Impaired histone inheritance accelerates breast cancer growth and metastasis, study shows NatureComms
Epigenetic aberrations are linked to various diseases, including cancer.
However, the role of parentalTo explore the impact of impaired parental histone inheritance on histone modification profiles in MCM2, a team from the Shenzhen Institute of Advanced Technology of the Chinese Academy of Sciences developed a tumor model that introduces an MCM2-2A mutation, which is defective in parental histone binding, into breast cancer cell lines.
United Kingdom Latest News, United Kingdom Headlines
Similar News:You can also read news stories similar to this one that we have collected from other news sources.
 RELA governs a network of islet-specific metabolic genes necessary for beta cell function - DiabetologiaAims/hypothesis NF-κB activation unites metabolic and inflammatory responses in many diseases yet less is known about the role that NF-κB plays in normal metabolism. In this study we investigated how RELA impacts the beta cell transcriptional landscape and provides network control over glucoregulation. Methods We generated novel mouse lines harbouring beta cell-specific deletion of either the Rela gene, encoding the canonical NF-κB transcription factor p65 (βp65KO mice), or the Ikbkg gene, encoding the NF-κB essential modulator NEMO (βNEMOKO mice), as well as βA20Tg mice that carry beta cell-specific and forced transgenic expression of the NF-κB-negative regulator gene Tnfaip3, which encodes the A20 protein. Mouse studies were complemented by bioinformatics analysis of human islet chromatin accessibility (assay for transposase-accessible chromatin with sequencing [ATAC-seq]), promoter capture Hi-C (pcHi-C) and p65 binding (chromatin immunoprecipitation–sequencing [ChIP-seq]) data to investigate genome-wide control of the human beta cell metabolic programme. Results Rela deficiency resulted in complete loss of stimulus-dependent inflammatory gene upregulation, consistent with its known role in governing inflammation. However, Rela deletion also rendered mice glucose intolerant because of functional loss of insulin secretion. Glucose intolerance was intrinsic to beta cells as βp65KO islets failed to secrete insulin ex vivo in response to a glucose challenge and were unable to restore metabolic control when transplanted into secondary chemical-induced hyperglycaemic recipients. Maintenance of glucose tolerance required Rela but was independent of classical NF-κB inflammatory cascades, as blocking NF-κB signalling in vivo by beta cell knockout of Ikbkg (NEMO), or beta cell overexpression of Tnfaip3 (A20), did not cause severe glucose intolerance. Thus, basal p65 activity has an essential and islet-intrinsic role in maintaining normal glucose homeostasis. Genome-wide bio
RELA governs a network of islet-specific metabolic genes necessary for beta cell function - DiabetologiaAims/hypothesis NF-κB activation unites metabolic and inflammatory responses in many diseases yet less is known about the role that NF-κB plays in normal metabolism. In this study we investigated how RELA impacts the beta cell transcriptional landscape and provides network control over glucoregulation. Methods We generated novel mouse lines harbouring beta cell-specific deletion of either the Rela gene, encoding the canonical NF-κB transcription factor p65 (βp65KO mice), or the Ikbkg gene, encoding the NF-κB essential modulator NEMO (βNEMOKO mice), as well as βA20Tg mice that carry beta cell-specific and forced transgenic expression of the NF-κB-negative regulator gene Tnfaip3, which encodes the A20 protein. Mouse studies were complemented by bioinformatics analysis of human islet chromatin accessibility (assay for transposase-accessible chromatin with sequencing [ATAC-seq]), promoter capture Hi-C (pcHi-C) and p65 binding (chromatin immunoprecipitation–sequencing [ChIP-seq]) data to investigate genome-wide control of the human beta cell metabolic programme. Results Rela deficiency resulted in complete loss of stimulus-dependent inflammatory gene upregulation, consistent with its known role in governing inflammation. However, Rela deletion also rendered mice glucose intolerant because of functional loss of insulin secretion. Glucose intolerance was intrinsic to beta cells as βp65KO islets failed to secrete insulin ex vivo in response to a glucose challenge and were unable to restore metabolic control when transplanted into secondary chemical-induced hyperglycaemic recipients. Maintenance of glucose tolerance required Rela but was independent of classical NF-κB inflammatory cascades, as blocking NF-κB signalling in vivo by beta cell knockout of Ikbkg (NEMO), or beta cell overexpression of Tnfaip3 (A20), did not cause severe glucose intolerance. Thus, basal p65 activity has an essential and islet-intrinsic role in maintaining normal glucose homeostasis. Genome-wide bio
Read more »
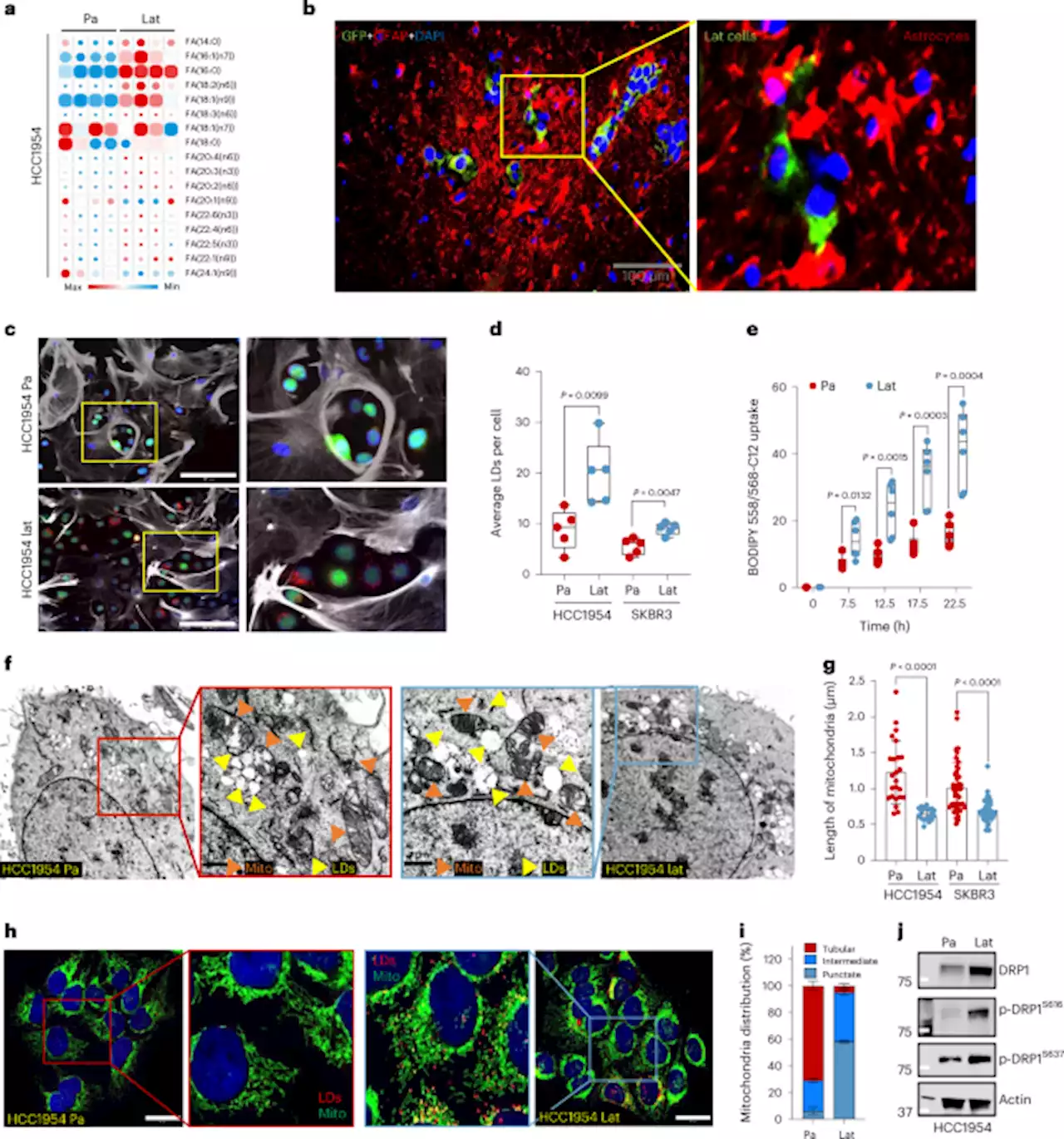 Limiting mitochondrial plasticity by targeting DRP1 induces metabolic reprogramming and reduces breast cancer brain metastases - Nature CancerMalladi and colleagues show that inhibiting DRP1 limits mitochondrial plasticity, resulting in increased mitochondrial fusion, impaired fatty acid oxidation and reduced metastasis formation in breast cancer models.
Limiting mitochondrial plasticity by targeting DRP1 induces metabolic reprogramming and reduces breast cancer brain metastases - Nature CancerMalladi and colleagues show that inhibiting DRP1 limits mitochondrial plasticity, resulting in increased mitochondrial fusion, impaired fatty acid oxidation and reduced metastasis formation in breast cancer models.
Read more »
 Prediction of treatment response to antipsychotic drugs for precision medicine approach to schizophrenia: randomized trials and multiomics analysis - Military Medical ResearchBackground Choosing the appropriate antipsychotic drug (APD) treatment for patients with schizophrenia (SCZ) can be challenging, as the treatment response to APD is highly variable and difficult to predict due to the lack of effective biomarkers. Previous studies have indicated the association between treatment response and genetic and epigenetic factors, but no effective biomarkers have been identified. Hence, further research is imperative to enhance precision medicine in SCZ treatment. Methods Participants with SCZ were recruited from two randomized trials. The discovery cohort was recruited from the CAPOC trial (n = 2307) involved 6 weeks of treatment and equally randomized the participants to the Olanzapine, Risperidone, Quetiapine, Aripiprazole, Ziprasidone, and Haloperidol/Perphenazine (subsequently equally assigned to one or the other) groups. The external validation cohort was recruited from the CAPEC trial (n = 1379), which involved 8 weeks of treatment and equally randomized the participants to the Olanzapine, Risperidone, and Aripiprazole groups. Additionally, healthy controls (n = 275) from the local community were utilized as a genetic/epigenetic reference. The genetic and epigenetic (DNA methylation) risks of SCZ were assessed using the polygenic risk score (PRS) and polymethylation score, respectively. The study also examined the genetic-epigenetic interactions with treatment response through differential methylation analysis, methylation quantitative trait loci, colocalization, and promoter-anchored chromatin interaction. Machine learning was used to develop a prediction model for treatment response, which was evaluated for accuracy and clinical benefit using the area under curve (AUC) for classification, R2 for regression, and decision curve analysis. Results Six risk genes for SCZ (LINC01795, DDHD2, SBNO1, KCNG2, SEMA7A, and RUFY1) involved in cortical morphology were identified as having a genetic-epigenetic interaction associated with treatment
Prediction of treatment response to antipsychotic drugs for precision medicine approach to schizophrenia: randomized trials and multiomics analysis - Military Medical ResearchBackground Choosing the appropriate antipsychotic drug (APD) treatment for patients with schizophrenia (SCZ) can be challenging, as the treatment response to APD is highly variable and difficult to predict due to the lack of effective biomarkers. Previous studies have indicated the association between treatment response and genetic and epigenetic factors, but no effective biomarkers have been identified. Hence, further research is imperative to enhance precision medicine in SCZ treatment. Methods Participants with SCZ were recruited from two randomized trials. The discovery cohort was recruited from the CAPOC trial (n = 2307) involved 6 weeks of treatment and equally randomized the participants to the Olanzapine, Risperidone, Quetiapine, Aripiprazole, Ziprasidone, and Haloperidol/Perphenazine (subsequently equally assigned to one or the other) groups. The external validation cohort was recruited from the CAPEC trial (n = 1379), which involved 8 weeks of treatment and equally randomized the participants to the Olanzapine, Risperidone, and Aripiprazole groups. Additionally, healthy controls (n = 275) from the local community were utilized as a genetic/epigenetic reference. The genetic and epigenetic (DNA methylation) risks of SCZ were assessed using the polygenic risk score (PRS) and polymethylation score, respectively. The study also examined the genetic-epigenetic interactions with treatment response through differential methylation analysis, methylation quantitative trait loci, colocalization, and promoter-anchored chromatin interaction. Machine learning was used to develop a prediction model for treatment response, which was evaluated for accuracy and clinical benefit using the area under curve (AUC) for classification, R2 for regression, and decision curve analysis. Results Six risk genes for SCZ (LINC01795, DDHD2, SBNO1, KCNG2, SEMA7A, and RUFY1) involved in cortical morphology were identified as having a genetic-epigenetic interaction associated with treatment
Read more »
 Limiting mitochondrial plasticity by targeting DRP1 induces metabolic reprogramming and reduces breast cancer brain metastases - Nature CancerMalladi and colleagues show that inhibiting DRP1 limits mitochondrial plasticity, resulting in increased mitochondrial fusion, impaired fatty acid oxidation and reduced metastasis formation in breast cancer models.
Limiting mitochondrial plasticity by targeting DRP1 induces metabolic reprogramming and reduces breast cancer brain metastases - Nature CancerMalladi and colleagues show that inhibiting DRP1 limits mitochondrial plasticity, resulting in increased mitochondrial fusion, impaired fatty acid oxidation and reduced metastasis formation in breast cancer models.
Read more »
 Heartache as mum-of-two dies from cancer two weeks after phone call from doctorA young mum has died from cancer just two weeks after she was told she wouldn't be able to go on holiday by a doctor
Heartache as mum-of-two dies from cancer two weeks after phone call from doctorA young mum has died from cancer just two weeks after she was told she wouldn't be able to go on holiday by a doctor
Read more »
 Mom, 37, with stage 3 breast cancer says trying on her swimsuit saved her lifeAfter Julie Devaney Hogan's “bikini saved her life,” the Boston mom started Season for Squeezin’, a campaign to encourage breast cancer awareness in younger women.
Mom, 37, with stage 3 breast cancer says trying on her swimsuit saved her lifeAfter Julie Devaney Hogan's “bikini saved her life,” the Boston mom started Season for Squeezin’, a campaign to encourage breast cancer awareness in younger women.
Read more »
