Many artists have tried to depict what Earth might have looked like billions of years ago, before life made its appearance. Many scenes trade snow-covered mountains for lava-gushing volcanoes and blue skies for lightning bolts pummeling what's below from a hazy sky.
Loathed by scientists, loved by nature: Sulfur and the origin of life retrieved 13 March 2024 from https://phys.org/news/2024-03-loathed-scientists-nature-sulfur-life.html
This document is subject to copyright. Apart from any fair dealing for the purpose of private study or research, no part may be reproduced without the written permission. The content is provided for information purposes only.Mar 12, 2024 Use this form if you have come across a typo, inaccuracy or would like to send an edit request for the content on this page. For general inquiries, please use ourThank you for taking time to provide your feedback to the editors.
Your feedback is important to us. However, we do not guarantee individual replies due to the high volume of messages.to let the recipient know who sent the email. Neither your address nor the recipient's address will be used for any other purpose. The information you enter will appear in your e-mail message and is not retained by Phys.org in any form.Get weekly and/or daily updates delivered to your inbox.
United Kingdom Latest News, United Kingdom Headlines
Similar News:You can also read news stories similar to this one that we have collected from other news sources.
 Fire but no brimstone: Where is the universe's missing sulfur?Robert Lea is a science journalist in the U.K. whose articles have been published in Physics World, New Scientist, Astronomy Magazine, All About Space, Newsweek and ZME Science. He also writes about science communication for Elsevier and the European Journal of Physics. Rob holds a bachelor of science degree in physics and astronomy from the U.K.
Fire but no brimstone: Where is the universe's missing sulfur?Robert Lea is a science journalist in the U.K. whose articles have been published in Physics World, New Scientist, Astronomy Magazine, All About Space, Newsweek and ZME Science. He also writes about science communication for Elsevier and the European Journal of Physics. Rob holds a bachelor of science degree in physics and astronomy from the U.K.
Read more »
 Healable cathode could unlock potential of solid-state lithium-sulfur batteriesEngineers developed a cathode material for lithium-sulfur (Li-S) batteries that is healable and highly conductive, overcoming longstanding challenges of traditional sulfur cathodes. The advance holds promise for bringing more energy dense and low-cost Li-S batteries closer to market.
Healable cathode could unlock potential of solid-state lithium-sulfur batteriesEngineers developed a cathode material for lithium-sulfur (Li-S) batteries that is healable and highly conductive, overcoming longstanding challenges of traditional sulfur cathodes. The advance holds promise for bringing more energy dense and low-cost Li-S batteries closer to market.
Read more »
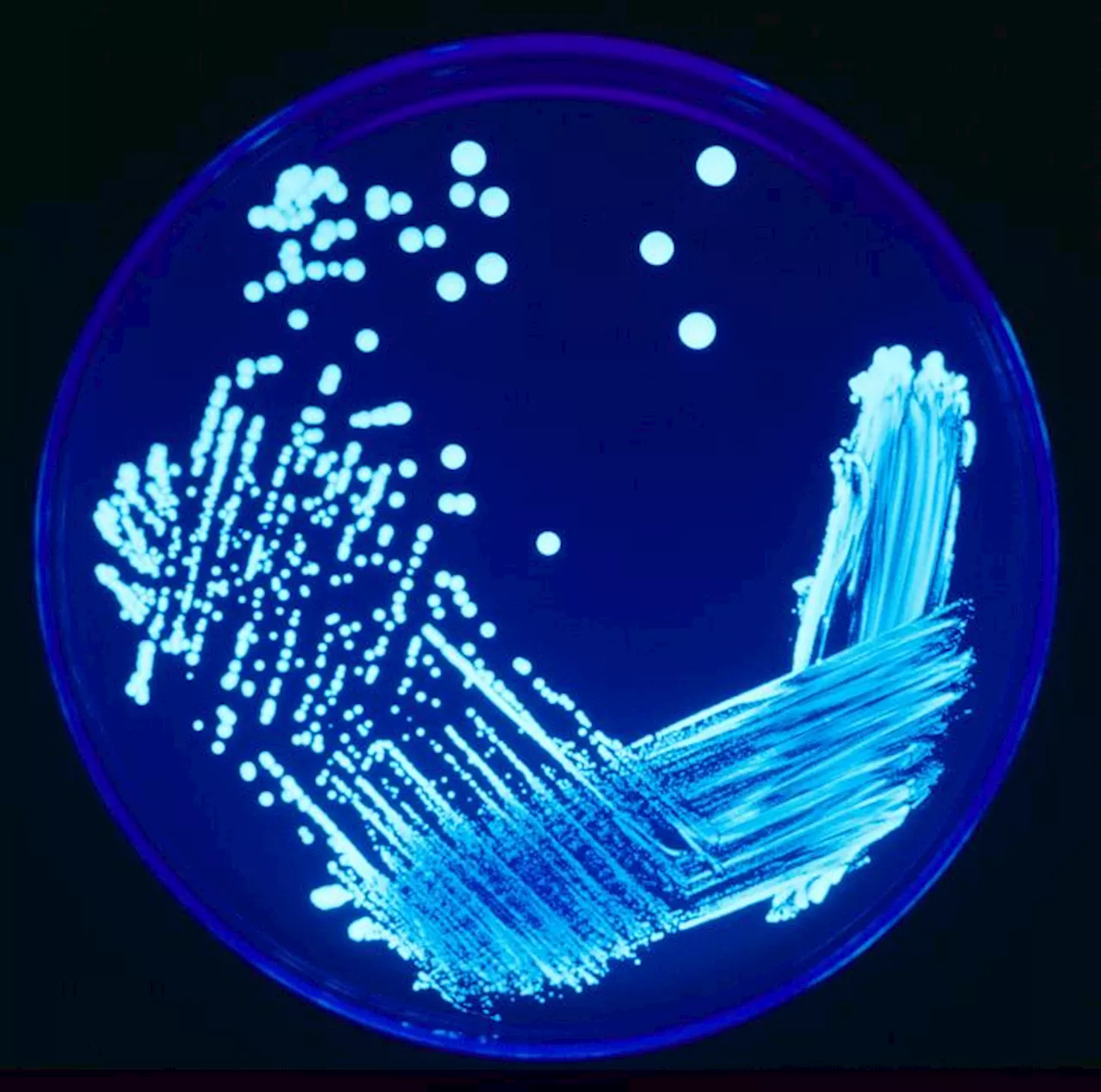 Researchers connect declining atmospheric sulfur dioxide levels to rise in Legionnaires' diseaseDeclining atmospheric sulfur dioxide levels might be related to the global rise in Legionnaires' disease—a severe form of pneumonia caused by inhaling the pathogenic bacteria Legionella.
Researchers connect declining atmospheric sulfur dioxide levels to rise in Legionnaires' diseaseDeclining atmospheric sulfur dioxide levels might be related to the global rise in Legionnaires' disease—a severe form of pneumonia caused by inhaling the pathogenic bacteria Legionella.
Read more »
 How global warming is disrupting life on EarthLearn about the effect of Global Warming: National Geographic.
How global warming is disrupting life on EarthLearn about the effect of Global Warming: National Geographic.
Read more »
 The Last Place on Earth: My Journey to Antarctica with National GeographicAntarctica might be the final frontier for terrestrial travel, but cruise lines like National Geographic make it a lot easier.
The Last Place on Earth: My Journey to Antarctica with National GeographicAntarctica might be the final frontier for terrestrial travel, but cruise lines like National Geographic make it a lot easier.
Read more »
 Georgetown's Elite Consulting Clubs Come Down to EarthThe website that Washington lives by.
Georgetown's Elite Consulting Clubs Come Down to EarthThe website that Washington lives by.
Read more »
