Researchers identify a specific genetic variant, rs2204985, linked to less severe lung involvement and a stronger immune response in COVID-19 patients with severe pneumonia. The study suggests that understanding this genetic marker could help identify high-risk individuals and enhance strategies for prevention and treatment.
By Vijay Kumar MalesuSep 25 2023Reviewed by Susha Cheriyedath, M.Sc. In a recent study published in the journal Science Advances, a group of researchers investigated the influence of rs2204985 polymorphism within the T-cell receptor alpha and T-cell receptor delta locus on the immune response and severity of coronavirus disease 2019 in patients with severe pneumonia.
About the study The present study unfolded within the intensive care unit of Clinique Ambroise Paré in Neuilly, France, from March 2020 to February 2022, encompassing 40 adult COVID-19 patients and 41 control patients with non-COVID-19 related diseases. A subgroup consented to a second examination six months post-recovery. The control group, admitted during the same period, consisted of individuals hospitalized for varied medical reasons.
Statistical analyses, utilizing tests like analysis of variance and Mann-Whitney across diverse software tools, were employed to explore the complex interactions between SARS-CoV-2 and the human body. These comprehensive methodologies yielded significant insights into the virus's nature, enhancing understanding and facilitating the development of precisely targeted therapeutic interventions.
The rs2204985 genotype's association was investigated with levels of thymopoiesis in patients, and the data indicated that GG patients have a higher median signal-joint TREC/DJbeta TREC ratio compared to GA and AA individuals, signaling an efficient adaptive immune response against SARS-CoV-2 during acute infection. This reflected a more substantial thymic output correlated with a higher number of circulating T cells, crucial in the immune response against the virus.
United Kingdom Latest News, United Kingdom Headlines
Similar News:You can also read news stories similar to this one that we have collected from other news sources.
 Researchers investigating whether meerkats pick up on human emotionsThey hope any findings might be able to help improve experts’ understanding and management of different species.
Researchers investigating whether meerkats pick up on human emotionsThey hope any findings might be able to help improve experts’ understanding and management of different species.
Read more »
 Researchers investigating whether meerkats pick up on human emotionsThey hope any findings might be able to help improve experts’ understanding and management of different species.
Researchers investigating whether meerkats pick up on human emotionsThey hope any findings might be able to help improve experts’ understanding and management of different species.
Read more »
 Researchers crack genetic code of rare kidney cancerThe genetic code of a rare form of kidney cancer, called reninoma, has been studied for the first time. In a paper, published in Nature Communications, researchers at the Wellcome Sanger Institute, Great Ormond Street Hospital and The Royal Free Hospital also revealed a new drug target that could serve as an alternative treatment if surgery is not recommended.
Researchers crack genetic code of rare kidney cancerThe genetic code of a rare form of kidney cancer, called reninoma, has been studied for the first time. In a paper, published in Nature Communications, researchers at the Wellcome Sanger Institute, Great Ormond Street Hospital and The Royal Free Hospital also revealed a new drug target that could serve as an alternative treatment if surgery is not recommended.
Read more »
 Researchers develop new method to deliver strong antibiotic drugs more safelyAntibiotic resistant bacteria are a threat to human lives, and yet the development of new drugs to treat bacterial infections is slow.
Researchers develop new method to deliver strong antibiotic drugs more safelyAntibiotic resistant bacteria are a threat to human lives, and yet the development of new drugs to treat bacterial infections is slow.
Read more »
 Researchers crack the genetic code of rare form of kidney cancerThe genetic code of a rare form of kidney cancer, called reninoma, has been studied for the first time. In the new paper, published today (25th September) in Nature Communications, researchers at the Wellcome Sanger Institute, Great Ormond Street Hospital and The Royal Free Hospital also revealed a new drug target that could serve as an alternative treatment if surgery is not recommended.
Researchers crack the genetic code of rare form of kidney cancerThe genetic code of a rare form of kidney cancer, called reninoma, has been studied for the first time. In the new paper, published today (25th September) in Nature Communications, researchers at the Wellcome Sanger Institute, Great Ormond Street Hospital and The Royal Free Hospital also revealed a new drug target that could serve as an alternative treatment if surgery is not recommended.
Read more »
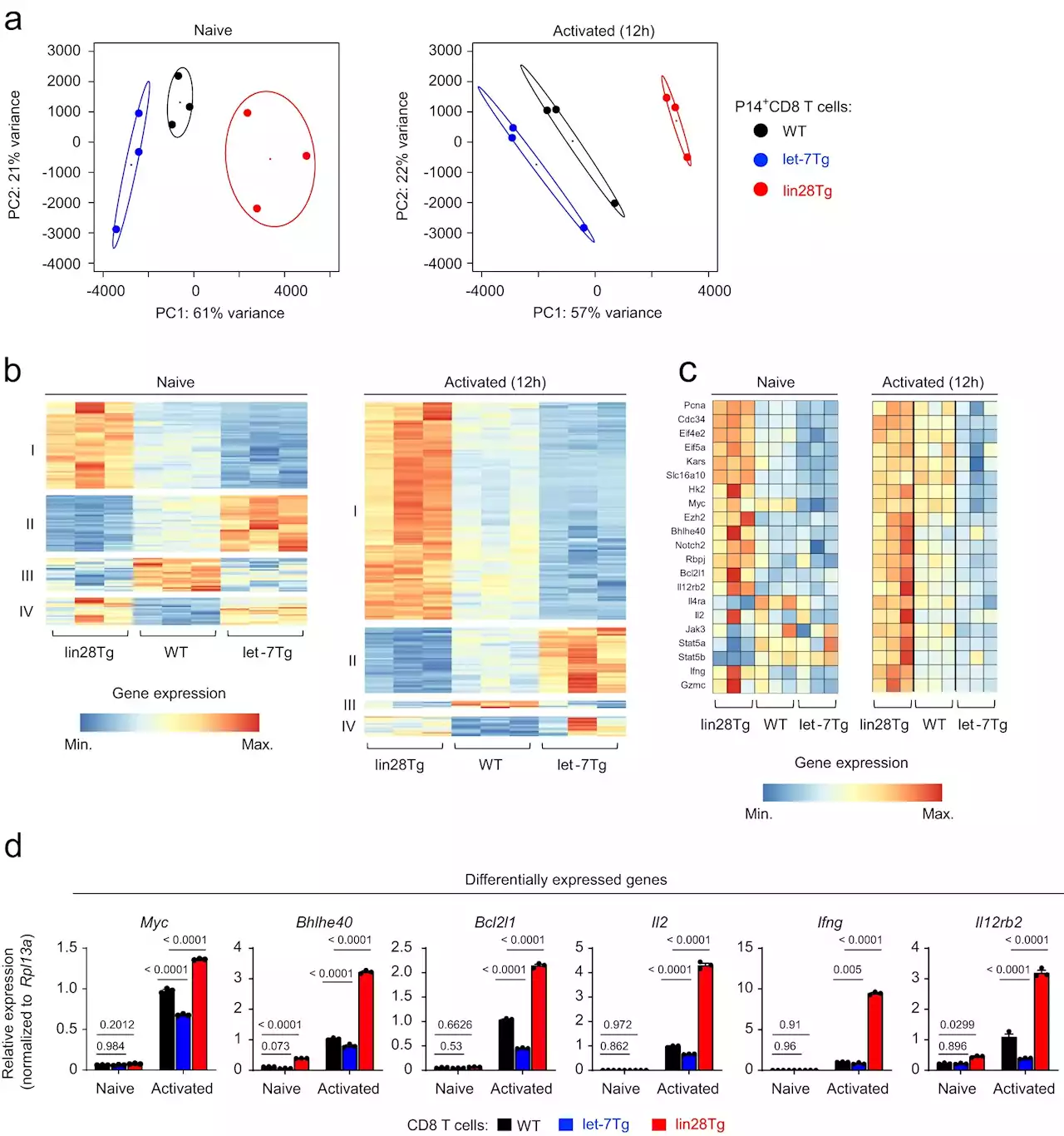 Researchers show how a small strand of RNA is key to fighting cancerA team of researchers at the University of Massachusetts Amherst has shown that a single, small strand of microRNA, or miRNA, known as let-7, governs the ability of T-cells to recognize and remember tumor cells. This cellular memory is the basis for how vaccines work. Boosting cellular memory to recognize tumors could help improve cancer therapies.
Researchers show how a small strand of RNA is key to fighting cancerA team of researchers at the University of Massachusetts Amherst has shown that a single, small strand of microRNA, or miRNA, known as let-7, governs the ability of T-cells to recognize and remember tumor cells. This cellular memory is the basis for how vaccines work. Boosting cellular memory to recognize tumors could help improve cancer therapies.
Read more »
