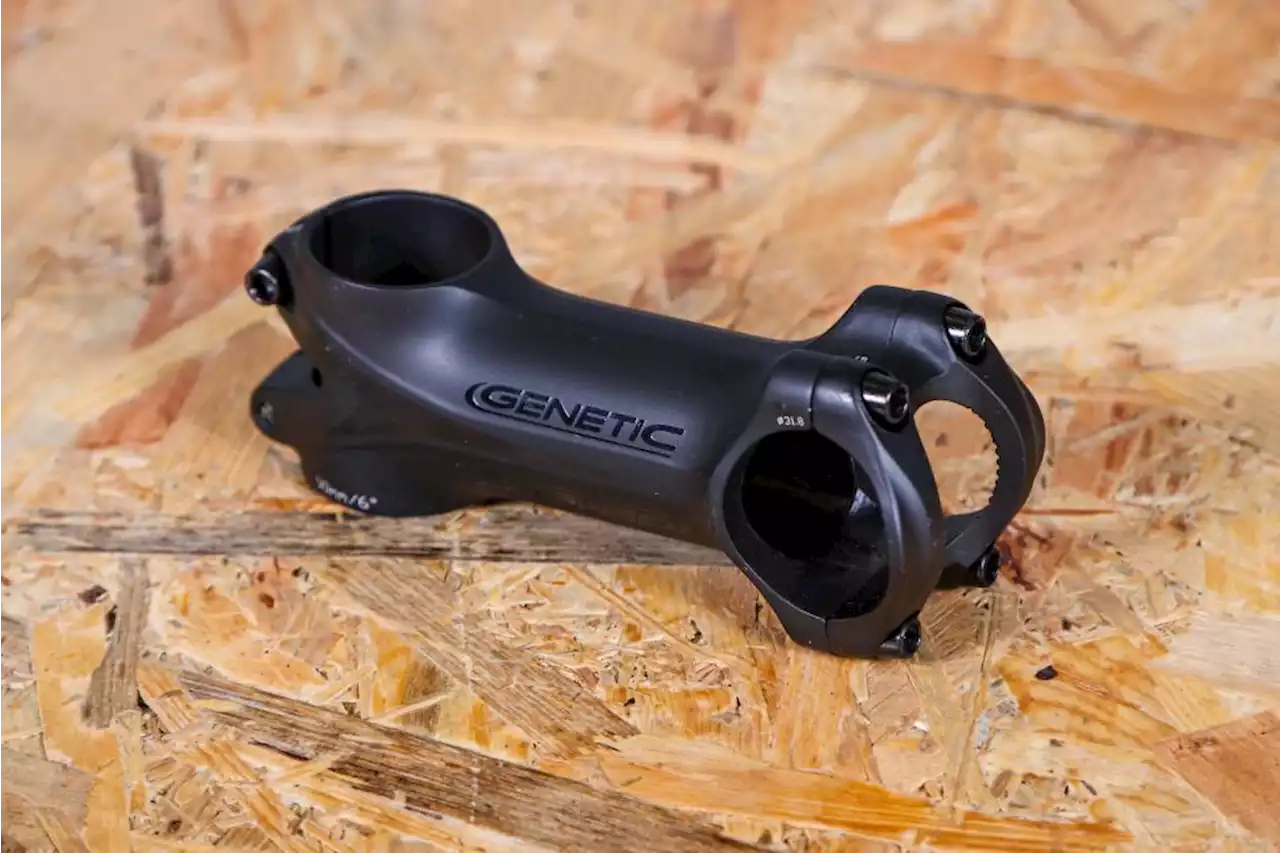
Review: Quality product at an attractive price Cycling geneticbikes
The Genetic STV stem is a good-looking bit of kit thanks to its stealthy finish and profiled shape. It does the job it's designed to do with ease – and without breaking the bank or the scales.
It gets a cool-looking stealth black finish on the logos, while the matt black paint has a high-quality look, giving a smooth finish around any sharp edges. It comes in a wide range of lengths too, from 60-130mm, which should mean that most of us can easily find the right one.The stem comes with black anodised bolts that have had threadlock applied to them to stop them rattling loose, and these take care of clamping duties effectively. I like the use of a single face plate, rather than a two-part affair, as I feel that this makes it easier to equally torque each bolt.
United Kingdom Latest News, United Kingdom Headlines
Similar News:You can also read news stories similar to this one that we have collected from other news sources.
 DGH-GO: dissecting the genetic heterogeneity of complex diseases using gene ontology - BMC BioinformaticsBackground Complex diseases such as neurodevelopmental disorders (NDDs) exhibit multiple etiologies. The multi-etiological nature of complex-diseases emerges from distinct but functionally similar group of genes. Different diseases sharing genes of such groups show related clinical outcomes that further restrict our understanding of disease mechanisms, thus, limiting the applications of personalized medicine approaches to complex genetic disorders. Results Here, we present an interactive and user-friendly application, called DGH-GO. DGH-GO allows biologists to dissect the genetic heterogeneity of complex diseases by stratifying the putative disease-causing genes into clusters that may contribute to distinct disease outcome development. It can also be used to study the shared etiology of complex-diseases. DGH-GO creates a semantic similarity matrix for the input genes by using Gene Ontology (GO). The resultant matrix can be visualized in 2D plots using different dimension reduction methods (T-SNE, Principal component analysis, umap and Principal coordinate analysis). In the next step, clusters of functionally similar genes are identified from genes functional similarities assessed through GO. This is achieved by employing four different clustering methods (K-means, Hierarchical, Fuzzy and PAM). The user may change the clustering parameters and explore their effect on stratification immediately. DGH-GO was applied to genes disrupted by rare genetic variants in Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) patients. The analysis confirmed the multi-etiological nature of ASD by identifying four clusters of genes that were enriched for distinct biological mechanisms and clinical outcome. In the second case study, the analysis of genes shared by different NDDs showed that genes causing multiple disorders tend to aggregate in similar clusters, indicating a possible shared etiology. Conclusion DGH-GO is a user-friendly application that allows biologists to study the multi-etiological natu
DGH-GO: dissecting the genetic heterogeneity of complex diseases using gene ontology - BMC BioinformaticsBackground Complex diseases such as neurodevelopmental disorders (NDDs) exhibit multiple etiologies. The multi-etiological nature of complex-diseases emerges from distinct but functionally similar group of genes. Different diseases sharing genes of such groups show related clinical outcomes that further restrict our understanding of disease mechanisms, thus, limiting the applications of personalized medicine approaches to complex genetic disorders. Results Here, we present an interactive and user-friendly application, called DGH-GO. DGH-GO allows biologists to dissect the genetic heterogeneity of complex diseases by stratifying the putative disease-causing genes into clusters that may contribute to distinct disease outcome development. It can also be used to study the shared etiology of complex-diseases. DGH-GO creates a semantic similarity matrix for the input genes by using Gene Ontology (GO). The resultant matrix can be visualized in 2D plots using different dimension reduction methods (T-SNE, Principal component analysis, umap and Principal coordinate analysis). In the next step, clusters of functionally similar genes are identified from genes functional similarities assessed through GO. This is achieved by employing four different clustering methods (K-means, Hierarchical, Fuzzy and PAM). The user may change the clustering parameters and explore their effect on stratification immediately. DGH-GO was applied to genes disrupted by rare genetic variants in Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) patients. The analysis confirmed the multi-etiological nature of ASD by identifying four clusters of genes that were enriched for distinct biological mechanisms and clinical outcome. In the second case study, the analysis of genes shared by different NDDs showed that genes causing multiple disorders tend to aggregate in similar clusters, indicating a possible shared etiology. Conclusion DGH-GO is a user-friendly application that allows biologists to study the multi-etiological natu
Read more »
 CRISPR and single-cell sequencing pinpoint causal genetic variants for traits and diseasesA major challenge in human genetics is understanding which parts of the genome drive specific traits or contribute to disease risk. This challenge is even greater for genetic variants found in the 98% of the genome that does not encode proteins.
CRISPR and single-cell sequencing pinpoint causal genetic variants for traits and diseasesA major challenge in human genetics is understanding which parts of the genome drive specific traits or contribute to disease risk. This challenge is even greater for genetic variants found in the 98% of the genome that does not encode proteins.
Read more »
 Researchers develop gene-edited stem cells to reduce arrhythmias in heart attack patientsIn a recent study published in the journal Cell Stem Cell, researchers hypothesized that pacemaker-like activity of human pluripotent stem cell-derived cardiomyocytes (hPSC-CMs) resulted in engraftment arrhythmias (EAs), which hampers the clinical use of cell-based therapy using hPSC-CMs for treatment of myocardial infarction (MI).
Researchers develop gene-edited stem cells to reduce arrhythmias in heart attack patientsIn a recent study published in the journal Cell Stem Cell, researchers hypothesized that pacemaker-like activity of human pluripotent stem cell-derived cardiomyocytes (hPSC-CMs) resulted in engraftment arrhythmias (EAs), which hampers the clinical use of cell-based therapy using hPSC-CMs for treatment of myocardial infarction (MI).
Read more »
US banks under fresh pressure as Nelson Peltz calls for Washington to stem crisis\n\t\t\tExpert insights, analysis and smart data help you cut through the noise to spot trends,\n\t\t\trisks and opportunities.\n\t\t\n\t\tJoin over 300,000 Finance professionals who already subscribe to the FT.
Read more »
 Breast Cancer Stem Cell–Derived Tumors Escape from γδ T-cell Immunosurveillance In Vivo by Modulating γδ T-cell LigandsAbstractThere are no targeted therapies for patients with triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC). TNBC is enriched in breast cancer stem cells (BCSC), which play a key role in metastasis, chemoresistance, relapse, and mortality. γδ T cells hold great potential in immunotherapy against cancer and might provide an approach to therapeutically target TNBC. γδ T cells are commonly observed to infiltrate solid tumors and have an extensive repertoire of tumor-sensing mechanisms, recognizing stress-induced molecules and phosphoantigens (pAgs) on transformed cells. Herein, we show that patient-derived triple-negative BCSCs are efficiently recognized and killed by ex vivo expanded γδ T cells from healthy donors. Orthotopically xenografted BCSCs, however, were refractory to γδ T-cell immunotherapy. We unraveled concerted differentiation and immune escape mechanisms: xenografted BCSCs lost stemness, expression of γδ T-cell ligands, adhesion molecules, and pAgs, thereby evading immune recognition by γδ T cells. Indeed, neither promigratory engineered γδ T cells, nor anti–PD-1 checkpoint blockade, significantly prolonged overall survival of tumor-bearing mice. BCSC immune escape was independent of the immune pressure exerted by the γδ T cells and could be pharmacologically reverted by zoledronate or IFNα treatment. These results pave the way for novel combinatorial immunotherapies for TNBC.
Breast Cancer Stem Cell–Derived Tumors Escape from γδ T-cell Immunosurveillance In Vivo by Modulating γδ T-cell LigandsAbstractThere are no targeted therapies for patients with triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC). TNBC is enriched in breast cancer stem cells (BCSC), which play a key role in metastasis, chemoresistance, relapse, and mortality. γδ T cells hold great potential in immunotherapy against cancer and might provide an approach to therapeutically target TNBC. γδ T cells are commonly observed to infiltrate solid tumors and have an extensive repertoire of tumor-sensing mechanisms, recognizing stress-induced molecules and phosphoantigens (pAgs) on transformed cells. Herein, we show that patient-derived triple-negative BCSCs are efficiently recognized and killed by ex vivo expanded γδ T cells from healthy donors. Orthotopically xenografted BCSCs, however, were refractory to γδ T-cell immunotherapy. We unraveled concerted differentiation and immune escape mechanisms: xenografted BCSCs lost stemness, expression of γδ T-cell ligands, adhesion molecules, and pAgs, thereby evading immune recognition by γδ T cells. Indeed, neither promigratory engineered γδ T cells, nor anti–PD-1 checkpoint blockade, significantly prolonged overall survival of tumor-bearing mice. BCSC immune escape was independent of the immune pressure exerted by the γδ T cells and could be pharmacologically reverted by zoledronate or IFNα treatment. These results pave the way for novel combinatorial immunotherapies for TNBC.
Read more »
 Chegg blames revenue slip on ChatGPT, stock price halvesStudent app maker says it's 'not a sky falling thing,' customizes own LLM just in case
Chegg blames revenue slip on ChatGPT, stock price halvesStudent app maker says it's 'not a sky falling thing,' customizes own LLM just in case
Read more »
