering.
Enhancing biomedical applications: The role of advanced Raman filters in spectroscopyThis article discusses how advanced Raman filters enhance Raman spectroscopy by providing real-time data on biological tissues, highlighting their potential in medicine, research, and biomedical engineering.
Read more »
 Frankie Bridge is a goddess in fitted 'tan enhancing' maxi dressFrankie looked unreal in the £50 Club L London dress
Frankie Bridge is a goddess in fitted 'tan enhancing' maxi dressFrankie looked unreal in the £50 Club L London dress
Read more »
 Enhancing adoptive T-cell therapy with nanowire innovationAdoptive T-cell therapy has revolutionized medicine. A patient's T-cells -; a type of white blood cell that is part of the body's immune system -; are extracted and modified in a lab and then infused back into the body, to seek and destroy infection, or cancer cells.
Enhancing adoptive T-cell therapy with nanowire innovationAdoptive T-cell therapy has revolutionized medicine. A patient's T-cells -; a type of white blood cell that is part of the body's immune system -; are extracted and modified in a lab and then infused back into the body, to seek and destroy infection, or cancer cells.
Read more »
 Rapeseed diacylglycerol oil may combat obesity by enhancing lipid metabolismA study in 'Nutrients' explores how rapeseed diacylglycerol oil (RDG) affects fat accumulation and metabolism in obese mice, showing significant benefits in reducing obesity-related indices and improving lipid metabolism.
Rapeseed diacylglycerol oil may combat obesity by enhancing lipid metabolismA study in 'Nutrients' explores how rapeseed diacylglycerol oil (RDG) affects fat accumulation and metabolism in obese mice, showing significant benefits in reducing obesity-related indices and improving lipid metabolism.
Read more »
 Enhancing neighborhood opportunities can be a promising approach to promote infant developmentGrowing up in neighborhoods with more educational and socioeconomic opportunities has a positive impact on infants' brain activity, according to new research from Boston Medical Center (BMC).
Enhancing neighborhood opportunities can be a promising approach to promote infant developmentGrowing up in neighborhoods with more educational and socioeconomic opportunities has a positive impact on infants' brain activity, according to new research from Boston Medical Center (BMC).
Read more »
