Exploring the mechanisms underpinning individual differences in autismspectrumdisorder using machinelearning NatureNeuro
Fig. 2: Functional connectivity correlates of autism spectrum disorder symptoms.
Fig. 3: Hierarchical clustering on brain–behavior dimension scores reveals four autism spectrum disorder subgroups. Fig. 4: Autism spectrum disorder subgroups have distinct atypical connectivity patterns in dimension-related RSFC features. Fig. 5: Transcriptomic correlates of atypical connectivity patterns in autism spectrum disorder subgroups.
Fig. 6: Protein–protein interaction networks reveal distinct connectivity-related genes with textual associations to autism spectrum disorder-related behaviors.The data that support the findings of this study are publicly available. The neuroimaging datasets are available from ABIDE I and ABIDE II and the the NDAR database . Users must register with the NITRC and 1000 Functional Connectomes Project to gain access to ABIDE I and ABIDE II.
United Kingdom Latest News, United Kingdom Headlines
Similar News:You can also read news stories similar to this one that we have collected from other news sources.
 CAR T-Cell therapy for the management of mantle cell lymphoma - Molecular CancerMantle cell lymphoma (MCL) is a subtype of Non-Hodgkin lymphoma (NHL) of mature B-cells characterized by translocation, which is typically due to excess expression of Cyclin D1. Although with the progress in our knowledge of the causes for MCL and available treatments for MCL, this cancer is still incurable. Age, male gender, rapid advancement, significant nodal involvement, elevated serum lactate dehydrogenase level, and prognostic indications including increased expression of Ki-67 and presence of TP53 mutation, are symbols of poor outcome. Advanced immunotherapy using chimeric antigen receptor (CAR)-T cells is advantageous for patients suffering from B-cell malignancies and MCL. Targeting B-cell antigens on the cell surface is a feasible approach in re-occurring (R/R) MCL because of significant responses obtained in other B-cell cancers. USFDA has approved brexucabtagene autoleucel (Tecartus, KTE-X19), a novel CAR T-cell therapy to be used in patients with MCL who have not responded to previous treatments or have relapsed. The FDA approved this new treatment depending on the outcomes of the ZUMA-2 clinical trial. Serious adverse reactions, moderate anti-tumor activity, allergen withdrawal, antigen escape, limited tumor infiltration, and trafficking are major barriers to successful CAR T-cell therapy. This review is a brief synopsis of the development of CAR T-cell therapy for MCL.
CAR T-Cell therapy for the management of mantle cell lymphoma - Molecular CancerMantle cell lymphoma (MCL) is a subtype of Non-Hodgkin lymphoma (NHL) of mature B-cells characterized by translocation, which is typically due to excess expression of Cyclin D1. Although with the progress in our knowledge of the causes for MCL and available treatments for MCL, this cancer is still incurable. Age, male gender, rapid advancement, significant nodal involvement, elevated serum lactate dehydrogenase level, and prognostic indications including increased expression of Ki-67 and presence of TP53 mutation, are symbols of poor outcome. Advanced immunotherapy using chimeric antigen receptor (CAR)-T cells is advantageous for patients suffering from B-cell malignancies and MCL. Targeting B-cell antigens on the cell surface is a feasible approach in re-occurring (R/R) MCL because of significant responses obtained in other B-cell cancers. USFDA has approved brexucabtagene autoleucel (Tecartus, KTE-X19), a novel CAR T-cell therapy to be used in patients with MCL who have not responded to previous treatments or have relapsed. The FDA approved this new treatment depending on the outcomes of the ZUMA-2 clinical trial. Serious adverse reactions, moderate anti-tumor activity, allergen withdrawal, antigen escape, limited tumor infiltration, and trafficking are major barriers to successful CAR T-cell therapy. This review is a brief synopsis of the development of CAR T-cell therapy for MCL.
Read more »
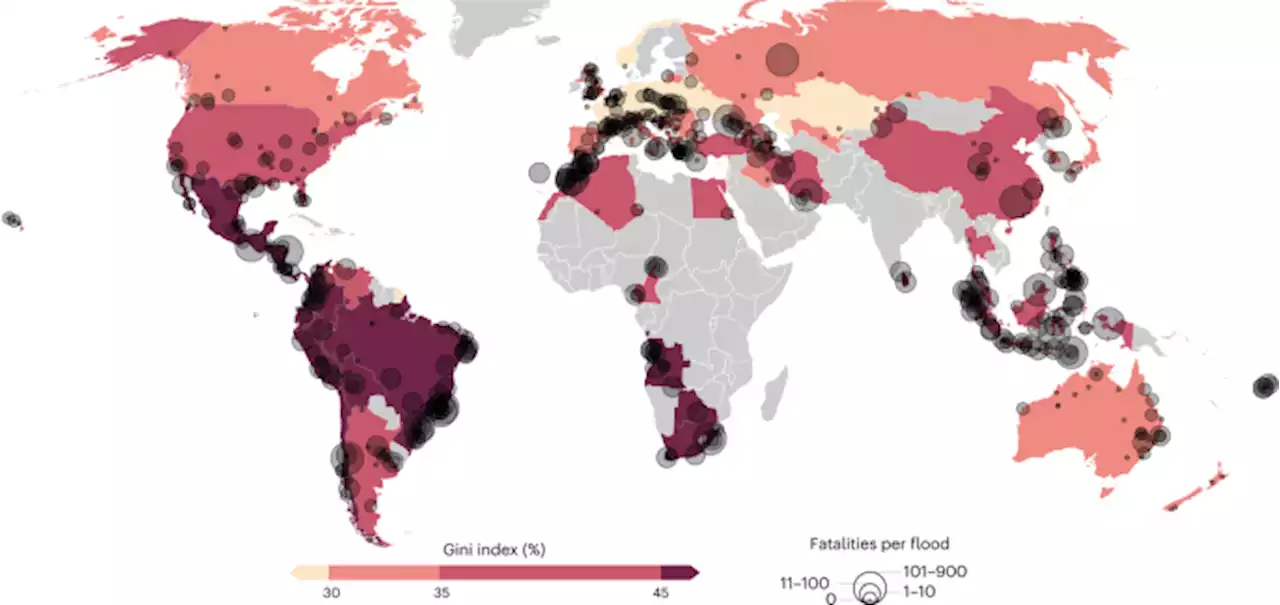 The wider the gap between rich and poor the higher the flood mortality - Nature SustainabilityA global analysis of income inequality and flood disasters in middle- and high-income countries between 1990 and 2018 shows that unequal countries tend to suffer higher flood fatalities.
The wider the gap between rich and poor the higher the flood mortality - Nature SustainabilityA global analysis of income inequality and flood disasters in middle- and high-income countries between 1990 and 2018 shows that unequal countries tend to suffer higher flood fatalities.
Read more »
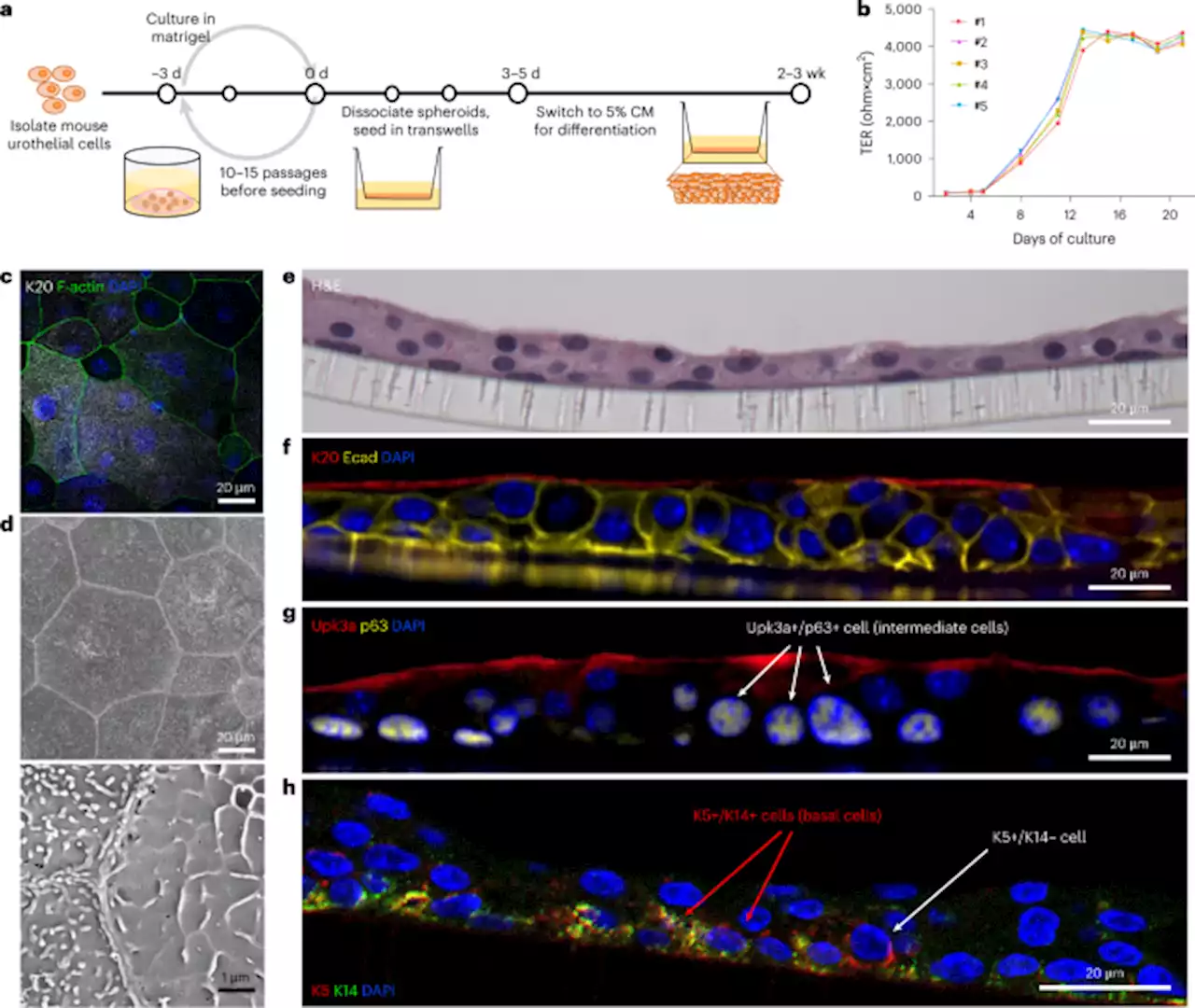 Uropathogenic Escherichia coli infection-induced epithelial trained immunity impacts urinary tract disease outcome - Nature MicrobiologyUropathogenic Escherichia coli infection induces epigenetic remodelling and trained immune responses in bladder epithelial stem cells that affect susceptibility to recurrent infection.
Uropathogenic Escherichia coli infection-induced epithelial trained immunity impacts urinary tract disease outcome - Nature MicrobiologyUropathogenic Escherichia coli infection induces epigenetic remodelling and trained immune responses in bladder epithelial stem cells that affect susceptibility to recurrent infection.
Read more »
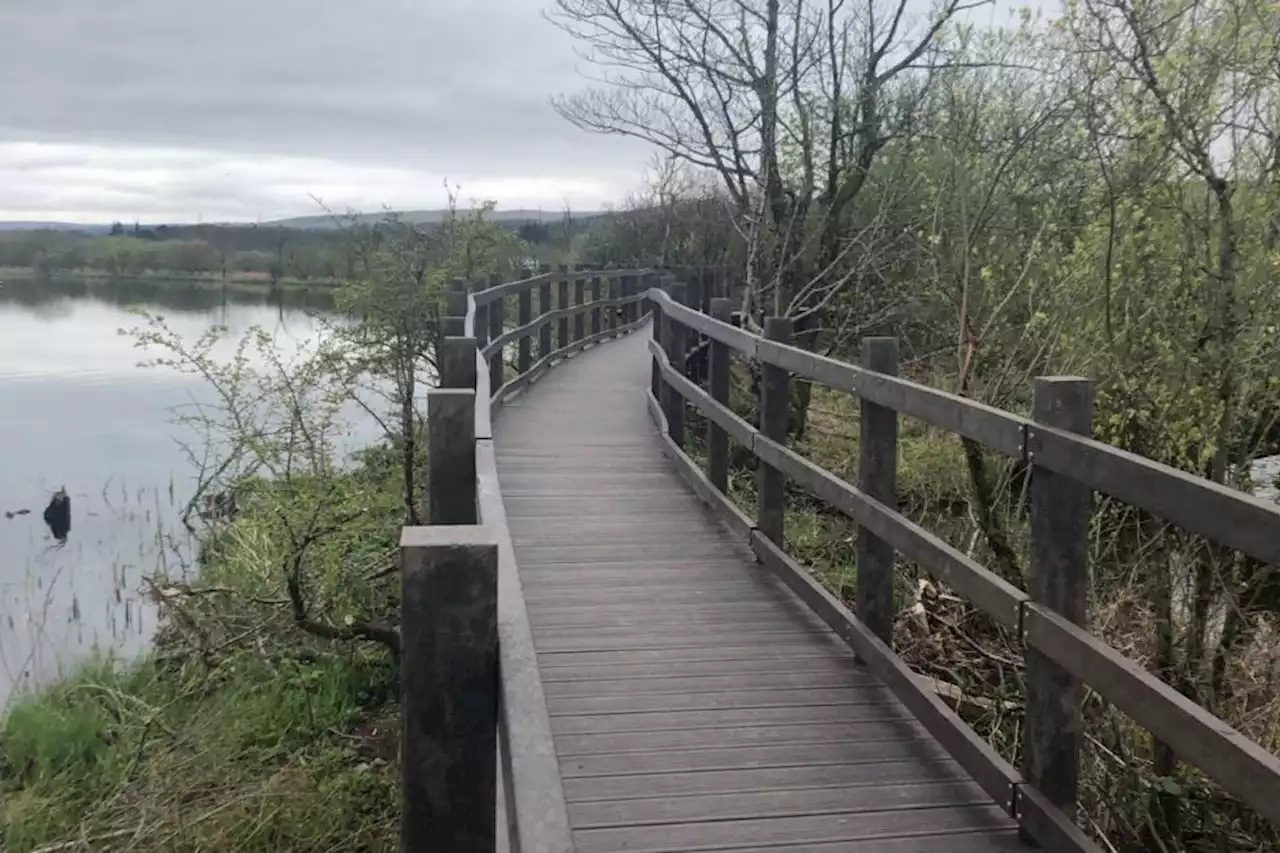 'Absolutely thrilled': New boardwalk opens at popular nature reserveThe 405m walkway follows an artificial bund which separates Aird Meadow Loch from the adjacent Castle Semple Loch.
'Absolutely thrilled': New boardwalk opens at popular nature reserveThe 405m walkway follows an artificial bund which separates Aird Meadow Loch from the adjacent Castle Semple Loch.
Read more »
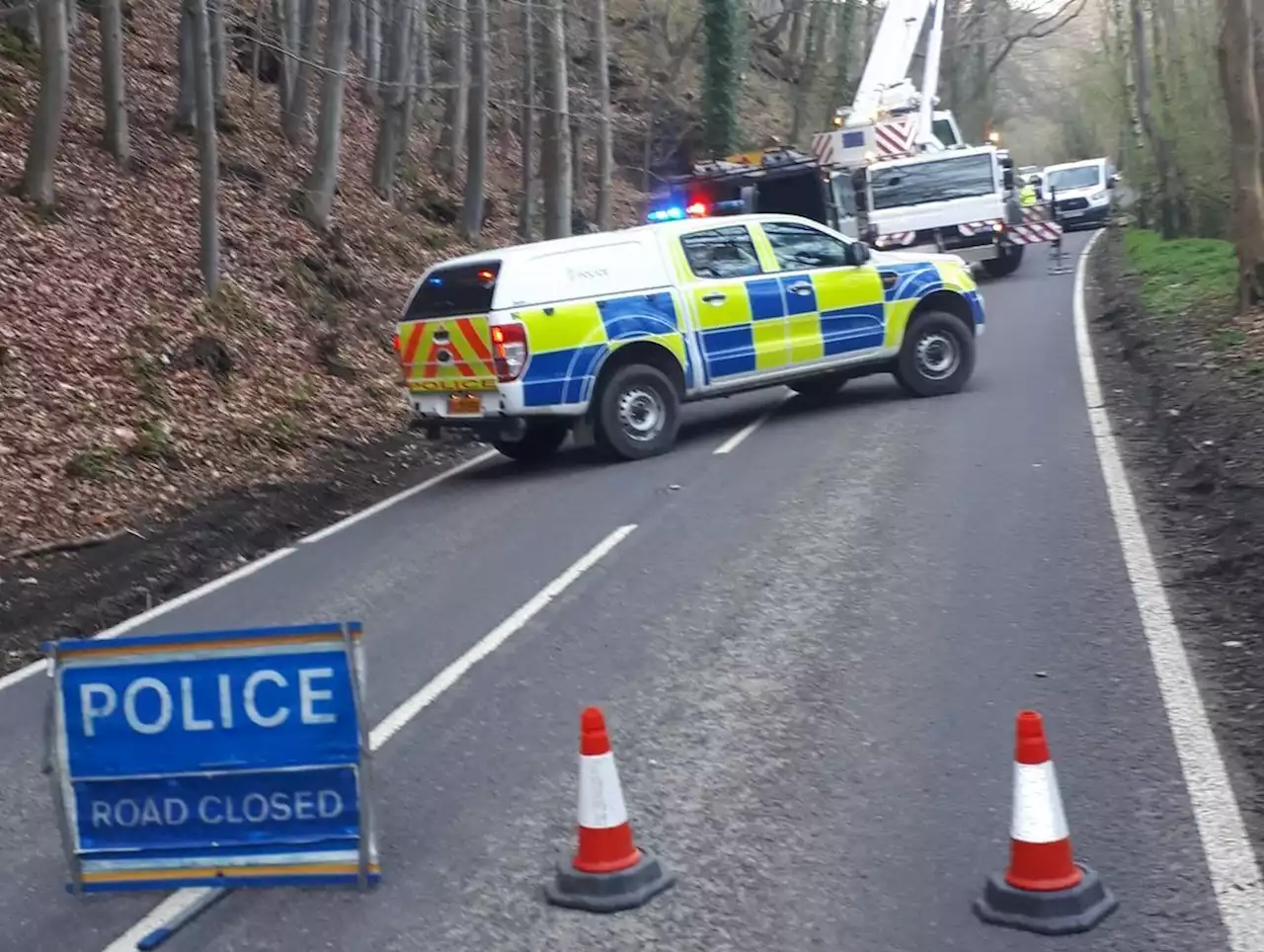 Landslide and falling trees cause road closure in Shropshire border nature reserveA road along the Welsh border was closed on Tuesday after a landslide.
Landslide and falling trees cause road closure in Shropshire border nature reserveA road along the Welsh border was closed on Tuesday after a landslide.
Read more »
 Distributed context-dependent choice information in mouse posterior cortex - Nature CommunicationsIn the posterior cortex, which is involved in decision making, the strength and area specificity of choice signals are highly variable. Here the authors show that the representation of choice in the posterior area of the mouse brain is orthogonal to that of sensory and movement-related signals, with modulations determined by task features and cognitive demands.
Distributed context-dependent choice information in mouse posterior cortex - Nature CommunicationsIn the posterior cortex, which is involved in decision making, the strength and area specificity of choice signals are highly variable. Here the authors show that the representation of choice in the posterior area of the mouse brain is orthogonal to that of sensory and movement-related signals, with modulations determined by task features and cognitive demands.
Read more »
