A new way to map the spread and evolution of pathogens, and their responses to vaccines and antibiotics, will provide key insights to help predict and prevent future outbreaks.
Wellcome Trust Sanger InstituteJul 3 2024 The approach combines a pathogen's genomic data with human travel patterns, taken from anonymized mobile phone data.
This is the first time researchers have been able to precisely quantify the fitness – their ability to survive and reproduce – of different pneumococcal strains. The insight could inform vaccine development to target the most harmful strains, and may be applicable to other pathogens. In this new study, researchers analyzed genome sequences from 6,910 pneumococcus samples collected in South Africa between 2000 and 2014 to track the distribution of different strains over time. They combined these data with anonymized records of human travel patterns collected by Meta.
Dr. Sophie Belman, first author of the study, former PhD student at the Wellcome Sanger Institute and now a Schmidt Science Fellow at the Barcelona Supercomputing Centre, Spain, said: "While we found that pneumococcal bacteria generally spread slowly, the use of vaccines and antimicrobials can quickly and significantly change these dynamics.
Pathogen Antibiotic Antibiotic Resistance Bacteria Children Genome Genomic Meningitis Penicillin Pneumonia Research Streptococcus Pneumoniae Vaccine
United Kingdom Latest News, United Kingdom Headlines
Similar News:You can also read news stories similar to this one that we have collected from other news sources.
 Chinese car brands hit accelerator on road tests for level three autonomous driving techTesla left out due to HD mapping roadblock
Chinese car brands hit accelerator on road tests for level three autonomous driving techTesla left out due to HD mapping roadblock
Read more »
 Mapping the heart to prevent damage caused by a heart attackScientists at the Victor Chang Cardiac Research Institute in Australia have produced a first of its kind integrated map of heart cells which unlocks the process of cardiac fibrosis—a major cause of heart failure.
Mapping the heart to prevent damage caused by a heart attackScientists at the Victor Chang Cardiac Research Institute in Australia have produced a first of its kind integrated map of heart cells which unlocks the process of cardiac fibrosis—a major cause of heart failure.
Read more »
 Mapping the heart to prevent damage caused by a heart attackScientists at the Victor Chang Cardiac Research Institute in Australia have produced a first of its kind integrated map of heart cells which unlocks the process of cardiac fibrosis – a major cause of heart failure.
Mapping the heart to prevent damage caused by a heart attackScientists at the Victor Chang Cardiac Research Institute in Australia have produced a first of its kind integrated map of heart cells which unlocks the process of cardiac fibrosis – a major cause of heart failure.
Read more »
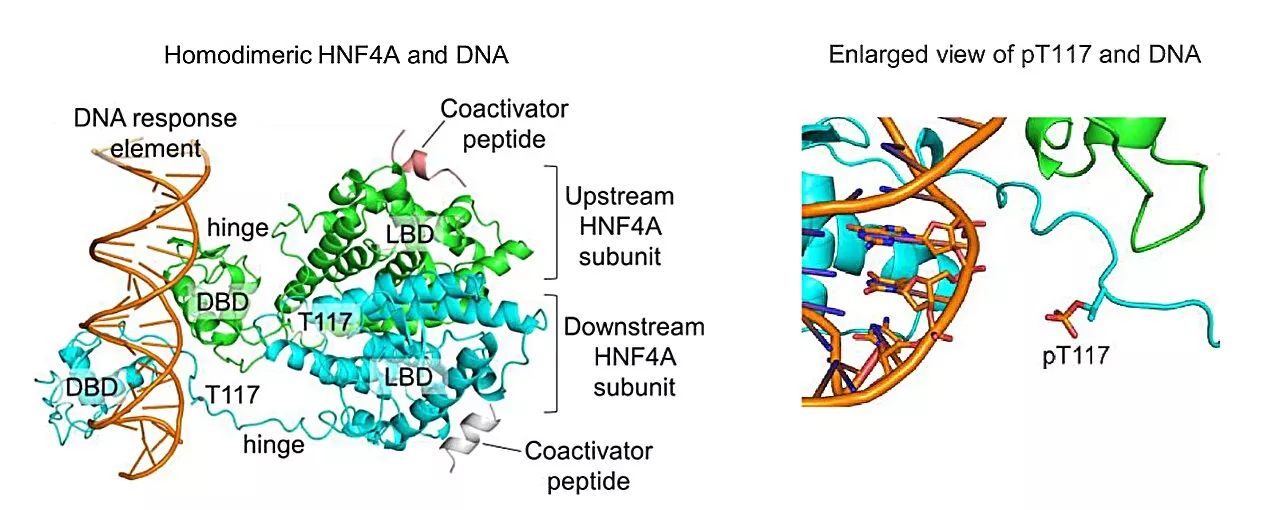 Molecular mapping reveals tissue-specific gene regulation by diabetes-linked transcription factorsScientists have generated a comprehensive map of the gene targets regulated by the transcription factors HNF4A and HNF1A in human pancreatic beta cells and liver cells.
Molecular mapping reveals tissue-specific gene regulation by diabetes-linked transcription factorsScientists have generated a comprehensive map of the gene targets regulated by the transcription factors HNF4A and HNF1A in human pancreatic beta cells and liver cells.
Read more »
 The AI we could have hadIn the late 1960s, a secret US lab was dedicated to mapping the edges of computing
The AI we could have hadIn the late 1960s, a secret US lab was dedicated to mapping the edges of computing
Read more »
 New study proposes multi-dimensional disease mapping for enhanced drug developmentTampere University researchers developed a method to map mechanistic connections between diseases, revealing deeper associations beyond traditional classifications based on affected organs and symptoms.
New study proposes multi-dimensional disease mapping for enhanced drug developmentTampere University researchers developed a method to map mechanistic connections between diseases, revealing deeper associations beyond traditional classifications based on affected organs and symptoms.
Read more »
