Researchers unveiled a novel therapy for diabetic wound healing. This research highlights the use of exosomal miR-4645-5p from hypoxic bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells (BMSCs) to significantly enhance wound healing by promoting keratinocyte autophagy.
Feb 20 2024TranSpread Researchers unveiled a novel therapy for diabetic wound healing. This research highlights the use of exosomal miR-4645-5p from hypoxic bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells to significantly enhance wound healing by promoting keratinocyte autophagy.
On a study published in the journal Burns & Trauma, researchers have pioneered a novel approach to heal diabetic wounds faster and more effectively than ever before. Their research centers on the use of special particles called exosomes, which are derived from stem cells grown under low oxygen conditions, known as hypoxic conditions. These exosomes contain a potent molecule, miR-4645-5p, that significantly boosts the healing process.
United Kingdom Latest News, United Kingdom Headlines
Similar News:You can also read news stories similar to this one that we have collected from other news sources.
 Researchers receive £2.4 million to generate evidence on the new NHS Pharmacy First serviceResearchers from the London School of Hygiene & Tropical Medicine (LSHTM) have been awarded £2.4m by the National Institute for Health and Care Research (NIHR) to generate evidence on the new National Health Service (NHS) Pharmacy First service.
Researchers receive £2.4 million to generate evidence on the new NHS Pharmacy First serviceResearchers from the London School of Hygiene & Tropical Medicine (LSHTM) have been awarded £2.4m by the National Institute for Health and Care Research (NIHR) to generate evidence on the new National Health Service (NHS) Pharmacy First service.
Read more »
 Researchers uncover how deadly MRSA pneumonia inhibits body's antimicrobial activityResearchers examined how heparan sulfate (HS) shedding impacts cathelicidin efficacy in Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) pneumonia.
Researchers uncover how deadly MRSA pneumonia inhibits body's antimicrobial activityResearchers examined how heparan sulfate (HS) shedding impacts cathelicidin efficacy in Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) pneumonia.
Read more »
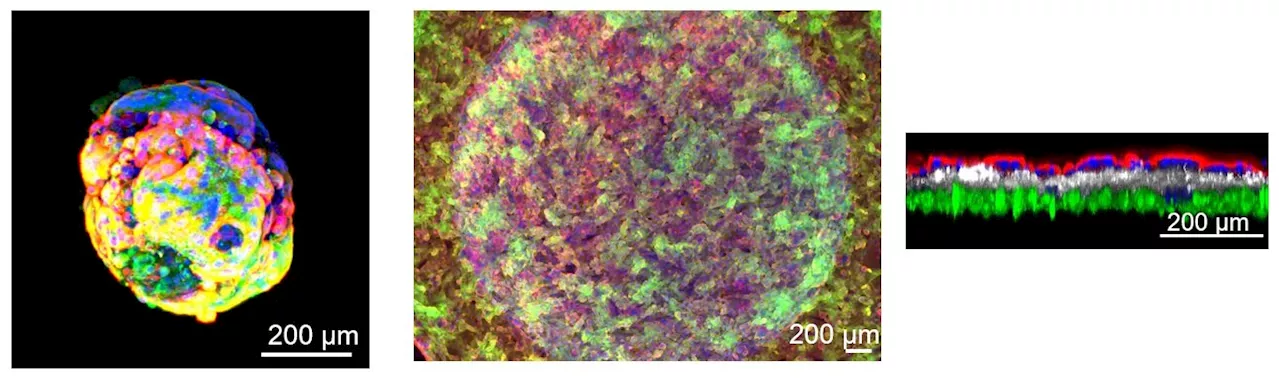 Researchers develop model to assess biology of human placental barrierDuring pregnancy, the human placenta plays multiple essential roles, including hormone production and nutrient/waste processing. It also serves as a barrier to protect the developing fetus from external toxic substances. However, the placental barrier can still be breached by certain drugs.
Researchers develop model to assess biology of human placental barrierDuring pregnancy, the human placenta plays multiple essential roles, including hormone production and nutrient/waste processing. It also serves as a barrier to protect the developing fetus from external toxic substances. However, the placental barrier can still be breached by certain drugs.
Read more »
 Researchers identify potential way to treat genetic epilepsy by replacing 'lost' enzymeScientists at the Francis Crick Institute have found a new treatment target for CDKL5 deficiency disorder (CDD), one of the most common types of genetic epilepsy.
Researchers identify potential way to treat genetic epilepsy by replacing 'lost' enzymeScientists at the Francis Crick Institute have found a new treatment target for CDKL5 deficiency disorder (CDD), one of the most common types of genetic epilepsy.
Read more »
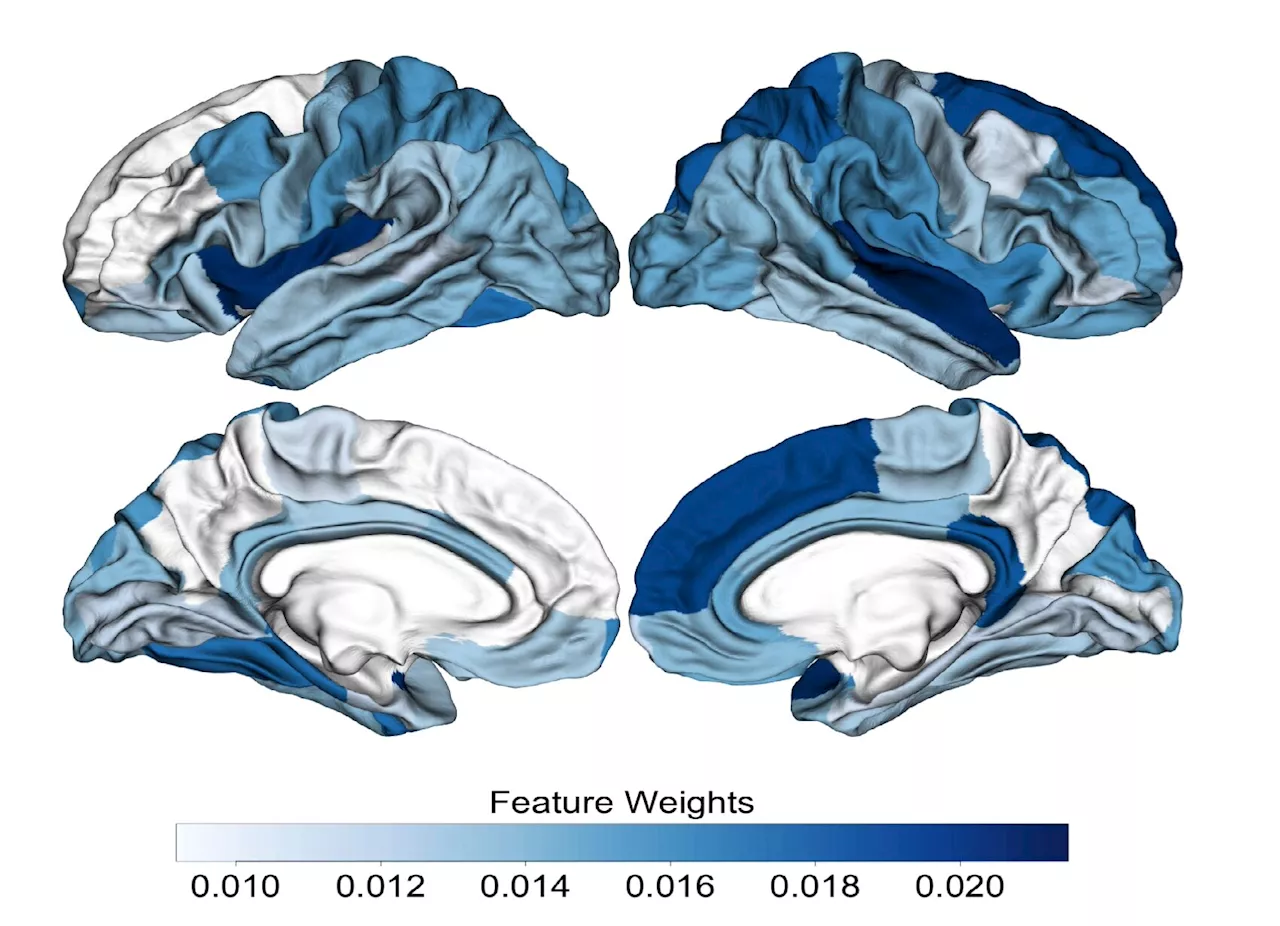 Researchers create machine learning-based classifier that could aid early diagnosis of psychosisThe onset of psychosis can be predicted before it occurs, using a machine-learning tool which can classify MRI brain scans into those who are healthy and those at risk of a psychotic episode.
Researchers create machine learning-based classifier that could aid early diagnosis of psychosisThe onset of psychosis can be predicted before it occurs, using a machine-learning tool which can classify MRI brain scans into those who are healthy and those at risk of a psychotic episode.
Read more »
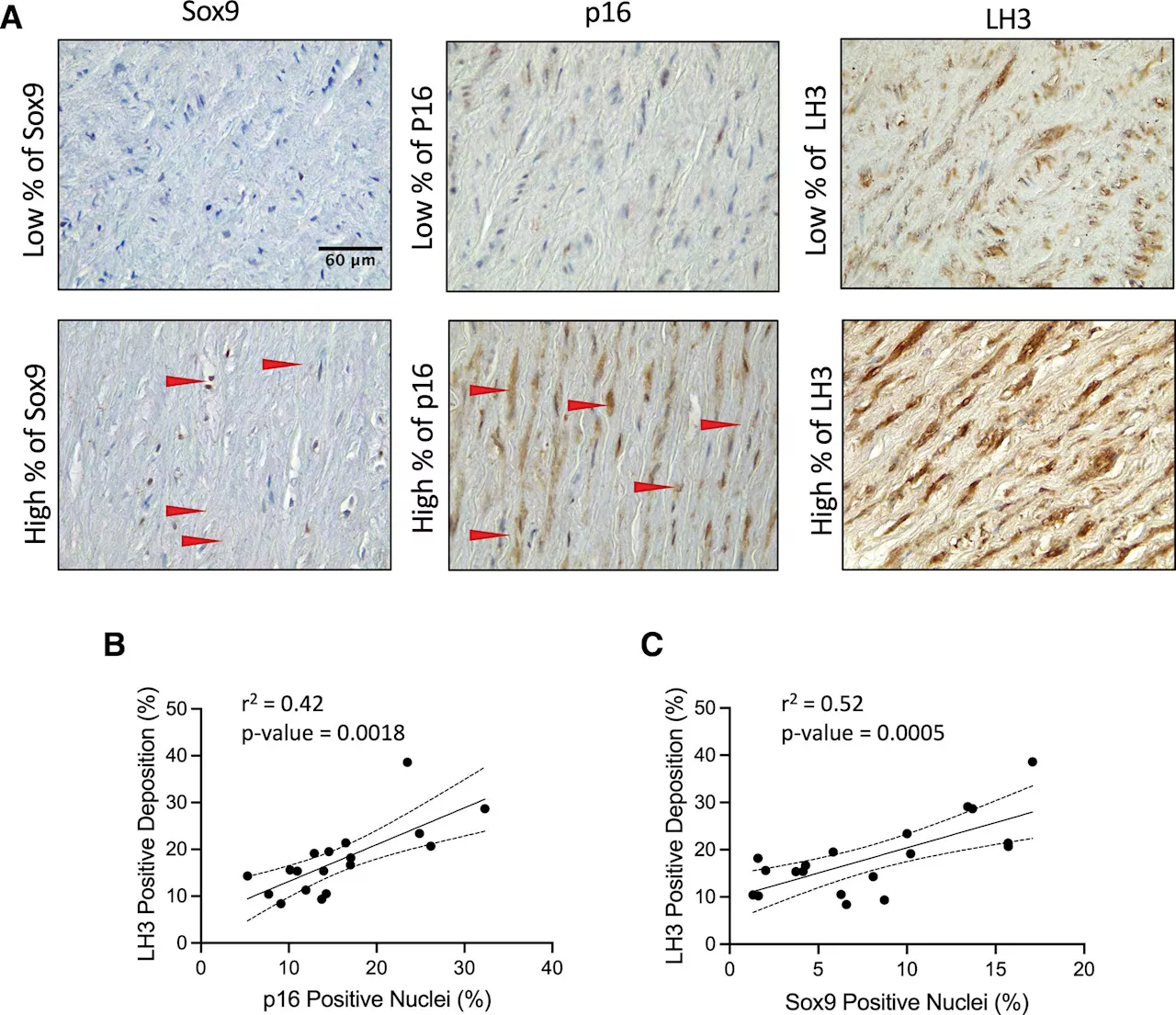 Researchers uncover key molecule influencing vascular agingA new study shows how the molecule Sox9 is involved in a positive feedback loop that accelerates the aging of blood vessels, which could be used as a target for new therapies.
Researchers uncover key molecule influencing vascular agingA new study shows how the molecule Sox9 is involved in a positive feedback loop that accelerates the aging of blood vessels, which could be used as a target for new therapies.
Read more »