Coronary heart disease is a major global health problem, especially among people with type 2 diabetes. Researchers have identified novel protein biomarkers that are associated with the development of CHD in people with and without diabetes.
Coronary heart disease is a major global health problem, especially among people with type 2 diabetes. Researchers at the German Center for Diabetes Research , Helmholtz Munich, and Ludwig-Maximilians-University Munich have identified novel protein biomarkers that are associated with the development of CHD in people with and without diabetes.
The researchers thus identified two proteins associated with incident CHD in individuals with diabetes and 29 proteins in those without baseline T2D. Six of these proteins are novel candidates for incident CHD. Association of plasma proteomics with incident coronary heart disease in individuals with and without type 2 diabetes: results from the population-based KORA studyAn analysis of a clinical trial of more than 2,500 people with Type 2 diabetes and kidney disease found that high levels of four biomarkers are strongly predictive for the development of heart and ...
United Kingdom Latest News, United Kingdom Headlines
Similar News:You can also read news stories similar to this one that we have collected from other news sources.
 Promising new technique treats infertility by turning skin cells into eggThe Oregon Health & Science University researchers state that this approach holds the potential to treat infertility.
Promising new technique treats infertility by turning skin cells into eggThe Oregon Health & Science University researchers state that this approach holds the potential to treat infertility.
Read more »
 Immunology: Good sleep stimulates the immune systemResearchers have shown that sleep enhances the migratory potential of T cells toward lymph nodes.
Immunology: Good sleep stimulates the immune systemResearchers have shown that sleep enhances the migratory potential of T cells toward lymph nodes.
Read more »
 FDA Approves First Drug-Coated Balloon to Treat Coronary In-Stent RestenosisThe Agent DCB, from Boston Scientific, was superior to uncoated balloon angioplasty for the treatment of coronary artery in-stent restenosis in a pivotal trial.
FDA Approves First Drug-Coated Balloon to Treat Coronary In-Stent RestenosisThe Agent DCB, from Boston Scientific, was superior to uncoated balloon angioplasty for the treatment of coronary artery in-stent restenosis in a pivotal trial.
Read more »
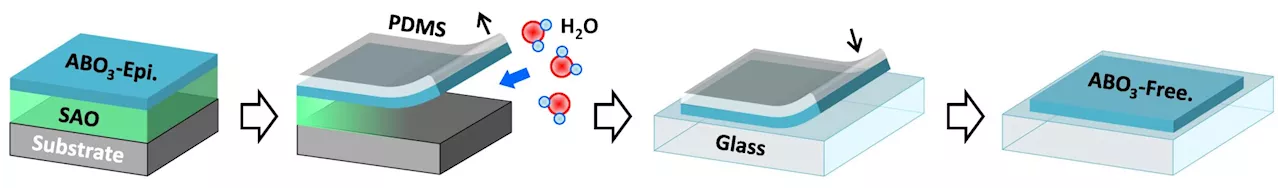 Researchers develop novel 'super-tetragonal' sacrificial layer for freestanding oxide membranesResearchers have developed a new water-soluble sacrificial layer, 'super-tectragonal' Sr4Al2O7 (SAOT), with broad tunability in lattice constants, which can be used to prepare high-quality freestanding oxide membrane. Their work is published in Science.
Researchers develop novel 'super-tetragonal' sacrificial layer for freestanding oxide membranesResearchers have developed a new water-soluble sacrificial layer, 'super-tectragonal' Sr4Al2O7 (SAOT), with broad tunability in lattice constants, which can be used to prepare high-quality freestanding oxide membrane. Their work is published in Science.
Read more »
 Revealing a hidden threat: Researchers show viral infections pose early heart risksIn a potentially game-changing development, scientists have revealed a new understanding of sometimes fatal viral infections that affect the heart. Traditionally, the focus has been on heart inflammation known as myocarditis, which is often triggered by the body's immune response to a viral infection.
Revealing a hidden threat: Researchers show viral infections pose early heart risksIn a potentially game-changing development, scientists have revealed a new understanding of sometimes fatal viral infections that affect the heart. Traditionally, the focus has been on heart inflammation known as myocarditis, which is often triggered by the body's immune response to a viral infection.
Read more »
 Stronger than nature: Optimized radicals as potential novel catalystsNature uses enzymes for various metabolic processes. These biological catalysts are extremely efficient. Biomimetic catalysts based on inexpensive starting materials from the laboratory that can reproduce the efficiency of the natural enzymes and can function at ambient conditions are therefore of great interest to research and industry.
Stronger than nature: Optimized radicals as potential novel catalystsNature uses enzymes for various metabolic processes. These biological catalysts are extremely efficient. Biomimetic catalysts based on inexpensive starting materials from the laboratory that can reproduce the efficiency of the natural enzymes and can function at ambient conditions are therefore of great interest to research and industry.
Read more »
