Further SARS-CoV-2 variants, and intermittent epidemics may become the 'new normal' Coronavirus Disease COVID Omicron VOCs Variants SARSCoV2 NatureComms TheQuadram imperialcollege UniofOxford
By Dr. Liji Thomas, MDAug 2 2022Reviewed by Benedette Cuffari, M.Sc. The outbreak of the severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 led to the coronavirus disease 2019 pandemic, which has claimed over 6.4 million deaths to date. Despite stringent efforts to limit viral transmission, SARS-CoV-2 has spread rapidly and mutated several times. This has led to the emergence of novel SARS-CoV-2 variants with higher transmissibility and immune evasion characteristics.
For example, the Omicron variant has 15 mutations in its receptor binding domain , which binds to the host angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 receptor. These mutations alter the sites where neutralizing antibodies bind to the RBD, subsequently allowing Omicron to escape neutralization, even after vaccination or prior infection with older SARS-CoV-2 variants.
The Omicron strains appeared to be primarily imported from or exported to the United States, Germany, and France. This might be due to the lower generation time for Omicron, which is estimated to be 28% less than that of the Delta variant. The higher rate of viral spread among younger and less vaccinated age groups who also mixed more in social circles could also be a contributing factor.
In late January 2022, the Rt increased to over one and subsequently declined throughout February; however, it tended to rise during this month. The prevalence of Omicron peaked in this group on January 28, 2022, at almost 11%. This was comparable to less than 8% on January 1, 2022, in those between the ages of 18 and 34.
Sublineage competition Previous models have shown that Omicron variants BA.1, BA.1.1, and BA.2 showed changing proportions over this period. Even as BA.2 increased, BA.1 prevalence declined. BA.1.1 became dominant in some countries before BA.1 even established itself, thus indicating its superior fitness through a greater number of beneficial mutations.
United Kingdom Latest News, United Kingdom Headlines
Similar News:You can also read news stories similar to this one that we have collected from other news sources.
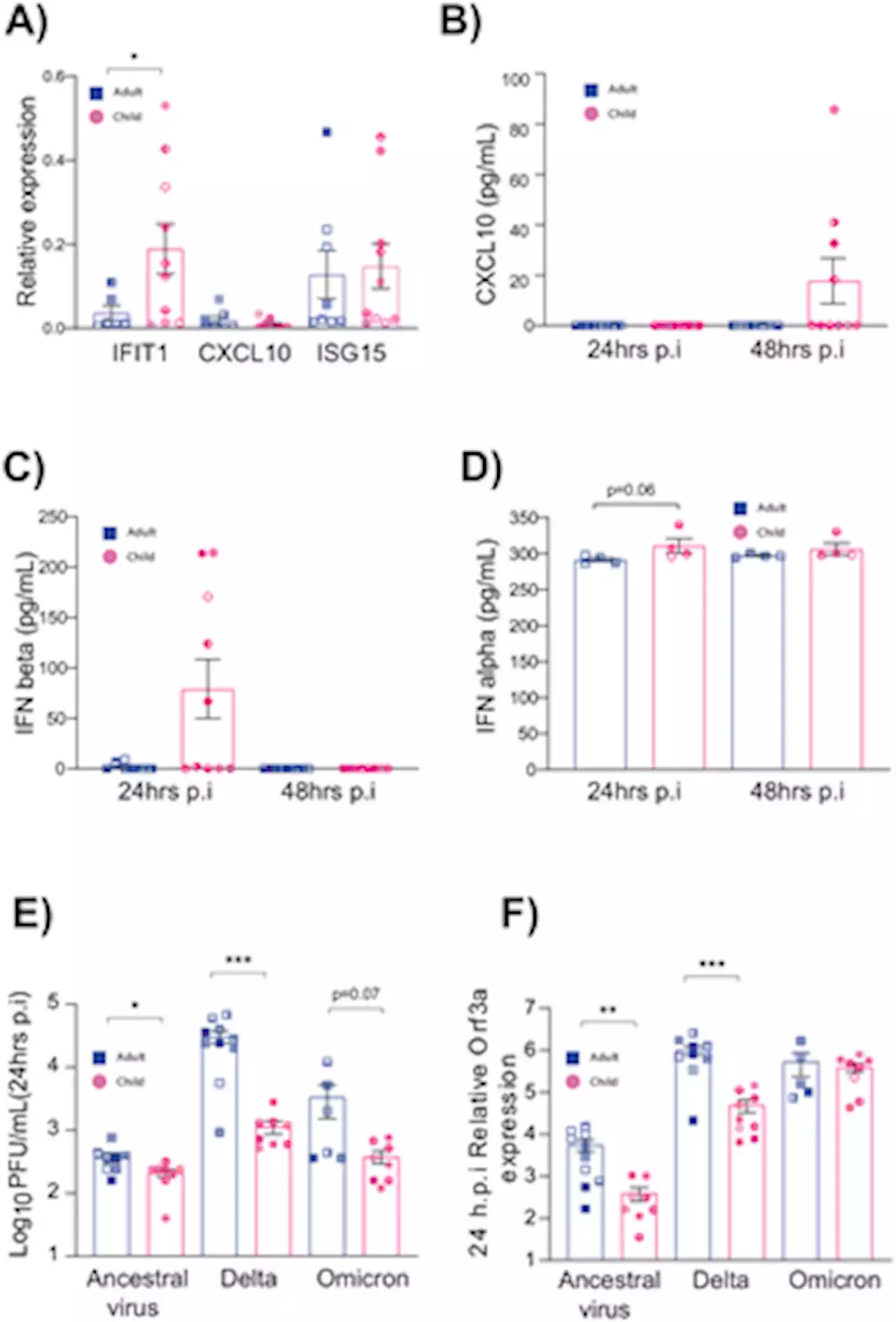 Ancestral SARS-CoV-2, but not Omicron, replicates less efficiently in primary pediatric nasal epithelial cellsChildren typically experience more mild symptoms of COVID-19 when compared to adults; why is this? This study uses nasal epithelial cells from children and adults to show that the ancestral SARS-CoV-2 and Delta, but not the Omicron variant, replicate less efficiently in pediatric nasal epithelial cells.
Ancestral SARS-CoV-2, but not Omicron, replicates less efficiently in primary pediatric nasal epithelial cellsChildren typically experience more mild symptoms of COVID-19 when compared to adults; why is this? This study uses nasal epithelial cells from children and adults to show that the ancestral SARS-CoV-2 and Delta, but not the Omicron variant, replicate less efficiently in pediatric nasal epithelial cells.
Read more »
 Study suggests peimine may be a potent inhibitor of SARS-CoV-2 variant infectionA recent study published in the Journal of Food Biochemistry discovered that peimine from Fritillaria might be a possible SARS-CoV-2 variant infection inhibitor.
Study suggests peimine may be a potent inhibitor of SARS-CoV-2 variant infectionA recent study published in the Journal of Food Biochemistry discovered that peimine from Fritillaria might be a possible SARS-CoV-2 variant infection inhibitor.
Read more »
 Long-term symptoms 23 months after SARS-CoV-2 infectionLong-term symptoms 23 months after SARS-CoV-2 infection symptoms COVID19 coronavirus covid infection SARSCoV2
Long-term symptoms 23 months after SARS-CoV-2 infectionLong-term symptoms 23 months after SARS-CoV-2 infection symptoms COVID19 coronavirus covid infection SARSCoV2
Read more »
 How can researchers profile post-COVID syndromes among distinct SARS-CoV-2 variants?How can researchers profile post-COVID syndromes among distinct SARS-CoV-2 variants? medrxivpreprint KingsCollegeLon SARSCoV2 COVID19 PostCOVIDSyndrome Variant
How can researchers profile post-COVID syndromes among distinct SARS-CoV-2 variants?How can researchers profile post-COVID syndromes among distinct SARS-CoV-2 variants? medrxivpreprint KingsCollegeLon SARSCoV2 COVID19 PostCOVIDSyndrome Variant
Read more »
 Hemopurifier containing Galanthus nivalis resin removes SARS-CoV-2 variantsHemopurifier containing Galanthus nivalis resin removes SARS-CoV-2 variants Antiviral Coronavirus Disease COVID Efficacy SARSCoV2 PLOSONE
Hemopurifier containing Galanthus nivalis resin removes SARS-CoV-2 variantsHemopurifier containing Galanthus nivalis resin removes SARS-CoV-2 variants Antiviral Coronavirus Disease COVID Efficacy SARSCoV2 PLOSONE
Read more »
 Study indicates that cross-reactive immunity against SARS-CoV-2 N protein was present in Africa prior to the pandemicResearchers assessed the pre-existing cross-protective immune responses against SARS-CoV-2 nucleocapsid protein and spike protein before the COVID-19 pandemic in individuals residing in North and South America, Europe and Africa in vitro and in vivo.
Study indicates that cross-reactive immunity against SARS-CoV-2 N protein was present in Africa prior to the pandemicResearchers assessed the pre-existing cross-protective immune responses against SARS-CoV-2 nucleocapsid protein and spike protein before the COVID-19 pandemic in individuals residing in North and South America, Europe and Africa in vitro and in vivo.
Read more »
