Hepatitis C can be cured in almost all cases with modern medication. However, if advanced liver damage is already present at the time of cure, there is still a residual risk of liver cancer and complications of portal hypertension, such as abdominal fluid, bleeding from the digestive tract and confusion.
Medical University of ViennaAug 14 2024 New studies by an international research group coordinated by MedUni Vienna show that liver stiffness should be the primary indicator used to assess the risk after the end of treatment. The study results published in the renowned specialist journals Hepatology and Journal of Hepatology make a significant contribution to determining the individual risk and enable individualized follow-up care.
In the first of the two current studies, the research group from MedUni Vienna's Department of Medicine III analyzed patients from a number of European countries whose hepatitis C infection was cured in advanced but still asymptomatic disease. Interestingly, there is no further decrease in the residual risk of cancer and complications of portal hypertension, such as abdominal fluid, bleeding from the digestive tract and confusion in the long term, i.e. up to 6 years after treatment. The good news, however, many patients can be reassured that they are at negligible risk, at least with regard to the above-mentioned complications of portal hypertension, i.e. hepatic decompensation events.
With regard to liver cancer, the situation is more complex, but a new model can be used to estimate the individual risk. However, even if the individual risk is low, a decision must be made together with the patient as to whether to discontinue surveillance by means of 6-monthly liver ultrasound," explains Georg Semmler.
Liver stiffness value after the end of therapy is key "In addition to our established criteria, the change in liver stiffness over time was also taken into account in Baveno VII. Based on our findings, however, at least in the context of cured hepatitis C, primary attention should be paid to the current liver stiffness value," states last author Mattias Mandorfer, who will chair the corresponding chapter of the next, internationally recognized Baveno VIII consensus.
Hepatitis Hepatitis C Liver Liver Disease Bleeding Hepatology Liver Cancer Research
United Kingdom Latest News, United Kingdom Headlines
Similar News:You can also read news stories similar to this one that we have collected from other news sources.
 Study finds targeting inflammation may not help reduce liver fibrosis in metabolic-associated fatty liver diseaseResearchers at UCLA Health uncovered new information about the role inflammation plays in mitigating liver fibrosis, which is associated with metabolic-associated fatty liver disease (MAFLD), one of the most common diseases in the world affecting up to 40% of U.S. adults.
Study finds targeting inflammation may not help reduce liver fibrosis in metabolic-associated fatty liver diseaseResearchers at UCLA Health uncovered new information about the role inflammation plays in mitigating liver fibrosis, which is associated with metabolic-associated fatty liver disease (MAFLD), one of the most common diseases in the world affecting up to 40% of U.S. adults.
Read more »
 Liver transplant outperforms other therapies for colorectal cancer that has spread to the liverColorectal cancer often spreads to the liver, and for some patients, surgical removal of their liver tumors is not an option.
Liver transplant outperforms other therapies for colorectal cancer that has spread to the liverColorectal cancer often spreads to the liver, and for some patients, surgical removal of their liver tumors is not an option.
Read more »
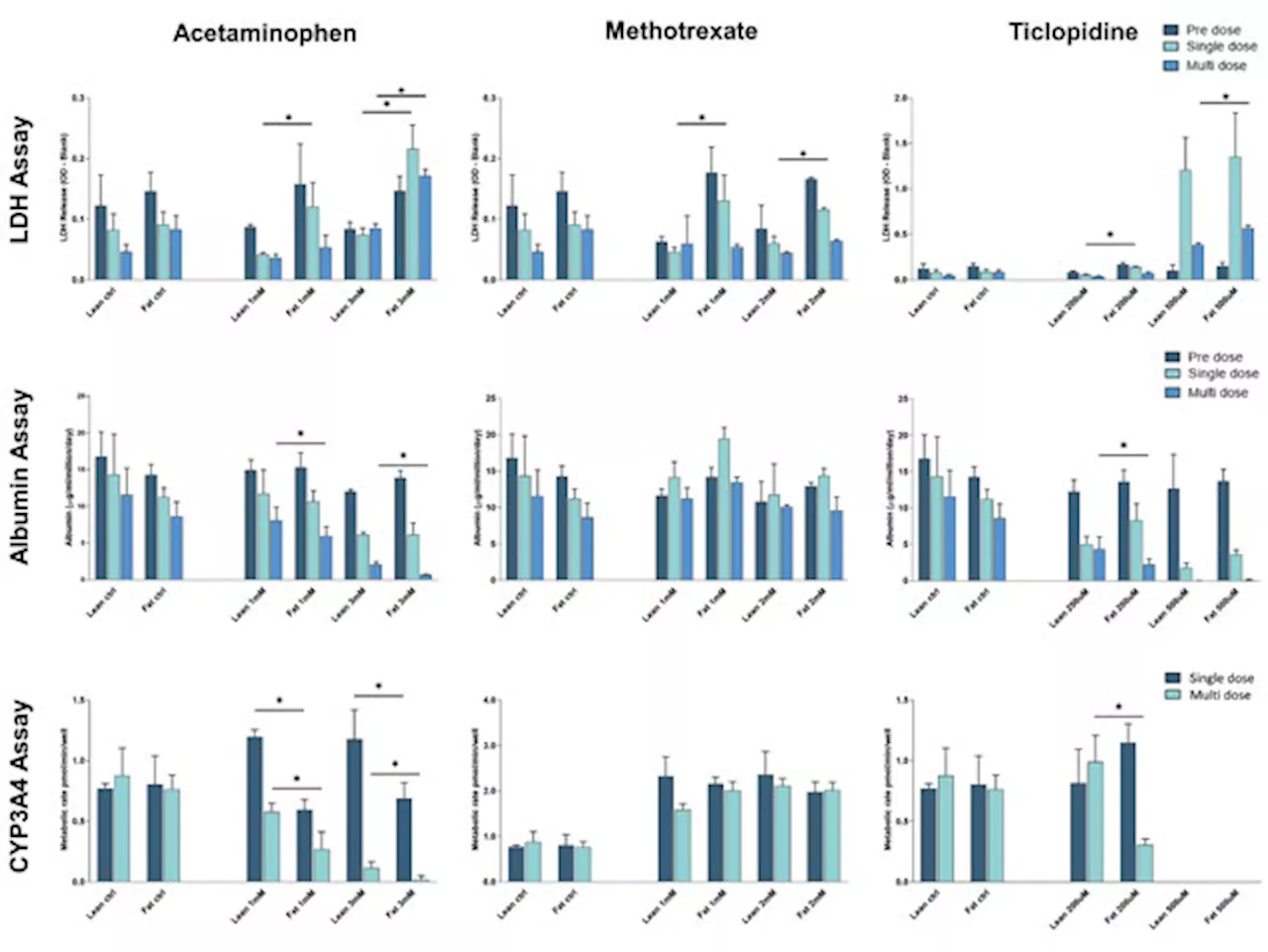 Using microphysiological systems to investigate fatty liver disease and drug-induced liver injury (DILI)This article explains how microphysiological systems can be used for research on fatty liver disease and assessing the risk of drug-induced liver injury
Using microphysiological systems to investigate fatty liver disease and drug-induced liver injury (DILI)This article explains how microphysiological systems can be used for research on fatty liver disease and assessing the risk of drug-induced liver injury
Read more »
 Rare metabolic disorder can cause liver inflammationMillions of people worldwide suffer from liver inflammation (hepatitis), an acute or chronic disease with a variety of causes. Liver inflammation frequently occurs in connection with metabolic disorders, for example fatty liver disease. Lysomal acid lipase (LAL) deficiency is a rare metabolic disorder that also causes liver inflammation.
Rare metabolic disorder can cause liver inflammationMillions of people worldwide suffer from liver inflammation (hepatitis), an acute or chronic disease with a variety of causes. Liver inflammation frequently occurs in connection with metabolic disorders, for example fatty liver disease. Lysomal acid lipase (LAL) deficiency is a rare metabolic disorder that also causes liver inflammation.
Read more »
 The Greater Manchester town that has 'eliminated' dangerous infectious diseaseIf left untreated, the illness can cause the liver to stop working properly and result in serious liver damage, including liver cancer
The Greater Manchester town that has 'eliminated' dangerous infectious diseaseIf left untreated, the illness can cause the liver to stop working properly and result in serious liver damage, including liver cancer
Read more »
 Alcoholic liver disease in China: A disease influenced by complex social factors that should not be neglectedAlcoholic liver disease (ALD) is a major cause of liver-related morbidity and mortality globally. Chronic alcohol consumption, a primary driver of ALD, leads to a spectrum of liver conditions ranging from fatty liver to cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma.
Alcoholic liver disease in China: A disease influenced by complex social factors that should not be neglectedAlcoholic liver disease (ALD) is a major cause of liver-related morbidity and mortality globally. Chronic alcohol consumption, a primary driver of ALD, leads to a spectrum of liver conditions ranging from fatty liver to cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma.
Read more »