Many bacteria produce substances to gain an advantage over competitors in their highly competitive natural environment. Researchers have discovered a new so-called lantibiotic, namely epilancin A37. It is produced by staphylococci that colonize the skin and acts specifically against their main competitors there, the corynebacteria.
This specificity is presumably mediated by a very special mechanism of action, which the researchers were able to decipher in detail.
Many bacteria produce substances to gain an advantage over competitors in their highly competitive natural environment. Researchers at the University Hospital Bonn , the University of Bonn and the German Center for Infection Research have discovered a new so-called lantibiotic, namely epilancin A37. It is produced by staphylococci that colonize the skin and acts specifically against their main competitors there, the corynebacteria.
The intestines and their bacteria are sometimes called our 'second brain', but studying these bacteria in their natural environment is difficult. Now researchers have developed a method ... Bacteria, fungi and plants sometimes produce metal-binding substances that can be harnessed, for example for the extraction of raw materials, for their separation, for cleaning soils or for medical ...
Wound inflammation which results in impaired wound healing can have serious consequences for patients. Researchers have discovered a new defensive mechanism which enables our skin to actively kill ...
Medical Topics Diseases And Conditions Today's Healthcare Bacteria Microbes And More New Species Microbiology
United Kingdom Latest News, United Kingdom Headlines
Similar News:You can also read news stories similar to this one that we have collected from other news sources.
 Researchers Discover Possible Solutions To Reverse the Impact of Alzheimer’s DiseaseScience, Space and Technology News 2024
Researchers Discover Possible Solutions To Reverse the Impact of Alzheimer’s DiseaseScience, Space and Technology News 2024
Read more »
 Texas researchers developing possible vaccine for people to prevent human Bird Flu infectionsWith growing concern among biologists about the spread of the so-called bird flu to cattle in the U.S., the worry now is that more humans could catch the virus.
Texas researchers developing possible vaccine for people to prevent human Bird Flu infectionsWith growing concern among biologists about the spread of the so-called bird flu to cattle in the U.S., the worry now is that more humans could catch the virus.
Read more »
 Texas researchers developing possible vaccine to prevent human bird flu infectionsWith growing concern among biologists about the spread of the so-called bird flu to cattle in the U.S., the worry now is that more humans could catch the virus.
Texas researchers developing possible vaccine to prevent human bird flu infectionsWith growing concern among biologists about the spread of the so-called bird flu to cattle in the U.S., the worry now is that more humans could catch the virus.
Read more »
 Researchers point to pyrite as possible source of lithiumNo 1 source of global mining news and opinion
Researchers point to pyrite as possible source of lithiumNo 1 source of global mining news and opinion
Read more »
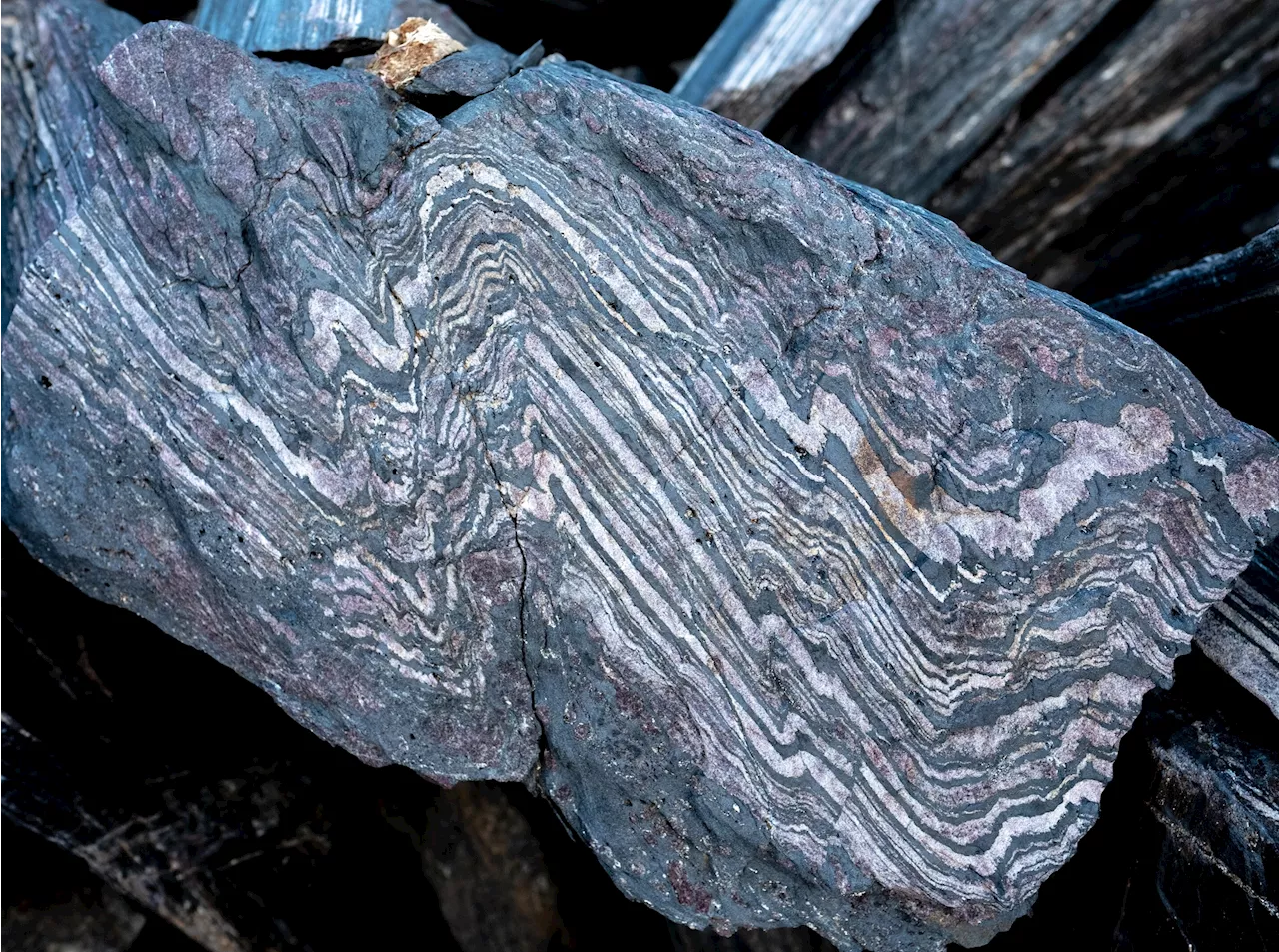 Researchers find oldest undisputed evidence of Earth's magnetic fieldA new study, led by the University of Oxford and MIT, has recovered a 3.7-billion-year-old record of Earth's magnetic field, and found that it appears remarkably similar to the field surrounding Earth today. The findings have been published in the Journal of Geophysical Research.
Researchers find oldest undisputed evidence of Earth's magnetic fieldA new study, led by the University of Oxford and MIT, has recovered a 3.7-billion-year-old record of Earth's magnetic field, and found that it appears remarkably similar to the field surrounding Earth today. The findings have been published in the Journal of Geophysical Research.
Read more »
 Researchers unveil PI3K enzyme's dual accelerator and brake mechanismsA group of researchers have expanded conventional knowledge on a critical enzyme that controls cell migration. In a publication in the journal Nature Communications, they reported that phosphoinositide 3-kinase (PI3K) not only acts as an accelerator to prompt cell motility, but it also has a built-in brake mechanism that impedes migration.
Researchers unveil PI3K enzyme's dual accelerator and brake mechanismsA group of researchers have expanded conventional knowledge on a critical enzyme that controls cell migration. In a publication in the journal Nature Communications, they reported that phosphoinositide 3-kinase (PI3K) not only acts as an accelerator to prompt cell motility, but it also has a built-in brake mechanism that impedes migration.
Read more »
