A team of scientists at Purple Mountain Observatory in China has determined that a non-rotating neutron star can't be much more than 2.25 solar masses, otherwise it would become a black hole.
When stars grow old and die, their mass determines their ultimate fate. Many supermassive stars have futures as neutron star s. But, the question is, how massive can their neutron star s get? That’s one that Professor Fan Yizhong and his team at Purple Mountain Observatory in China set out to answer. It turns out that a non-rotating neutron star can’t be much more than 2.25 solar masses. If it was more massive, it would face a much more dire fate: to become a black hole .
To figure this out, the team at Purple Mountain looked into what’s called the Oppenheimer limit. That’s the critical gravitational mass (abbreviated M) of a massive object. If a neutron star stays below that Oppenheimer limit, it will remain in that state. If it grows more massive, then it collapses into a black hole
Neutron Star Black Hole Mass Oppenheimer Limit Purple Mountain Observatory
United Kingdom Latest News, United Kingdom Headlines
Similar News:You can also read news stories similar to this one that we have collected from other news sources.
 Scientists create 5 new isotopes to learn how neutron star collisions forge goldRobert Lea is a science journalist in the U.K. whose articles have been published in Physics World, New Scientist, Astronomy Magazine, All About Space, Newsweek and ZME Science. He also writes about science communication for Elsevier and the European Journal of Physics. Rob holds a bachelor of science degree in physics and astronomy from the U.K.
Scientists create 5 new isotopes to learn how neutron star collisions forge goldRobert Lea is a science journalist in the U.K. whose articles have been published in Physics World, New Scientist, Astronomy Magazine, All About Space, Newsweek and ZME Science. He also writes about science communication for Elsevier and the European Journal of Physics. Rob holds a bachelor of science degree in physics and astronomy from the U.K.
Read more »
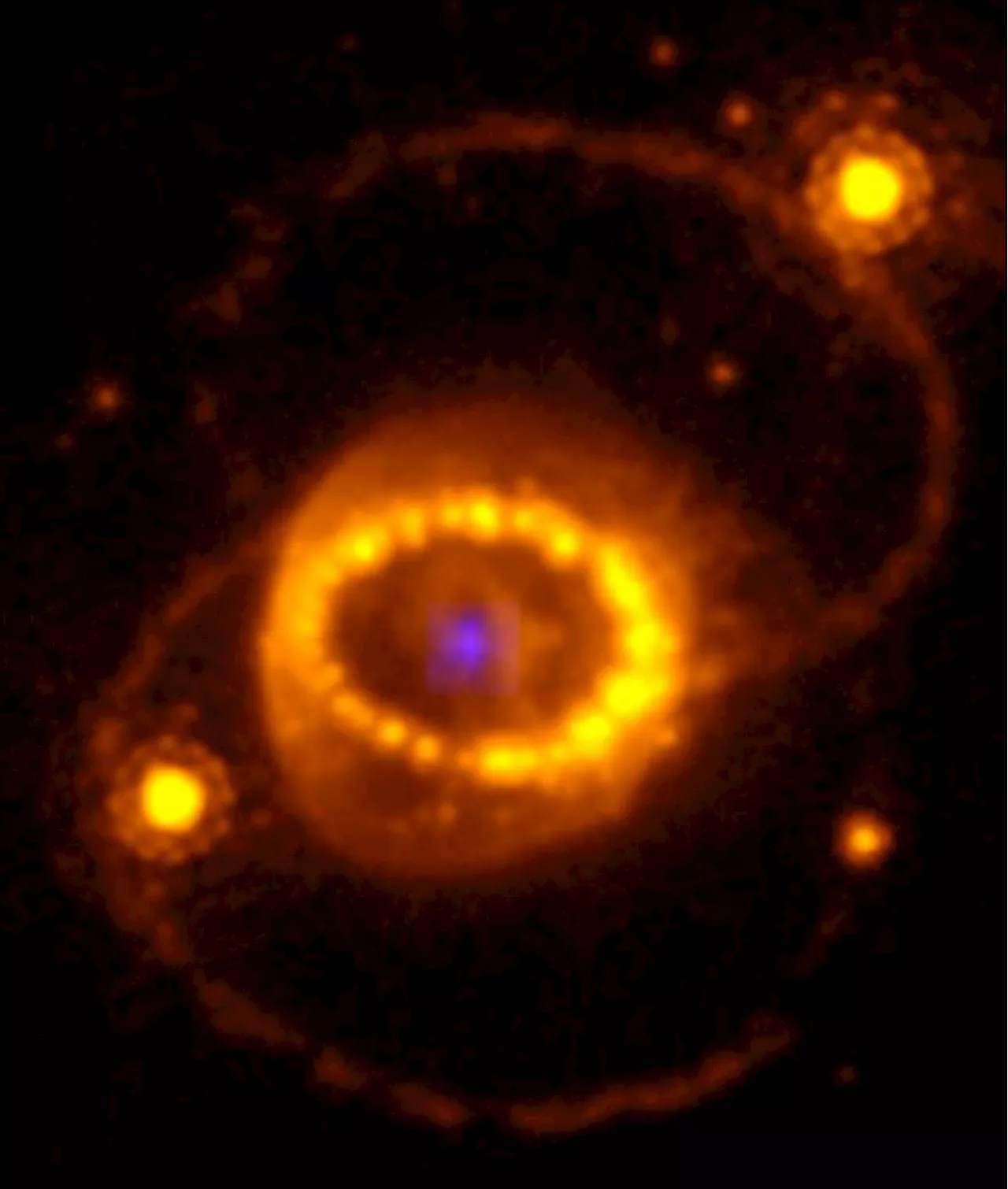 A Neutron Star Rests at Supernova 1987A’s CenterThe supernova has astonished experts since its discovery almost four decades ago
A Neutron Star Rests at Supernova 1987A’s CenterThe supernova has astonished experts since its discovery almost four decades ago
Read more »
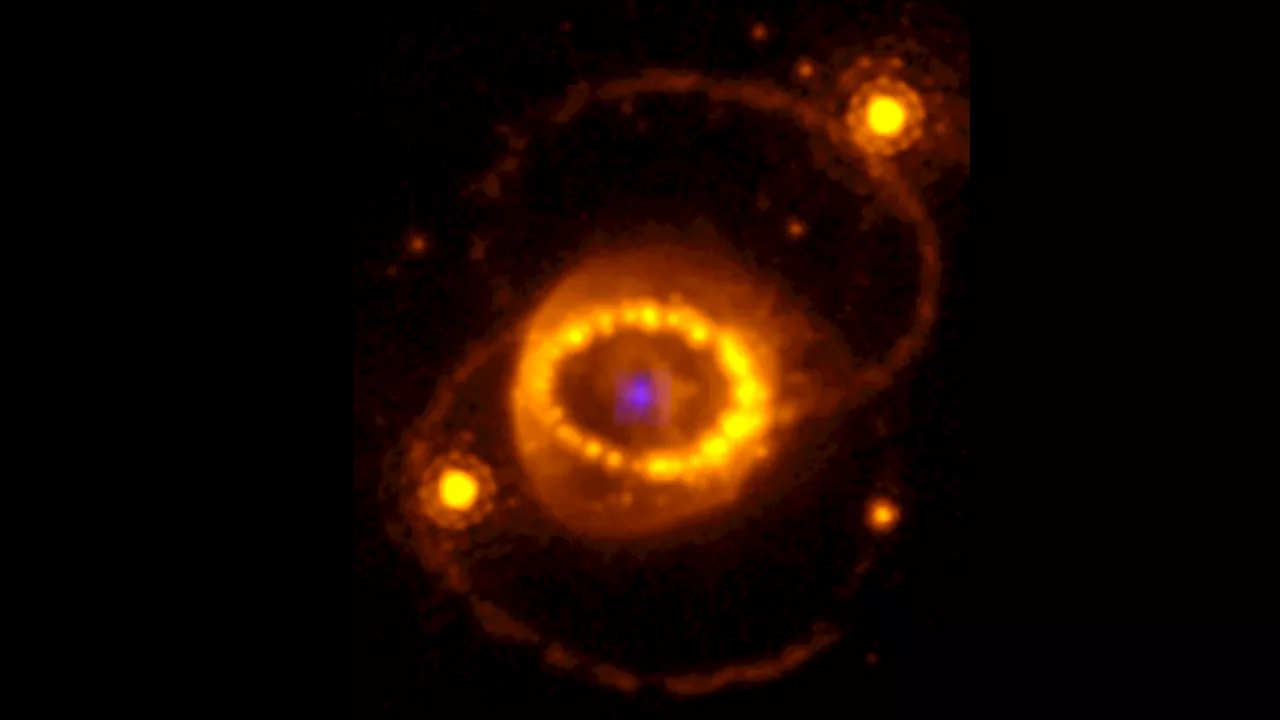 JWST spies hints of a neutron star left behind by supernova 1987ASigns of highly ionized atoms in dusty clouds at SN 1987A’s explosion site suggest a powerful source of X-rays — likely a neutron star — lurks within.
JWST spies hints of a neutron star left behind by supernova 1987ASigns of highly ionized atoms in dusty clouds at SN 1987A’s explosion site suggest a powerful source of X-rays — likely a neutron star — lurks within.
Read more »
 New kid on the block: Neutron imaging unveils hidden stories in fossilsDiscover how neutron imaging is reshaping our comprehension of Earth's history, from exposing hidden dinosaur insights to unveiling ancient artifacts.
New kid on the block: Neutron imaging unveils hidden stories in fossilsDiscover how neutron imaging is reshaping our comprehension of Earth's history, from exposing hidden dinosaur insights to unveiling ancient artifacts.
Read more »
 Webb finds evidence for neutron star at heart of young supernova remnantNASA's James Webb Space Telescope has found the best evidence yet for emission from a neutron star at the site of a recently observed supernova. The supernova, known as SN 1987A, was a core-collapse supernova, meaning the compacted remains at its core formed either a neutron star or a black hole.
Webb finds evidence for neutron star at heart of young supernova remnantNASA's James Webb Space Telescope has found the best evidence yet for emission from a neutron star at the site of a recently observed supernova. The supernova, known as SN 1987A, was a core-collapse supernova, meaning the compacted remains at its core formed either a neutron star or a black hole.
Read more »
 Finding new physics in debris from colliding neutron starsNeutron star mergers are a treasure trove for new physics signals, with implications for determining the true nature of dark matter, according to physicists.
Finding new physics in debris from colliding neutron starsNeutron star mergers are a treasure trove for new physics signals, with implications for determining the true nature of dark matter, according to physicists.
Read more »
