Researchers assessed a novel human papillomavirus (HPV) and host deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) methylation score for adenocarcinoma in-situ (AIS) and cervical adenocarcinoma (ADC) screening.
By Pooja Toshniwal PahariaSep 8 2023Reviewed by Danielle Ellis, B.Sc. In a recent study published in the Journal of the National Cancer Institute, researchers assessed a novel human papillomavirus and host deoxyribonucleic acid methylation score for adenocarcinoma in-situ and cervical adenocarcinoma screening.
The methylation score was calculated by averaging the percent methylation at 35 different predetermined CpG sites within the L2/L1 open reading frames of HPV-16, 18, and 45, and the promoter regions of two human genetic loci, heparan sulfate glucosamine 3-O-sulfotransferase 2 and deleted in colorectal cancer on chromosomes 16 and 18, respectively.
From electronic health records, deidentified race, ethnicity, smoking habits, and age-related data, as well as follow-up histopathological and cytological reports, were obtained, with clinical outcomes accessible until 2014. Results AIS/ADC tumors and CIN3/SCC tumors had a greater proportion of white females compared to those whose HPC infections cleared . Seven to ten percent of the individuals were current smokers, and 10% to 15% were past cigarette users.
The comparable proportions for CIN3/SCC were 46%, 82%, and 68%, respectively. Using HPV-clearers as controls, the OR for the DNA methylation score for AIS and ADC was 49. CIN3 and SCC patients showed similar but weaker relationships with the DNA methylation scores.
United Kingdom Latest News, United Kingdom Headlines
Similar News:You can also read news stories similar to this one that we have collected from other news sources.
 Single-dose HPV vaccine effective in preventing cervical cancer globallyAdministering one dose of the human papillomavirus (HPV) vaccine in routine immunization programs for adolescent girls would still significantly reduce cervical cancer burden globally, new research suggests.
Single-dose HPV vaccine effective in preventing cervical cancer globallyAdministering one dose of the human papillomavirus (HPV) vaccine in routine immunization programs for adolescent girls would still significantly reduce cervical cancer burden globally, new research suggests.
Read more »
 It may not be too late to get your HPV vaccineKentucky has the highest rate of cancers caused by the human papillomavirus (HPV) in the U.S.—a dire statistic considering these cancers can be largely preventable through vaccination.
It may not be too late to get your HPV vaccineKentucky has the highest rate of cancers caused by the human papillomavirus (HPV) in the U.S.—a dire statistic considering these cancers can be largely preventable through vaccination.
Read more »
 One in three men carry HPV: The ignored reservoir in the fight against cancerOne in three men over 15 globally have at least one incidence of genital HPV, underscoring the need to include males in HPV prevention strategies. The prevalence remains high from young adulthood through later life, particularly for high-risk HPV types linked to cancers.
One in three men carry HPV: The ignored reservoir in the fight against cancerOne in three men over 15 globally have at least one incidence of genital HPV, underscoring the need to include males in HPV prevention strategies. The prevalence remains high from young adulthood through later life, particularly for high-risk HPV types linked to cancers.
Read more »
 Online AI-based test for Parkinson's disease severity shows promising resultsAn artificial intelligence tool developed by researchers at the University of Rochester can help people with Parkinson's disease remotely assess the severity of their symptoms within minutes. A study in npj Digital Medicine describes the new tool, which has users tap their fingers 10 times in front of a webcam to assess motor performance on a scale of 0–4.
Online AI-based test for Parkinson's disease severity shows promising resultsAn artificial intelligence tool developed by researchers at the University of Rochester can help people with Parkinson's disease remotely assess the severity of their symptoms within minutes. A study in npj Digital Medicine describes the new tool, which has users tap their fingers 10 times in front of a webcam to assess motor performance on a scale of 0–4.
Read more »
 Is psilocybin a promising therapy for treatment-resistant depression?A growing body of evidence suggests that psychedelic drugs may be useful in treating various mental health conditions. However, many challenges remain in defining their clinical benefits and overcoming the complex regulatory obstacles to their use. The September issue of Journal of Psychiatric Practice presents a research review and update on therapeutic use of psychedelics—focusing on the use of psilocybin for treatment of depression.
Is psilocybin a promising therapy for treatment-resistant depression?A growing body of evidence suggests that psychedelic drugs may be useful in treating various mental health conditions. However, many challenges remain in defining their clinical benefits and overcoming the complex regulatory obstacles to their use. The September issue of Journal of Psychiatric Practice presents a research review and update on therapeutic use of psychedelics—focusing on the use of psilocybin for treatment of depression.
Read more »
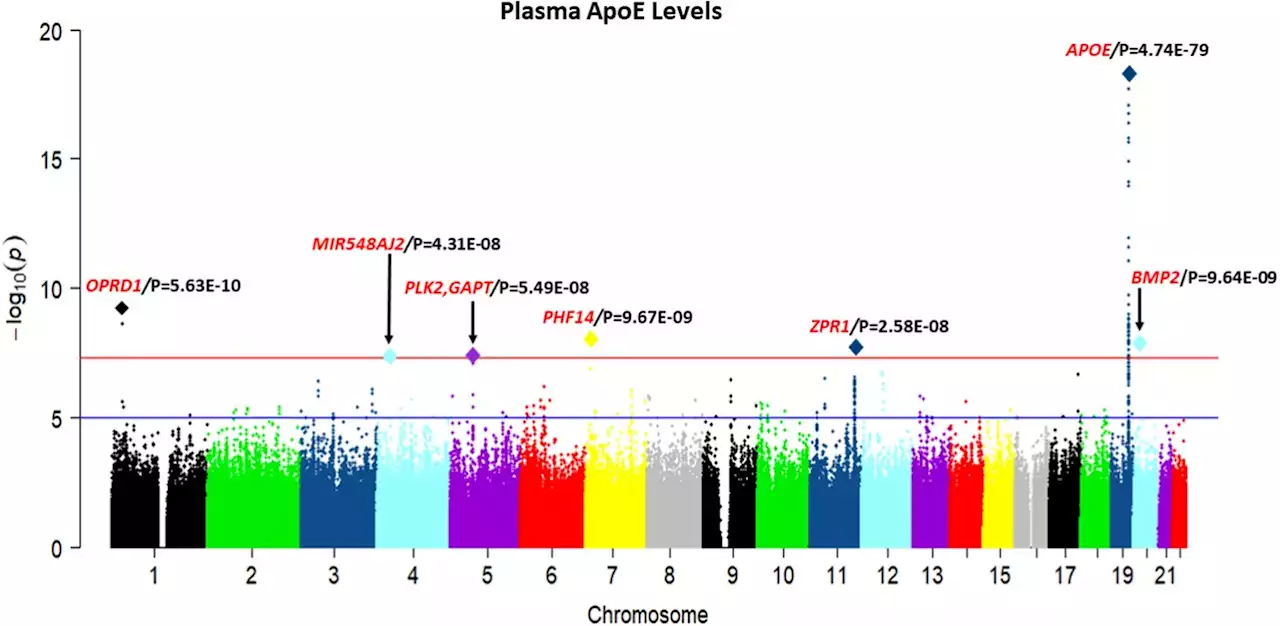 Researchers uncover new genetic traits influencing Alzheimer's riskResearchers at the University of Pittsburgh analyzed thousands of human genomes to find new gene variations responsible for controlling the levels of blood plasma molecules linked to Alzheimer's disease risk. The findings, published recently in Molecular Psychiatry, could contribute to the future development of simple blood tests for the disease.
Researchers uncover new genetic traits influencing Alzheimer's riskResearchers at the University of Pittsburgh analyzed thousands of human genomes to find new gene variations responsible for controlling the levels of blood plasma molecules linked to Alzheimer's disease risk. The findings, published recently in Molecular Psychiatry, could contribute to the future development of simple blood tests for the disease.
Read more »