With the growing computational needs associated with prime enumeration tasks, traditional implementations of the Sieve algorithm remain a bottleneck.
This paper is available on arxiv under CC 4.0 license. Authors: Evan Ning, Milton Academy & evan_ning24@milton.edu; David R. Kaeli, Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering & Northeastern University kaeli@ece.neu.edu. Table of Links Introduction Sieve Optimizations Mathematical Optimization Implementation Results and Discussions Conclusions, Source Code & References 2.
The main range can be split so that each thread works on contiguous segments of numbers, reducing the complexity of merging the results. 2.3 Multithreaded Tasks A thread, often termed a lightweight process, represents the smallest sequence of programmed instructions that can be managed independently by a scheduler. Each thread is responsible for sieving out multiples of primes in its assigned range.
United Kingdom Latest News, United Kingdom Headlines
Similar News:You can also read news stories similar to this one that we have collected from other news sources.
 Memory Efficient Multithreaded Incremental Segmented Sieve Algorithm: Results and DiscussionsWith the growing computational needs associated with prime enumeration tasks, traditional implementations of the Sieve algorithm remain a bottleneck.
Memory Efficient Multithreaded Incremental Segmented Sieve Algorithm: Results and DiscussionsWith the growing computational needs associated with prime enumeration tasks, traditional implementations of the Sieve algorithm remain a bottleneck.
Read more »
 Memory Efficient Multithreaded Algorithm: Conclusions, Source Code & ReferencesWith the growing computational needs associated with prime enumeration tasks, traditional implementations of the Sieve algorithm remain a bottleneck.
Memory Efficient Multithreaded Algorithm: Conclusions, Source Code & ReferencesWith the growing computational needs associated with prime enumeration tasks, traditional implementations of the Sieve algorithm remain a bottleneck.
Read more »
 Towards the selective and energy-efficient synthesis of ethylene via carbon dioxide reductionThe synthesis of carbon-based chemicals via the electrochemical reduction of carbon dioxide (CO2) has become the key objective of numerous recent energy research efforts.
Towards the selective and energy-efficient synthesis of ethylene via carbon dioxide reductionThe synthesis of carbon-based chemicals via the electrochemical reduction of carbon dioxide (CO2) has become the key objective of numerous recent energy research efforts.
Read more »
 Lucid chief: highly-efficient EVs the 'holy grail' for decarbonisationPeter Rawlinson sets target of 6.2mpkWh to cut battery sizes and "save the planet"
Lucid chief: highly-efficient EVs the 'holy grail' for decarbonisationPeter Rawlinson sets target of 6.2mpkWh to cut battery sizes and "save the planet"
Read more »
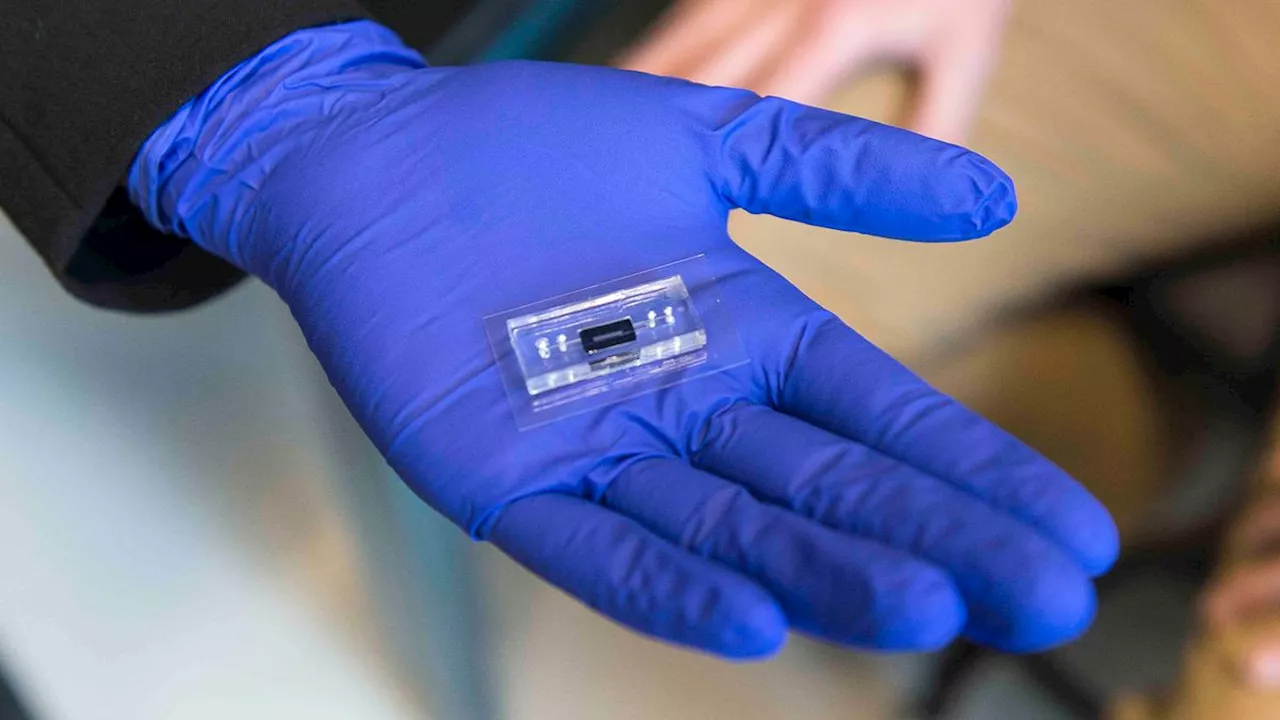 New DNA-infused computer chip can perform calculations and make future AI models far more efficientKeumars is the technology editor at Live Science. He has written for a variety of publications including ITPro, The Week Digital, ComputerActive, The Independent, The Observer, Metro and TechRadar Pro. He has worked as a technology journalist for more than five years, having previously held the role of features editor with ITPro.
New DNA-infused computer chip can perform calculations and make future AI models far more efficientKeumars is the technology editor at Live Science. He has written for a variety of publications including ITPro, The Week Digital, ComputerActive, The Independent, The Observer, Metro and TechRadar Pro. He has worked as a technology journalist for more than five years, having previously held the role of features editor with ITPro.
Read more »
 How Atmosic’s energy-efficient chips are forging a battery-free futureEveryone can appreciate the convenience aspect of battery-free power for IoT, regardless of their views on global warming.
How Atmosic’s energy-efficient chips are forging a battery-free futureEveryone can appreciate the convenience aspect of battery-free power for IoT, regardless of their views on global warming.
Read more »
