Researchers have developed a noninvasive technology combining a holographic acoustic device with genetic engineering that allows them to precisely target affected neurons in the brain, creating the potential to precisely modulate selected cell types in multiple diseased brain regions.
Human brain diseases, such as Parkinson's disease, involve damage in more than one region of the brain, requiring technology that could precisely and flexibly address all affected regions simultaneously. Researchers at Washington University in St.
"By enabling precise and flexible cell-type-specific neuromodulation without invasive procedures, AhSonogenetics provides a powerful tool for investigating intact neural circuits and offers promising interventions for neurological disorders," Chen said. Chen and her team, including first authors Zhongtao Hu, a former postdoctoral research associate, and Yang, designed each Airy-beam metasurface individually as the foundation for wearable ultrasound devices that were tailored for different applications and for precise locations in the brain.
Hu said the device, which costs roughly $50 to make, can be tailored in size to fit various brain sizes, expanding its potential applications.
Nervous System Brain Tumor Medical Imaging Brain Injury Brain-Computer Interfaces Neuroscience Disorders And Syndromes
United Kingdom Latest News, United Kingdom Headlines
Similar News:You can also read news stories similar to this one that we have collected from other news sources.
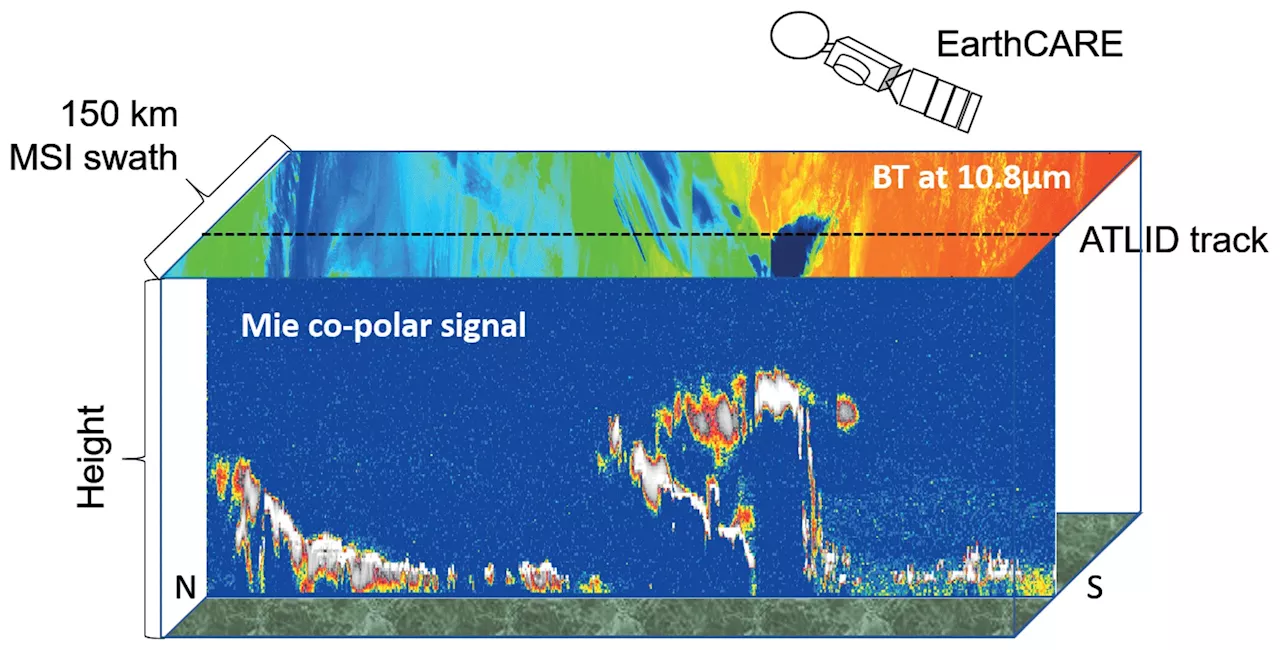 Researchers create new software for the new European-Japanese Earth observation satellite EarthCAREPreparations for the launch of the new Earth observation satellite EarthCARE (Earth Cloud Aerosol and Radiation Explorer) at the end of May are in full swing. The joint mission of the European Space Agency (ESA) and the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA) will measure clouds, aerosol and radiation more accurately than ever before.
Researchers create new software for the new European-Japanese Earth observation satellite EarthCAREPreparations for the launch of the new Earth observation satellite EarthCARE (Earth Cloud Aerosol and Radiation Explorer) at the end of May are in full swing. The joint mission of the European Space Agency (ESA) and the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA) will measure clouds, aerosol and radiation more accurately than ever before.
Read more »
 Researchers reveal new pathway to improve traumatic brain injury outcomesWorking together to understand the factors which could be used to predict outcome following TBI, researchers examined factors related to social support, health, clinical care, biological markers, acute interventions, and longer-term outcomes.
Researchers reveal new pathway to improve traumatic brain injury outcomesWorking together to understand the factors which could be used to predict outcome following TBI, researchers examined factors related to social support, health, clinical care, biological markers, acute interventions, and longer-term outcomes.
Read more »
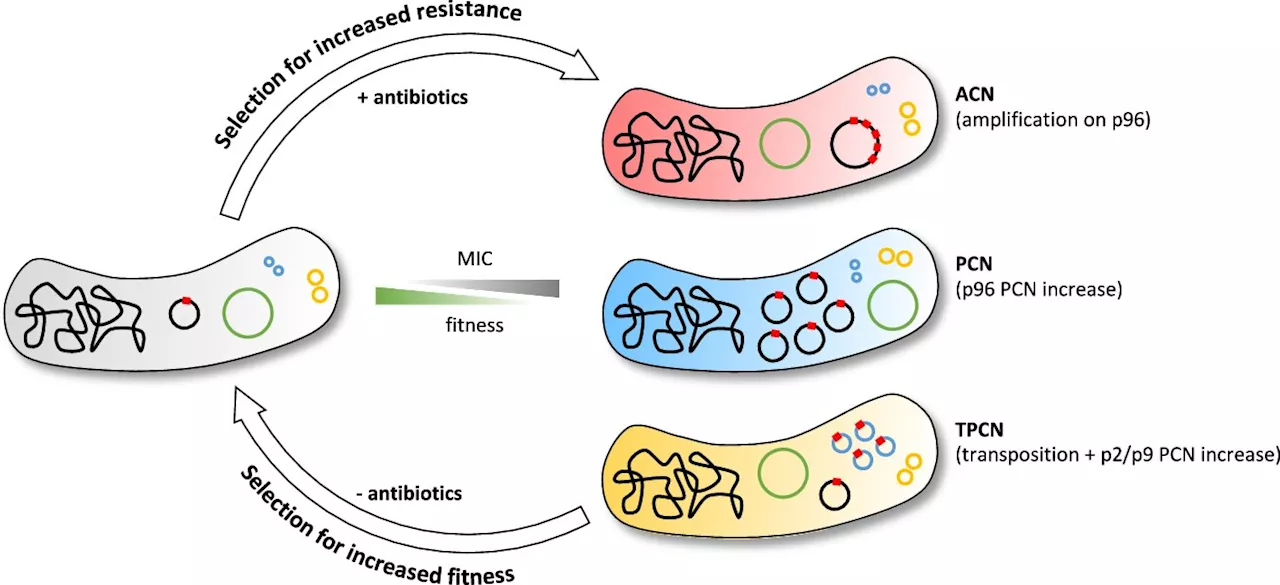 Researchers identify new drivers of antibiotic resistance in bacteriaTwo newly discovered mechanisms in bacteria have been identified that can contribute to the development of antibiotic resistance. Changing the number of copies of resistance genes in bacteria increases antibiotic resistance, and can do so very quickly.
Researchers identify new drivers of antibiotic resistance in bacteriaTwo newly discovered mechanisms in bacteria have been identified that can contribute to the development of antibiotic resistance. Changing the number of copies of resistance genes in bacteria increases antibiotic resistance, and can do so very quickly.
Read more »
 Chemistry researchers showcase new method to aid in pharma, agrochemical compound developmentResearchers at Colorado State University have published findings in Nature that could be useful to speed the development of new pharmaceuticals and pesticides.
Chemistry researchers showcase new method to aid in pharma, agrochemical compound developmentResearchers at Colorado State University have published findings in Nature that could be useful to speed the development of new pharmaceuticals and pesticides.
Read more »
 PMAT: Researchers develop a new tool for efficient assembly of plant mitochondrial genomesPlant mitochondrial genomes (mitogenomes) are crucial for understanding nucleocytoplasmic interactions, plant evolution, and breeding of cytoplasmic male sterile lines. However, their complete assembly is challenging due to frequent recombination events and horizontal gene transfers.
PMAT: Researchers develop a new tool for efficient assembly of plant mitochondrial genomesPlant mitochondrial genomes (mitogenomes) are crucial for understanding nucleocytoplasmic interactions, plant evolution, and breeding of cytoplasmic male sterile lines. However, their complete assembly is challenging due to frequent recombination events and horizontal gene transfers.
Read more »
 Researchers Identify New Genetic Form of Alzheimer’s DiseaseScience, Space and Technology News 2024
Researchers Identify New Genetic Form of Alzheimer’s DiseaseScience, Space and Technology News 2024
Read more »
