A groundbreaking study published in Nature Communications reveals distinct immune environments within pancreatic cancer tumors, offering potential for new therapeutic strategies. The research highlights the role of specific immune cells and identifies potential targets for personalized immunotherapy.
University of Birmingham researchers have uncovered promising insights into potential precision treatments for pancreatic cancer . A new study, published in Nature Communications, provides the most comprehensive immune map for pancreatic cancer to date.
Led by Associate Professor Shivan Sivakumar from the University of Birmingham and Associate Professor Rachael Bashford-Rogers at the University of Oxford, the research team analyzed immune cells from twelve pancreatic cancer patients, creating a single-cell map that revealed distinct immune environments within tumors. This map, coupled with gene expression, single-cell TCR and BCR sequencing, and protein identification, offered a detailed understanding of how the immune system interacts with pancreatic cancer.The findings suggest that some tumor cells are more susceptible to T cell treatments, while others exhibit a higher infiltration of myeloid cells, such as macrophages. This suggests that macrophage-based therapies could be a viable option for treating certain pancreatic cancer subtypes. Furthermore, the study identified specific immune cells, including activated regulatory T cells (Tregs) and B cells, that play a crucial role in the disease's progression. These cells could help distinguish patients who might benefit from targeted treatments that activate the existing immune response in tumor areas rich in B and T cells, from those with a highly suppressive tumor environment dominated by myeloid cells.The research team validated their findings using two additional large publicly available pancreatic cancer datasets, strengthening the significance of their discoveries. Dr. Sivakumar emphasized the urgency for future clinical trials to assess the dynamic nature of immune infiltration over time. He highlighted the study's potential to pave the way for novel therapeutic strategies, including boosting certain immune responses and depleting suppressive immune cells. The identification of potential targets, such as TIGIT and CD47, offers promising avenues for further investigation and development of targeted therapies. Ultimately, the study's comprehensive analysis of the immune landscape in pancreatic cancer provides valuable insights that could lead to more effective and personalized treatment approaches for this deadly disease
Pancreatic Cancer Immunotherapy Precision Medicine Immune Cells T Cells Macrophages Regulatory T Cells B Cells TIGIT CD47
United Kingdom Latest News, United Kingdom Headlines
Similar News:You can also read news stories similar to this one that we have collected from other news sources.
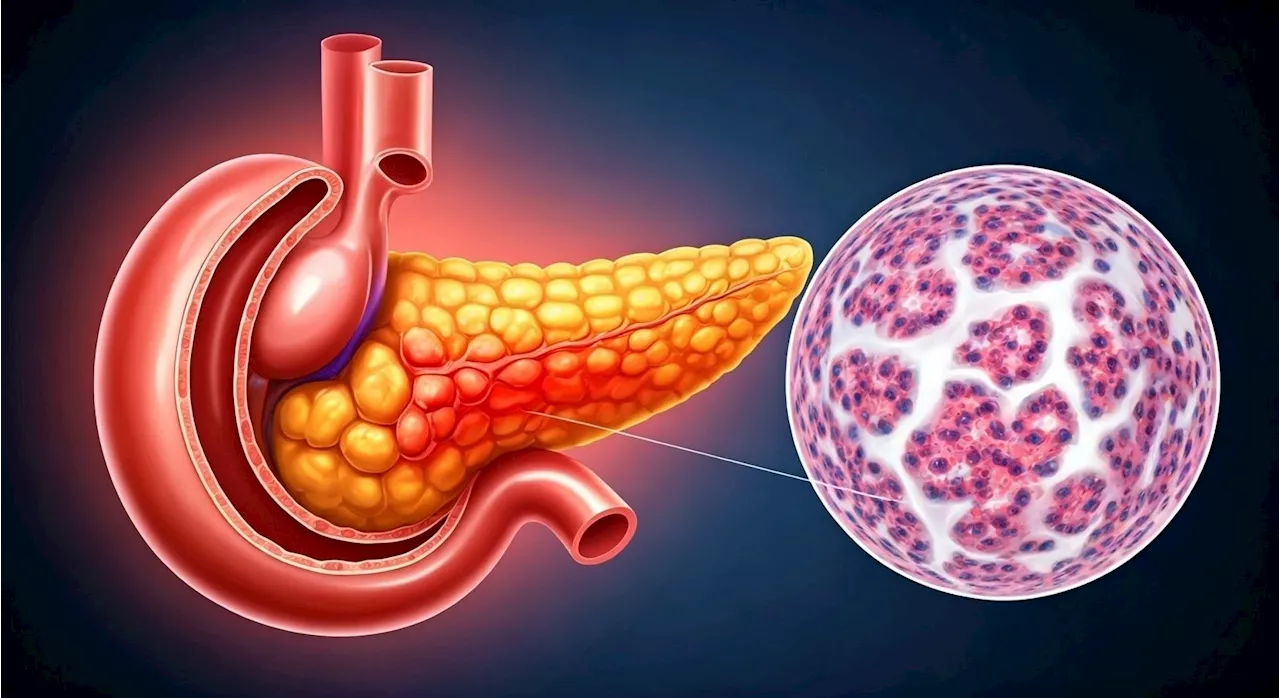 Pancreatic cancer insights: How pORG classifications predict survival and guide treatmentResearchers identify distinct molecular and immune profiles that impact the prognosis of patients with metastatic pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma.
Pancreatic cancer insights: How pORG classifications predict survival and guide treatmentResearchers identify distinct molecular and immune profiles that impact the prognosis of patients with metastatic pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma.
Read more »
 New rabbit model provides insights into CF-related pancreatic endocrine pathologyCystic fibrosis (CF) is a life-threatening genetic disease affecting multiple organ systems, with pancreatic dysfunction representing a critical and often overlooked complication.
New rabbit model provides insights into CF-related pancreatic endocrine pathologyCystic fibrosis (CF) is a life-threatening genetic disease affecting multiple organ systems, with pancreatic dysfunction representing a critical and often overlooked complication.
Read more »
 Comprehensive Atlas of Pancreatic Islet Endothelial Cells Provides New Insights into DiabetesResearchers at Weill Cornell Medicine have generated a groundbreaking atlas detailing the unique characteristics of islet-specific endothelial cells (ISECs), a cell population essential for supporting insulin production in the pancreas. This atlas provides new insights into the biology of diabetes and could lead to the development of novel therapies.
Comprehensive Atlas of Pancreatic Islet Endothelial Cells Provides New Insights into DiabetesResearchers at Weill Cornell Medicine have generated a groundbreaking atlas detailing the unique characteristics of islet-specific endothelial cells (ISECs), a cell population essential for supporting insulin production in the pancreas. This atlas provides new insights into the biology of diabetes and could lead to the development of novel therapies.
Read more »
 New insights into rare liver cancer as clinical trial for treatment beginsLike many rare diseases, fibrolamellar hepatocellular carcinoma (FLC) mounts a ferocious attack against an unlucky few-in this case, children, adolescents, and young adults.
New insights into rare liver cancer as clinical trial for treatment beginsLike many rare diseases, fibrolamellar hepatocellular carcinoma (FLC) mounts a ferocious attack against an unlucky few-in this case, children, adolescents, and young adults.
Read more »
 New Microscopy Technique Reveals Insights into Cancer Cell Metabolism and Treatment ResistanceResearchers at the University of Kentucky have developed a novel microscopy technique that uses standard fluorescence microscopes to analyze metabolic changes in individual cancer cells. This approach provides a cost-effective and accessible way to study how tumors adapt to therapies and develop resistance.
New Microscopy Technique Reveals Insights into Cancer Cell Metabolism and Treatment ResistanceResearchers at the University of Kentucky have developed a novel microscopy technique that uses standard fluorescence microscopes to analyze metabolic changes in individual cancer cells. This approach provides a cost-effective and accessible way to study how tumors adapt to therapies and develop resistance.
Read more »
 Prostate Cancer Overtakes Breast Cancer as England's Most Common CancerRecent research highlights the alarming rise of prostate cancer in England, surpassing breast cancer as the most prevalent cancer. This shift is attributed to increased awareness and earlier detection efforts.
Prostate Cancer Overtakes Breast Cancer as England's Most Common CancerRecent research highlights the alarming rise of prostate cancer in England, surpassing breast cancer as the most prevalent cancer. This shift is attributed to increased awareness and earlier detection efforts.
Read more »
