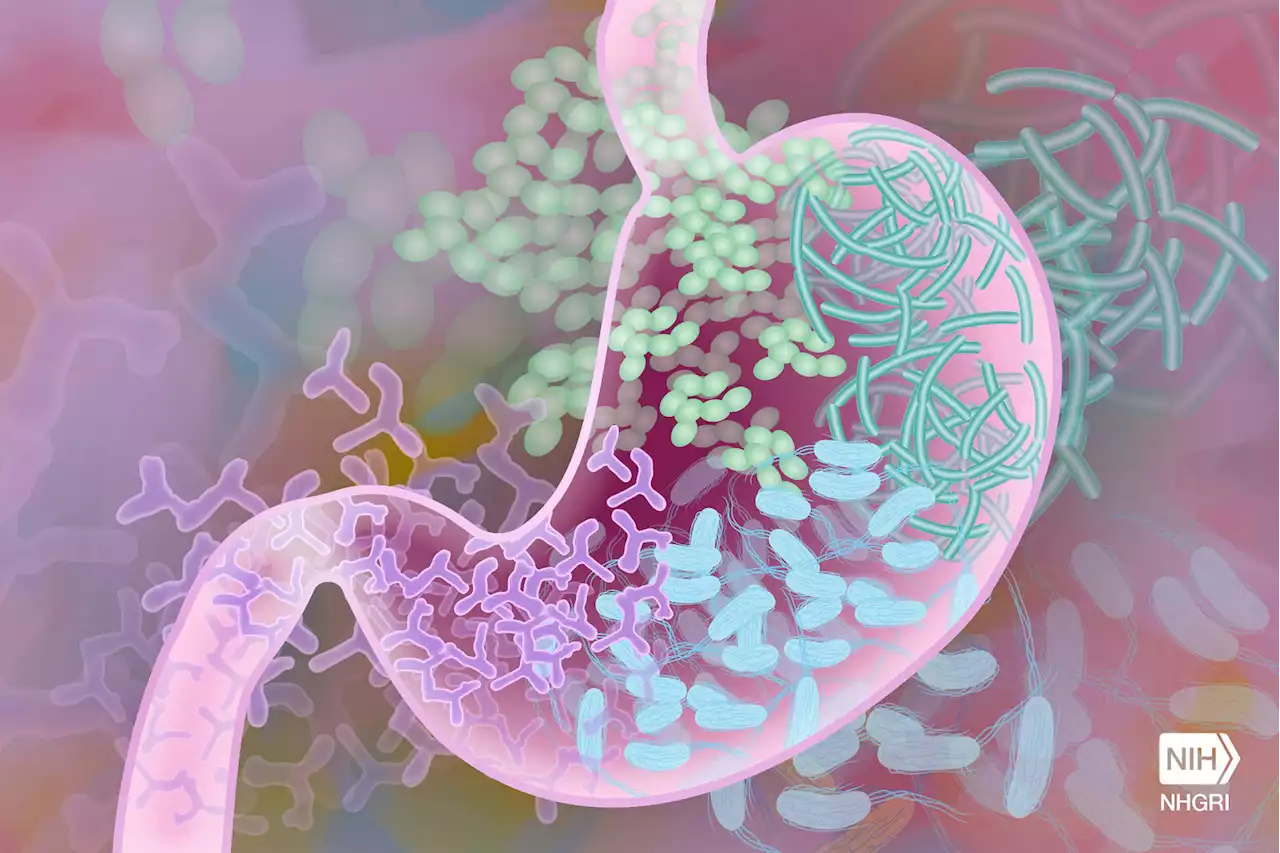
Immune system cells in the gut linked to stress-induced depression natimmunol
, suggesting that CSDS-induced social avoidance behavior may be the result of lower levels of the bacteria and γδ T cell changes."
For this experiment, mice were fed a dose of pachyman, which was shown in previous research to affect immune function. Data from flow cytometry analysis—a technology used to measure the physical and chemical characteristics of a population of cells—provided evidence that dectin-1 binds to pachyman, inhibiting CSDS-induced γδ17 T cell activity and easing social avoidance behavior.
Stool samples were collected from all study participants, who had comprehensive evaluations including psychiatric history and standard screening assessments for depression and anxiety. In these assessments, higher scores indicate greater depressive symptoms. Genetic analysis of theshowed no difference in the diversity of intestinal bacteria between the subjects with MDD and the control group.
United Kingdom Latest News, United Kingdom Headlines
Similar News:You can also read news stories similar to this one that we have collected from other news sources.
 Identification of biomarkers related to copper metabolism in patients with pulmonary arterial hypertension - BMC Pulmonary MedicineBackground The pathogenesis of pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH) and associated biomarkers remain to be studied. Copper metabolism is an emerging metabolic research direction in many diseases, but its role in PAH is still unclear. Methods PAH-related datasets were downloaded from the Gene Expression Omnibus database, and 2067 copper metabolism-related genes (CMGs) were obtained from the GeneCards database. Differential expression analysis and the Venn algorithm were used to acquire the differentially expressed CMGs (DE-CMGs). DE-CMGs were then used for the coexpression network construction to screen candidate key genes associated with PAH. Furthermore, the predictive performance of the model was verified by receiver operating characteristic (ROC) analysis, and genes with area under the curve (AUC) values greater than 0.8 were selected as diagnostic genes. Then support vector machine, least absolute shrinkage and selection operator regression, and Venn diagrams were applied to detect biomarkers. Moreover, gene set enrichment analysis was performed to explore the function of the biomarkers, and immune-related analyses were utilized to study the infiltration of immune cells. The drug-gene interaction database was used to predict potential therapeutic drugs for PAH using the biomarkers. Biomarkers expression in clinical samples was verified by real-time quantitative PCR. Results Four biomarkers (DDIT3, NFKBIA, OSM, and PTGER4) were screened. The ROC analysis showed that the 4 biomarkers performed well (AUCs | 0.7). The high expression groups for the 4 biomarkers were enriched in protein activity-related pathways including protein export, spliceosome and proteasome. Furthermore, 8 immune cell types were significantly different between the two groups, including naive B cells, memory B cells, and resting memory CD4 T cells. Afterward, a gene-drug network was constructed. This network illustrated that STREPTOZOCIN, IBUPROFEN, and CELECOXIB were shared by the PTGER4 and
Identification of biomarkers related to copper metabolism in patients with pulmonary arterial hypertension - BMC Pulmonary MedicineBackground The pathogenesis of pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH) and associated biomarkers remain to be studied. Copper metabolism is an emerging metabolic research direction in many diseases, but its role in PAH is still unclear. Methods PAH-related datasets were downloaded from the Gene Expression Omnibus database, and 2067 copper metabolism-related genes (CMGs) were obtained from the GeneCards database. Differential expression analysis and the Venn algorithm were used to acquire the differentially expressed CMGs (DE-CMGs). DE-CMGs were then used for the coexpression network construction to screen candidate key genes associated with PAH. Furthermore, the predictive performance of the model was verified by receiver operating characteristic (ROC) analysis, and genes with area under the curve (AUC) values greater than 0.8 were selected as diagnostic genes. Then support vector machine, least absolute shrinkage and selection operator regression, and Venn diagrams were applied to detect biomarkers. Moreover, gene set enrichment analysis was performed to explore the function of the biomarkers, and immune-related analyses were utilized to study the infiltration of immune cells. The drug-gene interaction database was used to predict potential therapeutic drugs for PAH using the biomarkers. Biomarkers expression in clinical samples was verified by real-time quantitative PCR. Results Four biomarkers (DDIT3, NFKBIA, OSM, and PTGER4) were screened. The ROC analysis showed that the 4 biomarkers performed well (AUCs | 0.7). The high expression groups for the 4 biomarkers were enriched in protein activity-related pathways including protein export, spliceosome and proteasome. Furthermore, 8 immune cell types were significantly different between the two groups, including naive B cells, memory B cells, and resting memory CD4 T cells. Afterward, a gene-drug network was constructed. This network illustrated that STREPTOZOCIN, IBUPROFEN, and CELECOXIB were shared by the PTGER4 and
Read more »
 Water intake, hydration status and 2-year changes in cognitive performance: a prospective cohort study - BMC MedicineBackground Water intake and hydration status have been suggested to impact cognition; however, longitudinal evidence is limited and often inconsistent. This study aimed to longitudinally assess the association between hydration status and water intake based on current recommendations, with changes in cognition in an older Spanish population at high cardiovascular disease risk. Methods A prospective analysis was conducted of a cohort of 1957 adults (aged 55–75) with overweight/obesity (BMI between ≥ 27 and | 40 kg/m2) and metabolic syndrome from the PREDIMED-Plus study. Participants had completed bloodwork and validated, semiquantitative beverage and food frequency questionnaires at baseline, as well as an extensive neuropsychological battery of 8 validated tests at baseline and 2 years of follow-up. Hydration status was determined by serum osmolarity calculation and categorized as | 295 mmol/L (hydrated), 295–299.9 mmol/L (impending dehydration), and ≥ 300 mmol/L (dehydrated). Water intake was assessed as total drinking water intake and total water intake from food and beverages and according to EFSA recommendations. Global cognitive function was determined as a composite z-score summarizing individual participant results from all neuropsychological tests. Multivariable linear regression models were fitted to assess the associations between baseline hydration status and fluid intake, continuously and categorically, with 2-year changes in cognitive performance. Results The mean baseline daily total water intake was 2871 ± 676 mL/day (2889 ± 677 mL/day in men; 2854 ± 674 mL/day in women), and 80.2% of participants met the ESFA reference values for an adequate intake. Serum osmolarity (mean 298 ± 24 mmol/L, range 263 to 347 mmol/L) indicated that 56% of participants were physiologically dehydrated. Lower physiological hydration status (i.e., greater serum osmolarity) was associated with a greater decline in global cognitive function z-score over a 2-year period (β: − 0
Water intake, hydration status and 2-year changes in cognitive performance: a prospective cohort study - BMC MedicineBackground Water intake and hydration status have been suggested to impact cognition; however, longitudinal evidence is limited and often inconsistent. This study aimed to longitudinally assess the association between hydration status and water intake based on current recommendations, with changes in cognition in an older Spanish population at high cardiovascular disease risk. Methods A prospective analysis was conducted of a cohort of 1957 adults (aged 55–75) with overweight/obesity (BMI between ≥ 27 and | 40 kg/m2) and metabolic syndrome from the PREDIMED-Plus study. Participants had completed bloodwork and validated, semiquantitative beverage and food frequency questionnaires at baseline, as well as an extensive neuropsychological battery of 8 validated tests at baseline and 2 years of follow-up. Hydration status was determined by serum osmolarity calculation and categorized as | 295 mmol/L (hydrated), 295–299.9 mmol/L (impending dehydration), and ≥ 300 mmol/L (dehydrated). Water intake was assessed as total drinking water intake and total water intake from food and beverages and according to EFSA recommendations. Global cognitive function was determined as a composite z-score summarizing individual participant results from all neuropsychological tests. Multivariable linear regression models were fitted to assess the associations between baseline hydration status and fluid intake, continuously and categorically, with 2-year changes in cognitive performance. Results The mean baseline daily total water intake was 2871 ± 676 mL/day (2889 ± 677 mL/day in men; 2854 ± 674 mL/day in women), and 80.2% of participants met the ESFA reference values for an adequate intake. Serum osmolarity (mean 298 ± 24 mmol/L, range 263 to 347 mmol/L) indicated that 56% of participants were physiologically dehydrated. Lower physiological hydration status (i.e., greater serum osmolarity) was associated with a greater decline in global cognitive function z-score over a 2-year period (β: − 0
Read more »
 Mediterranean diet adherence is associated with lower dementia risk, independent of genetic predisposition: findings from the UK Biobank prospective cohort study - BMC MedicineBackground The identification of effective dementia prevention strategies is a major public health priority, due to the enormous and growing societal cost of this condition. Consumption of a Mediterranean diet (MedDiet) has been proposed to reduce dementia risk. However, current evidence is inconclusive and is typically derived from small cohorts with limited dementia cases. Additionally, few studies have explored the interaction between diet and genetic risk of dementia. Methods We used Cox proportional hazard regression models to explore the associations between MedDiet adherence, defined using two different scores (Mediterranean Diet Adherence Screener [MEDAS] continuous and Mediterranean diet Pyramid [PYRAMID] scores), and incident all-cause dementia risk in 60,298 participants from UK Biobank, followed for an average 9.1 years. The interaction between diet and polygenic risk for dementia was also tested. Results Higher MedDiet adherence was associated with lower dementia risk (MEDAS continuous: HR = 0.77, 95% CI = 0.65–0.91; PYRAMID: HR = 0.86, 95% CI = 0.73–1.02 for highest versus lowest tertiles). There was no significant interaction between MedDiet adherence defined by the MEDAS continuous and PYRAMID scores and polygenic risk for dementia. Conclusions Higher adherence to a MedDiet was associated with lower dementia risk, independent of genetic risk, underlining the importance of diet in dementia prevention interventions.
Mediterranean diet adherence is associated with lower dementia risk, independent of genetic predisposition: findings from the UK Biobank prospective cohort study - BMC MedicineBackground The identification of effective dementia prevention strategies is a major public health priority, due to the enormous and growing societal cost of this condition. Consumption of a Mediterranean diet (MedDiet) has been proposed to reduce dementia risk. However, current evidence is inconclusive and is typically derived from small cohorts with limited dementia cases. Additionally, few studies have explored the interaction between diet and genetic risk of dementia. Methods We used Cox proportional hazard regression models to explore the associations between MedDiet adherence, defined using two different scores (Mediterranean Diet Adherence Screener [MEDAS] continuous and Mediterranean diet Pyramid [PYRAMID] scores), and incident all-cause dementia risk in 60,298 participants from UK Biobank, followed for an average 9.1 years. The interaction between diet and polygenic risk for dementia was also tested. Results Higher MedDiet adherence was associated with lower dementia risk (MEDAS continuous: HR = 0.77, 95% CI = 0.65–0.91; PYRAMID: HR = 0.86, 95% CI = 0.73–1.02 for highest versus lowest tertiles). There was no significant interaction between MedDiet adherence defined by the MEDAS continuous and PYRAMID scores and polygenic risk for dementia. Conclusions Higher adherence to a MedDiet was associated with lower dementia risk, independent of genetic risk, underlining the importance of diet in dementia prevention interventions.
Read more »
 Effects of music therapy as an alternative treatment on depression in children and adolescents with ADHD by activating serotonin and improving stress coping ability - BMC Complementary Medicine and TherapiesObjective The objective of this study was to determine the effect of music therapy as an alternative treatment on depression in children and adolescents with attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) by activating serotonin (5-HT) and improving stress coping ability. Methods This study is designed based on randomization method. A total of 36 subjects participated in the experiment, consisting of an ADHD control group (n=18) and ADHD music therapy group (n=18). The ADHD control group received standard care, while the ADHD music therapy group received music therapy and standard care. The ADHD music therapy group received both active music therapy (improvisation) and receptive music therapy (music listening) for 50 minutes, twice a week, for 3 months: a total of 24 times. From a neurophysiological perspective, changes in depression and stress were tracked by measuring 5-HT secretion, cortisol expression, blood pressure (BP), heart rate (HR), and CDI and DHQ psychological scales. Results The ADHD music therapy group’s 5-HT secretion increased (p | 0.001), whereas cortisol expression (p | 0.001), BP (p | 0.001) and HR (p | 0.001) decreased. The CDI and DHQ psychological scales also showed positive changes (p | 0.01 and p | 0.001, respectively). However, the ADHD Con G’s (who did not receive music therapy) 5-HT secretion did not increase, whereas cortisol expression, BP, and HR did not decrease. In addition, the CDI and DHQ psychological scales did not display positive changes. Conclusions In conclusion, the application of music therapy as an alternative treatment for ADHD children and adolescents showed positive neurophysiological and psychological effects. Therefore, this study would like to propose a new alternative to medicine for preventing and treating depression through various uses of music therapy.
Effects of music therapy as an alternative treatment on depression in children and adolescents with ADHD by activating serotonin and improving stress coping ability - BMC Complementary Medicine and TherapiesObjective The objective of this study was to determine the effect of music therapy as an alternative treatment on depression in children and adolescents with attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) by activating serotonin (5-HT) and improving stress coping ability. Methods This study is designed based on randomization method. A total of 36 subjects participated in the experiment, consisting of an ADHD control group (n=18) and ADHD music therapy group (n=18). The ADHD control group received standard care, while the ADHD music therapy group received music therapy and standard care. The ADHD music therapy group received both active music therapy (improvisation) and receptive music therapy (music listening) for 50 minutes, twice a week, for 3 months: a total of 24 times. From a neurophysiological perspective, changes in depression and stress were tracked by measuring 5-HT secretion, cortisol expression, blood pressure (BP), heart rate (HR), and CDI and DHQ psychological scales. Results The ADHD music therapy group’s 5-HT secretion increased (p | 0.001), whereas cortisol expression (p | 0.001), BP (p | 0.001) and HR (p | 0.001) decreased. The CDI and DHQ psychological scales also showed positive changes (p | 0.01 and p | 0.001, respectively). However, the ADHD Con G’s (who did not receive music therapy) 5-HT secretion did not increase, whereas cortisol expression, BP, and HR did not decrease. In addition, the CDI and DHQ psychological scales did not display positive changes. Conclusions In conclusion, the application of music therapy as an alternative treatment for ADHD children and adolescents showed positive neurophysiological and psychological effects. Therefore, this study would like to propose a new alternative to medicine for preventing and treating depression through various uses of music therapy.
Read more »
 Developing postoperative delirium associated with a faster rate of cognitive decline, says studyResearch published today (March 20) in the JAMA Internal Medicine finds that developing postoperative delirium is associated with a 40% faster rate of cognitive decline over those who do not develop delirium.
Developing postoperative delirium associated with a faster rate of cognitive decline, says studyResearch published today (March 20) in the JAMA Internal Medicine finds that developing postoperative delirium is associated with a 40% faster rate of cognitive decline over those who do not develop delirium.
Read more »
 Biological BMI: Researchers dig deep into data to determine better measures of metabolic healthInstitute for Systems Biology (ISB) researchers have constructed biological body mass index (BMI) measures that offer a more accurate representation of metabolic health and are more varied, informative and actionable than the traditional, long-used BMI equation. The work was published in the journal Nature Medicine.
Biological BMI: Researchers dig deep into data to determine better measures of metabolic healthInstitute for Systems Biology (ISB) researchers have constructed biological body mass index (BMI) measures that offer a more accurate representation of metabolic health and are more varied, informative and actionable than the traditional, long-used BMI equation. The work was published in the journal Nature Medicine.
Read more »