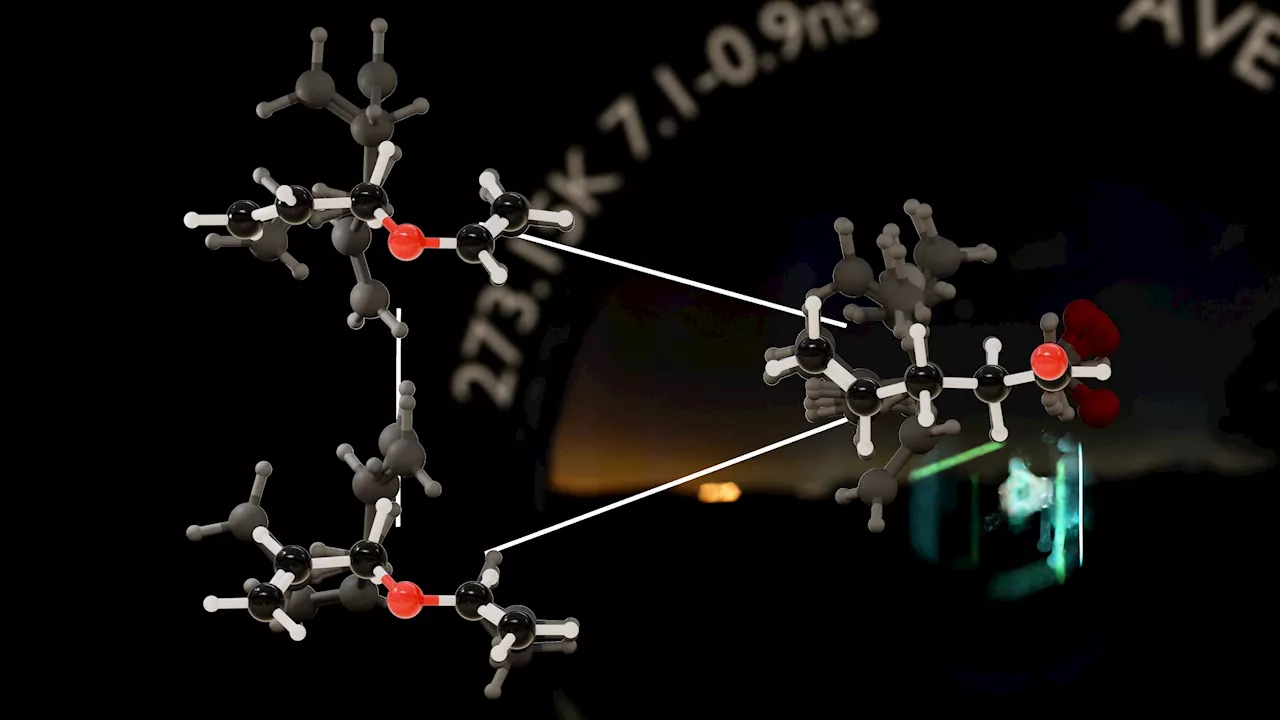
Chemical reactions are commonly depicted as transitions from reactants to products. However, such reactions involve many molecules, and the individual molecules themselves undergo frequently-occurring structural changes as they transform from the reactants to the products.
New research employs shutter speed analogies to validate 55-year-old theory about chemical reaction ratesAs the observation interval lengthens—akin to slowing down a camera's shutter speed—the dances of the molecules overlap and emerge as a blur of frequent changes, masking the intricate ballet of atoms in motion. Credit: Yumi Teruya
The dendrogram of indistinguishability of the Claisen rearrangement of allyl vinyl ether. Each colored step indicates an observation where exact coarse-graining applies. Credit: Yutaka Nagahata The team identified key observation intervals at which different molecular shapes"blur together" and the system appears to become simpler. They created a"systematic diagram" that shows how the reaction process appears more and more simplified as the observation interval increases, eventually appearing as a one-step process at long observation intervals.
Physics News Science News Technology News Physics Materials Nanotech Technology Science
United Kingdom Latest News, United Kingdom Headlines
Similar News:You can also read news stories similar to this one that we have collected from other news sources.
 Researchers create new AI pipeline for identifying molecular interactionsAI developments in chemical biology could unlock new types of disease treatments.
Researchers create new AI pipeline for identifying molecular interactionsAI developments in chemical biology could unlock new types of disease treatments.
Read more »
 Emerging AI technologies make it easier for bad actors to 'conceptualize and conduct' chemical, biological, radiological or nuclear attacks: DHSA new report cites a lack of regulations in chemical and biological enforcement.
Emerging AI technologies make it easier for bad actors to 'conceptualize and conduct' chemical, biological, radiological or nuclear attacks: DHSA new report cites a lack of regulations in chemical and biological enforcement.
Read more »
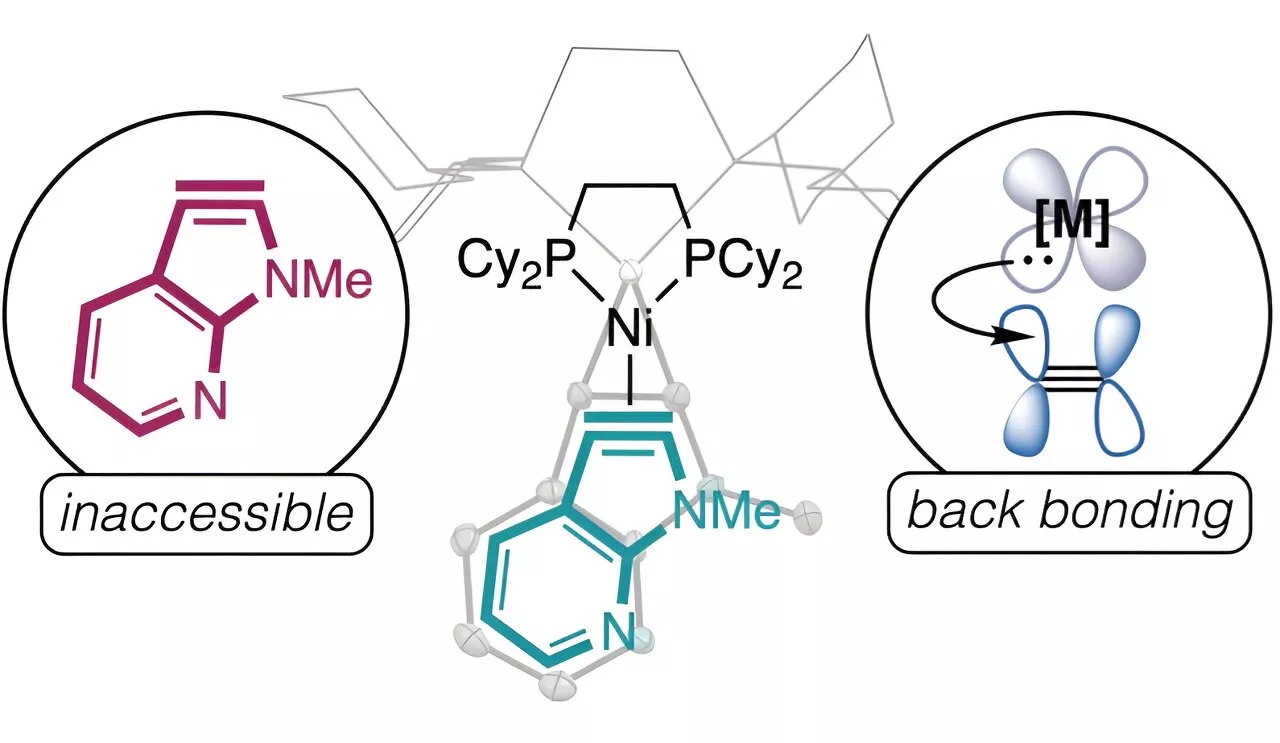 Researchers create new chemical compound to solve 120-year-old problemFor the first time, chemists in the University of Minnesota Twin Cities College of Science and Engineering have created a highly reactive chemical compound that has eluded scientists for more than 120 years. The discovery could lead to new drug treatments, safer agricultural products, and better electronics. The study is published in Science.
Researchers create new chemical compound to solve 120-year-old problemFor the first time, chemists in the University of Minnesota Twin Cities College of Science and Engineering have created a highly reactive chemical compound that has eluded scientists for more than 120 years. The discovery could lead to new drug treatments, safer agricultural products, and better electronics. The study is published in Science.
Read more »
 Researchers create new chemical compound to solve 120-year-old problemChemists have created a highly reactive chemical compound that has eluded scientists for more than 120 years. The discovery could lead to new drug treatments, safer agricultural products, and better electronics.
Researchers create new chemical compound to solve 120-year-old problemChemists have created a highly reactive chemical compound that has eluded scientists for more than 120 years. The discovery could lead to new drug treatments, safer agricultural products, and better electronics.
Read more »
 See Exclusive Images From the New Chemical Brothers Book ‘Paused in Cosmic Reflection’Spanning 35 years of history, the duo's retrospective book, 'Paused in Cosmic Reflection', is out today (May 7.)
See Exclusive Images From the New Chemical Brothers Book ‘Paused in Cosmic Reflection’Spanning 35 years of history, the duo's retrospective book, 'Paused in Cosmic Reflection', is out today (May 7.)
Read more »
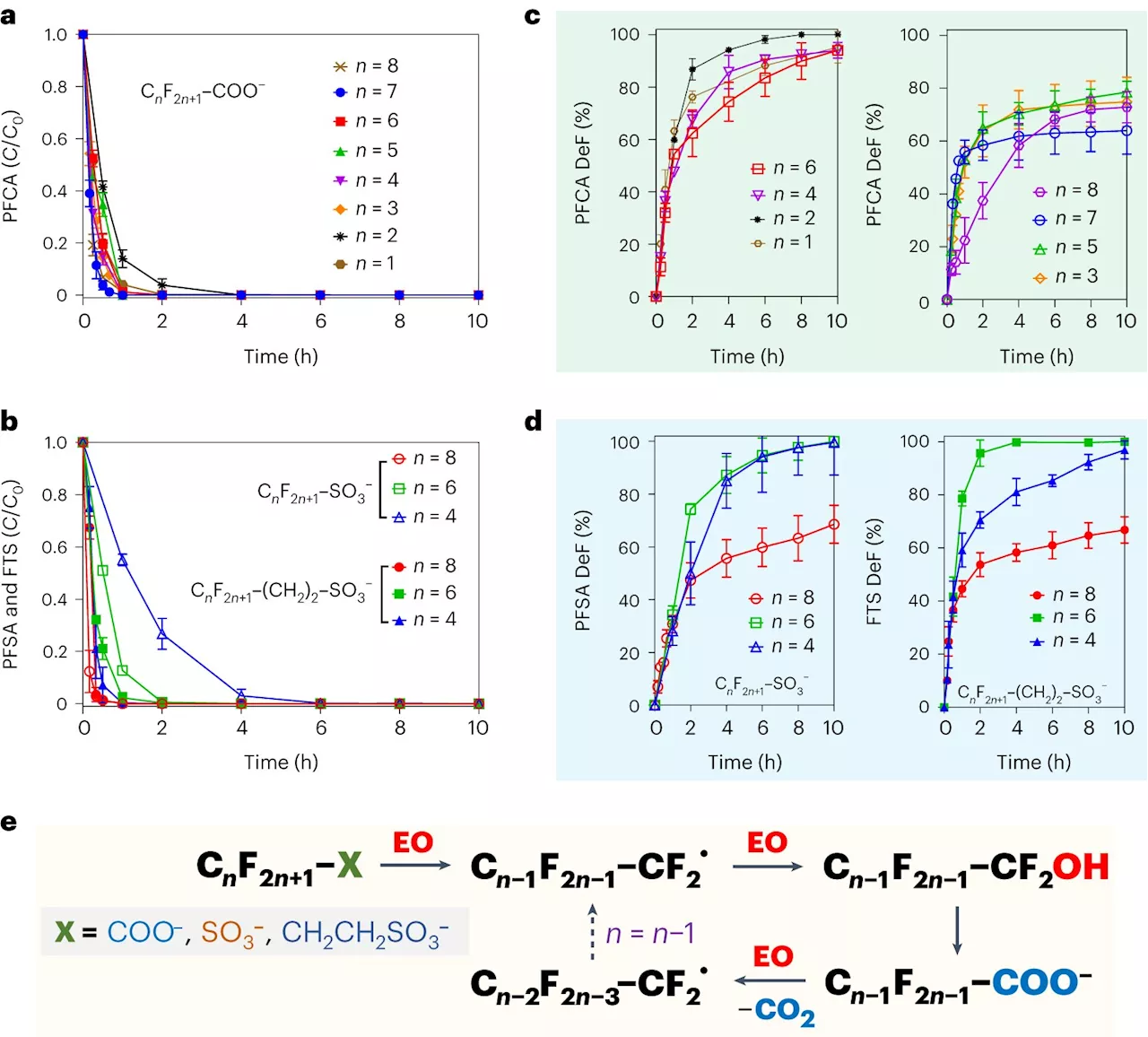 New 'forever chemical' cleanup strategy discoveredAs the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency cracks down on insidious 'forever chemical' pollution in the environment, military and commercial aviation officials are seeking ways to clean up such pollution from decades of use of fire suppressant foams at military air bases and commercial airports.
New 'forever chemical' cleanup strategy discoveredAs the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency cracks down on insidious 'forever chemical' pollution in the environment, military and commercial aviation officials are seeking ways to clean up such pollution from decades of use of fire suppressant foams at military air bases and commercial airports.
Read more »