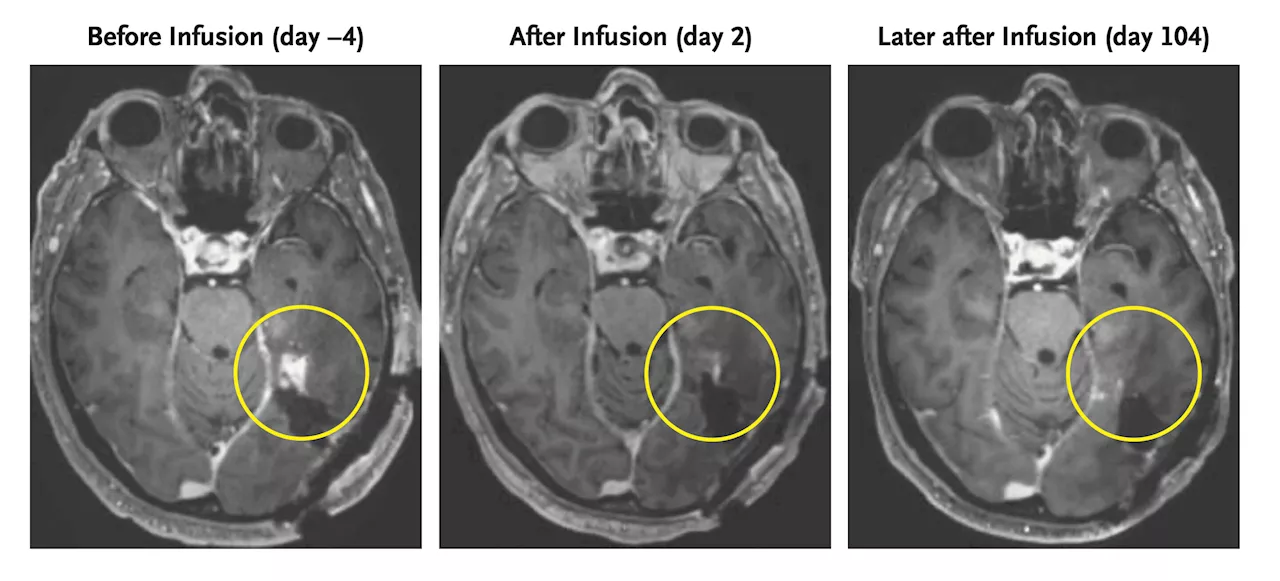
A new strategy to attack aggressive brain cancer has shown promising results in two early tests. The strategy involves using a combination of drugs that target specific genetic mutations in the cancer cells.
A new strategy to attack aggressive brain cancer has shown promising results in two early tests. The strategy involves using a combination of drugs that target specific genetic mutations in the cancer cells.
In the first test, the tumors shrank by 50% in 70% of the patients. In the second test, the tumors completely disappeared in 40% of the patients. The researchers are hopeful that this new strategy could lead to more effective treatments for aggressive brain cancer.
Brain Cancer Tumors Genetic Mutations Drugs Treatment
United Kingdom Latest News, United Kingdom Headlines
Similar News:You can also read news stories similar to this one that we have collected from other news sources.
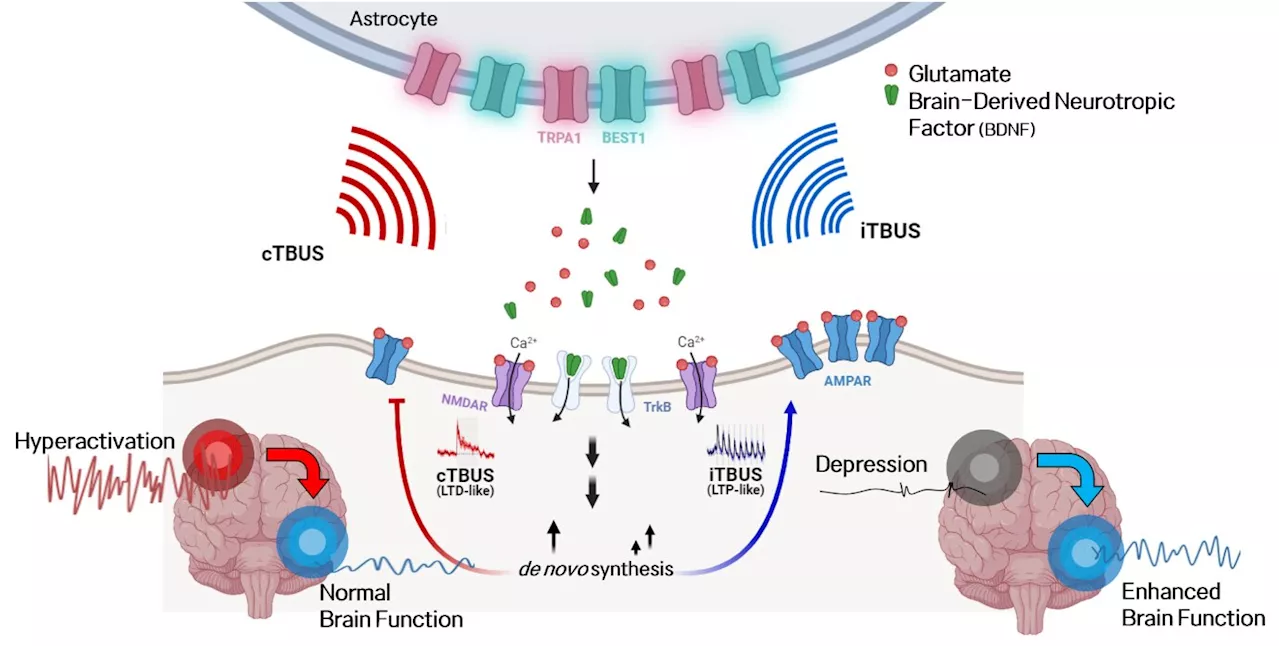 New brain stimulation technique shows promise for treating brain disordersThe human brain's adaptability to internal and external changes, known as neural plasticity, forms the foundation for understanding cognitive functions like memory and learning, as well as various neurological disorders.
New brain stimulation technique shows promise for treating brain disordersThe human brain's adaptability to internal and external changes, known as neural plasticity, forms the foundation for understanding cognitive functions like memory and learning, as well as various neurological disorders.
Read more »
 AI smartphone app shows promise in diagnosing ear infections in childrenA new cellphone app developed by physician-scientists at UPMC and the University of Pittsburgh, which uses artificial intelligence (AI) to accurately diagnose ear infections, or acute otitis media (AOM), could help decrease unnecessary antibiotic use in young children, according to new research published today in JAMA Pediatrics.
AI smartphone app shows promise in diagnosing ear infections in childrenA new cellphone app developed by physician-scientists at UPMC and the University of Pittsburgh, which uses artificial intelligence (AI) to accurately diagnose ear infections, or acute otitis media (AOM), could help decrease unnecessary antibiotic use in young children, according to new research published today in JAMA Pediatrics.
Read more »
 Apple cider vinegar shows promise in weight loss and metabolic healthThe effects of apple cider vinegar (ACV) intake on weight, blood glucose, triglyceride, and cholesterol levels among Lebanese individuals.
Apple cider vinegar shows promise in weight loss and metabolic healthThe effects of apple cider vinegar (ACV) intake on weight, blood glucose, triglyceride, and cholesterol levels among Lebanese individuals.
Read more »
 Novel dual-target CAR T cell therapy shows promise in treating recurrent glioblastomaTargeting two brain tumor-associated proteins-;rather than one-;with CAR T cell therapy shows promise as a strategy for reducing solid tumor growth in patients with recurrent glioblastoma (GBM), an aggressive form of brain cancer, according to early results from the first six patients treated in an ongoing Phase I clinical trial led by researchers...
Novel dual-target CAR T cell therapy shows promise in treating recurrent glioblastomaTargeting two brain tumor-associated proteins-;rather than one-;with CAR T cell therapy shows promise as a strategy for reducing solid tumor growth in patients with recurrent glioblastoma (GBM), an aggressive form of brain cancer, according to early results from the first six patients treated in an ongoing Phase I clinical trial led by researchers...
Read more »
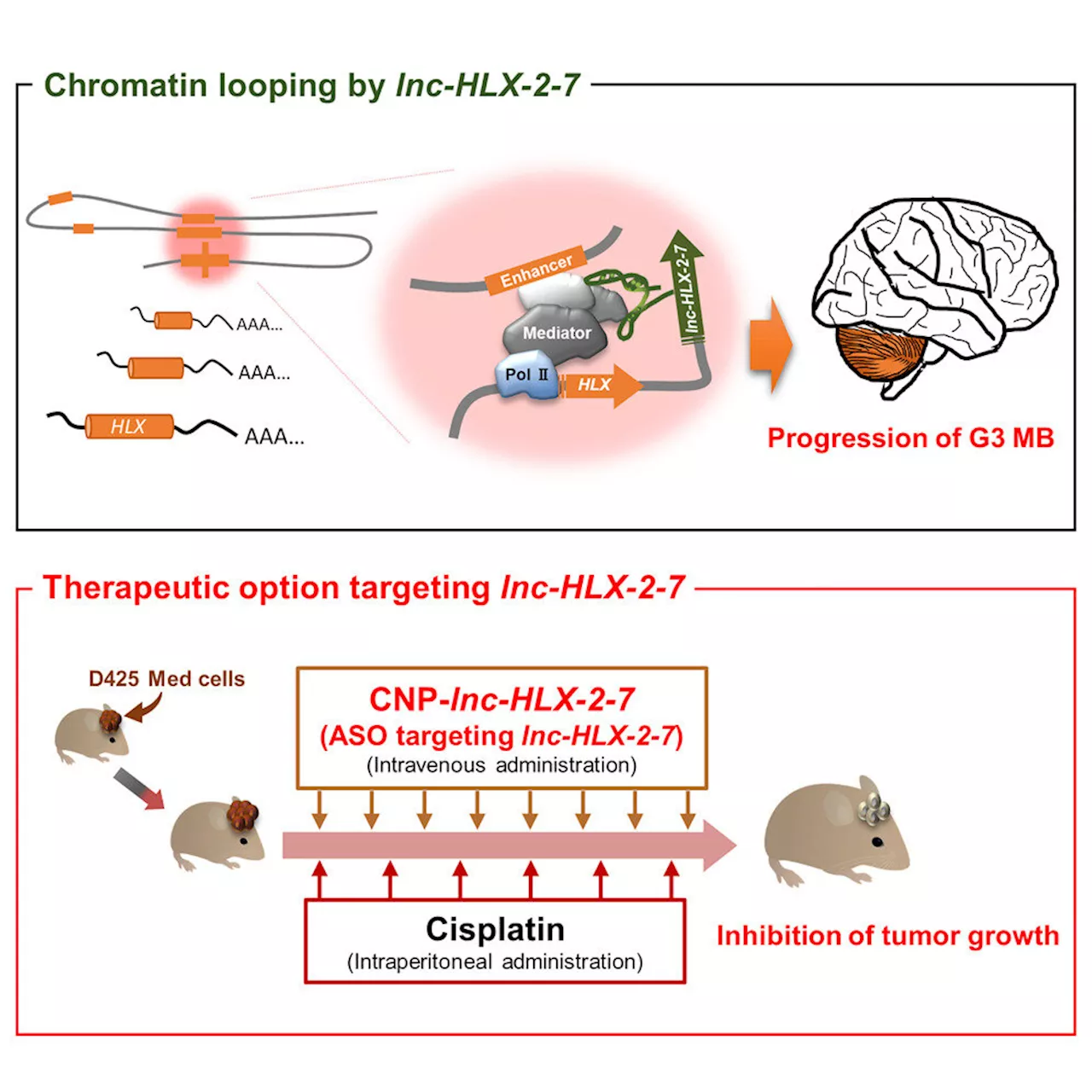 RNA-based therapy shows promise against aggressive childhood brain tumors in miceTargeting a non-encoding stretch of RNA may help shrink tumors caused by an aggressive type of brain cancer in children, according to new research in mice reported March 8 in Cell Reports by Johns Hopkins Kimmel Cancer Center investigators.
RNA-based therapy shows promise against aggressive childhood brain tumors in miceTargeting a non-encoding stretch of RNA may help shrink tumors caused by an aggressive type of brain cancer in children, according to new research in mice reported March 8 in Cell Reports by Johns Hopkins Kimmel Cancer Center investigators.
Read more »
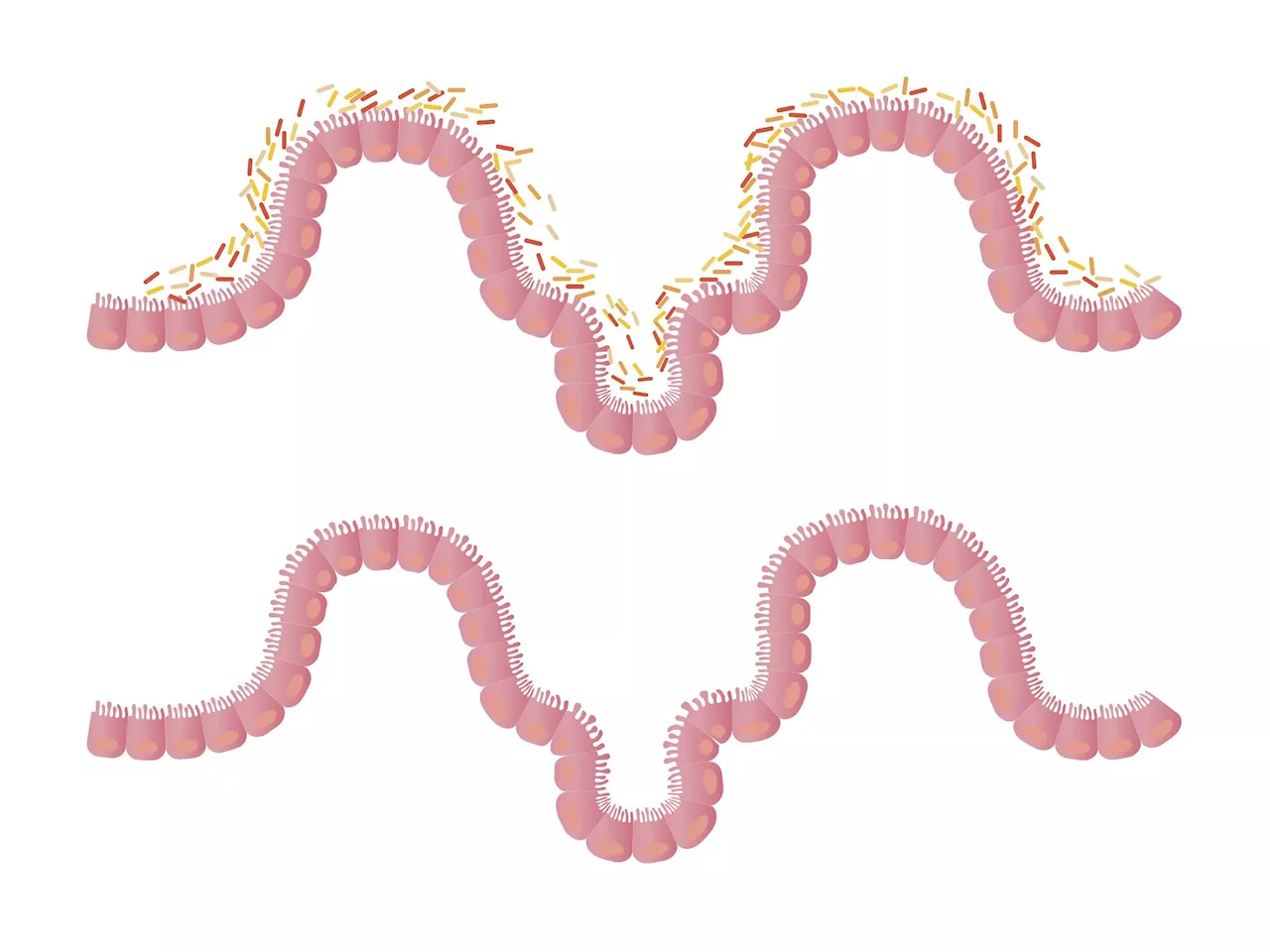 New understanding of the gut immune system may hold promise for Crohn's disease patientsTricks played by certain disease-driving gut bacteria might help explain differences in how patients experience Crohn's disease (CD)—a severe and painful chronic inflammatory bowel disease.
New understanding of the gut immune system may hold promise for Crohn's disease patientsTricks played by certain disease-driving gut bacteria might help explain differences in how patients experience Crohn's disease (CD)—a severe and painful chronic inflammatory bowel disease.
Read more »