Researchers have developed new chemistry to achieve commercially relevant stability and performance for perovskite solar cells.
Solar power is not only the fastest growing energy technology in recent history but also one of the cheapest energy sources and the most impactful in terms of reducing greenhouse gas emissions.) -- the type of crystal currently used to make the highest-efficiency perovskite solar cells -- into ultrastable, high-quality photovoltaic films.
"Perovskite crystals get broken in two ways: chemically -- destroying the molecules that make up the crystal -- and structurally -- reordering the molecules to form a different crystal," said Isaac Metcalf, a Rice materials science and nanoengineering graduate student and a lead author on the study."Of the various crystals that we use in solar cells, the most chemically stable are also the least structurally stable and vice versa.
Although it is the most widely used semiconductor in photovoltaic cells, silicon entails manufacturing processes that are more resource-intensive than those of emerging alternatives. Among these, halide perovskites stand out for their soaring efficiencies, which have gone from 3.9% in 2009 to over 26% currently.
Mohite underscored that advancements in solar energy technologies and infrastructure are critical for achieving the greenhouse gas emissions 2030 target and preventing a 1.5 degrees Celsius rise in global temperatures, which"would then set us on the right course to achieve net zero carbon emissions by 2050."
"I would like to give a lot of credit to Siraj, who started this project based on a theoretical idea by Professor Jacky Even at the University of Rennes," Mohite said."I would also like to thank our collaborators at the national labs and at several universities in the U.S. and abroad whose help was instrumental to this work."
Energy And Resources Energy Policy Graphene Petroleum Energy Technology Chemistry Materials Science
United Kingdom Latest News, United Kingdom Headlines
Similar News:You can also read news stories similar to this one that we have collected from other news sources.
 Postdoctoral Fellow in Systems Immunology (dry lab) - Boston, Massachusetts (US) job with Boston University Atomic LabAtomic Lab (https://atomic-lab.org/) at the National Emerging Infectious Diseases Laboratories, Boston seeks a Postdoctoral Fellow with a background in AI, data science and bioinformatics.
Postdoctoral Fellow in Systems Immunology (dry lab) - Boston, Massachusetts (US) job with Boston University Atomic LabAtomic Lab (https://atomic-lab.org/) at the National Emerging Infectious Diseases Laboratories, Boston seeks a Postdoctoral Fellow with a background in AI, data science and bioinformatics.
Read more »
 In a significant first, researchers detect water frost on solar system's tallest volcanoesAn international team of planetary scientists has detected patches of water frost sitting atop the Tharsis volcanoes on Mars, which are not only the tallest volcanic mountains on the Red Planet but in the entire solar system.
In a significant first, researchers detect water frost on solar system's tallest volcanoesAn international team of planetary scientists has detected patches of water frost sitting atop the Tharsis volcanoes on Mars, which are not only the tallest volcanic mountains on the Red Planet but in the entire solar system.
Read more »
 US funding boosts Rocket Lab’s space-grade solar cell production by 50%Rocket Lab receives $23.9 million in CHIPS Act funding to expand production of space-grade solar cells, boosting semiconductor manufacturing.
US funding boosts Rocket Lab’s space-grade solar cell production by 50%Rocket Lab receives $23.9 million in CHIPS Act funding to expand production of space-grade solar cells, boosting semiconductor manufacturing.
Read more »
 Psychology researchers find collaborative imagination increases social connectionThe ability to imagine is pivotal for human development, driving creativity and problem-solving. It may also influence our relationship with others, according to new research.
Psychology researchers find collaborative imagination increases social connectionThe ability to imagine is pivotal for human development, driving creativity and problem-solving. It may also influence our relationship with others, according to new research.
Read more »
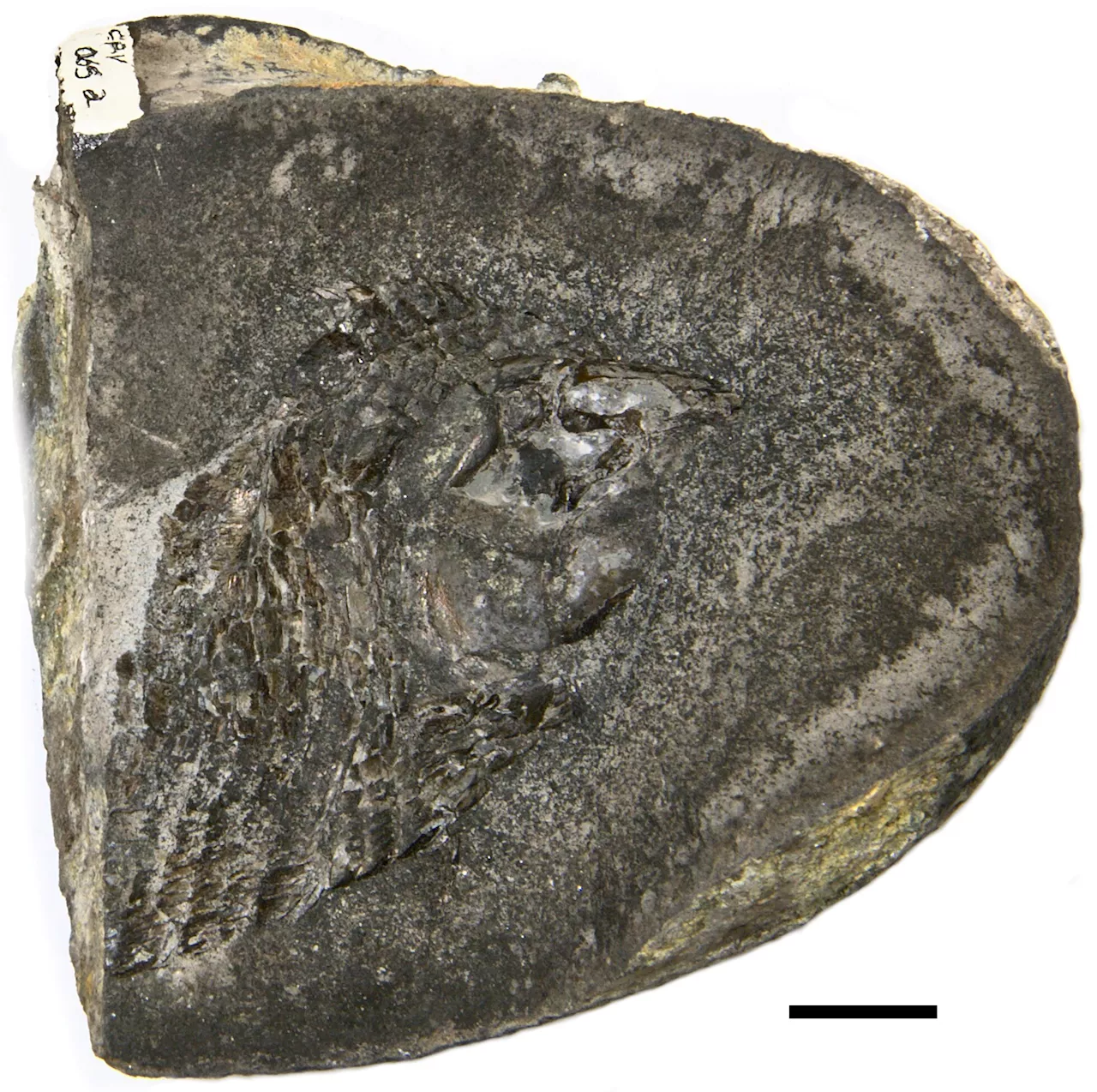 Researchers find rare organ preservation in Brazilian fossil fishesFossils in Brazil indicate a more complex evolutionary history for ray-finned fish brains than previously anticipated, according to new research.
Researchers find rare organ preservation in Brazilian fossil fishesFossils in Brazil indicate a more complex evolutionary history for ray-finned fish brains than previously anticipated, according to new research.
Read more »
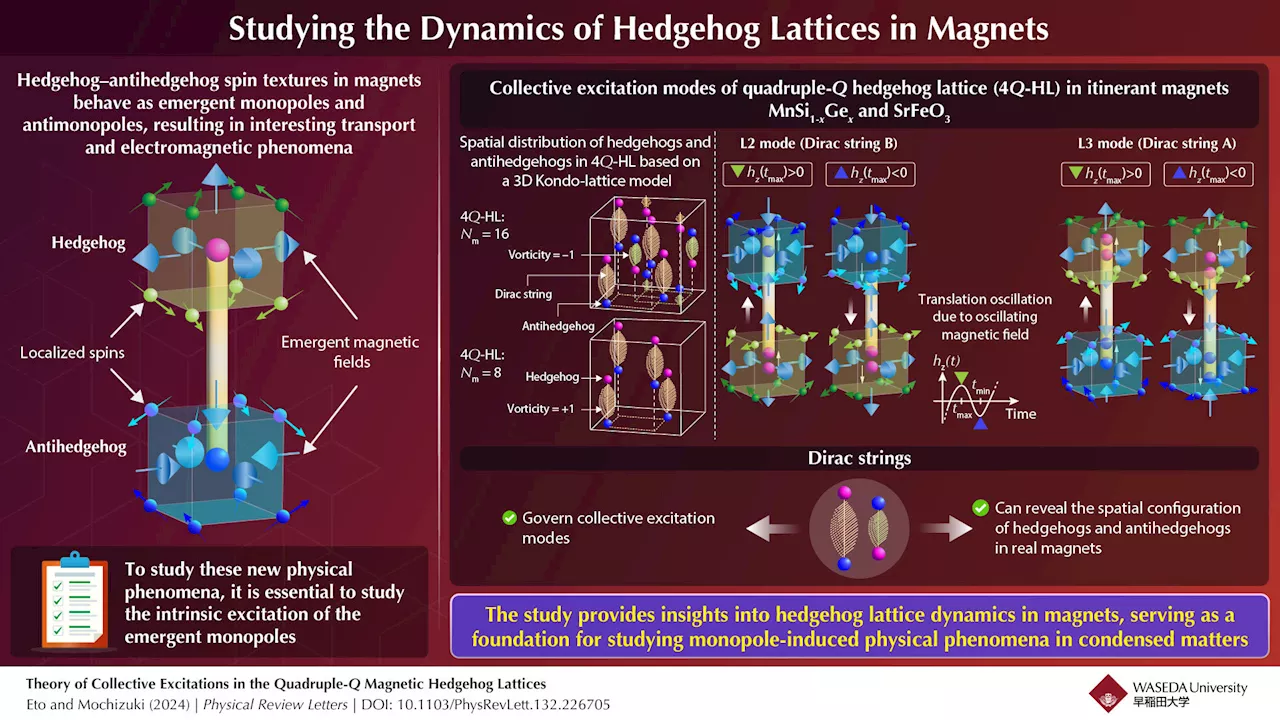 Researchers unveil the dynamical nature of emergent magnetic monopoles in real magnets for the first timeMagnetic monopoles are elementary particles with isolated magnetic charges in three dimensions. In other words, they behave as isolated north or south poles of a magnet. Magnetic monopoles have attracted continuous research interest since physicist Paul Dirac's first proposal in 1931.
Researchers unveil the dynamical nature of emergent magnetic monopoles in real magnets for the first timeMagnetic monopoles are elementary particles with isolated magnetic charges in three dimensions. In other words, they behave as isolated north or south poles of a magnet. Magnetic monopoles have attracted continuous research interest since physicist Paul Dirac's first proposal in 1931.
Read more »
