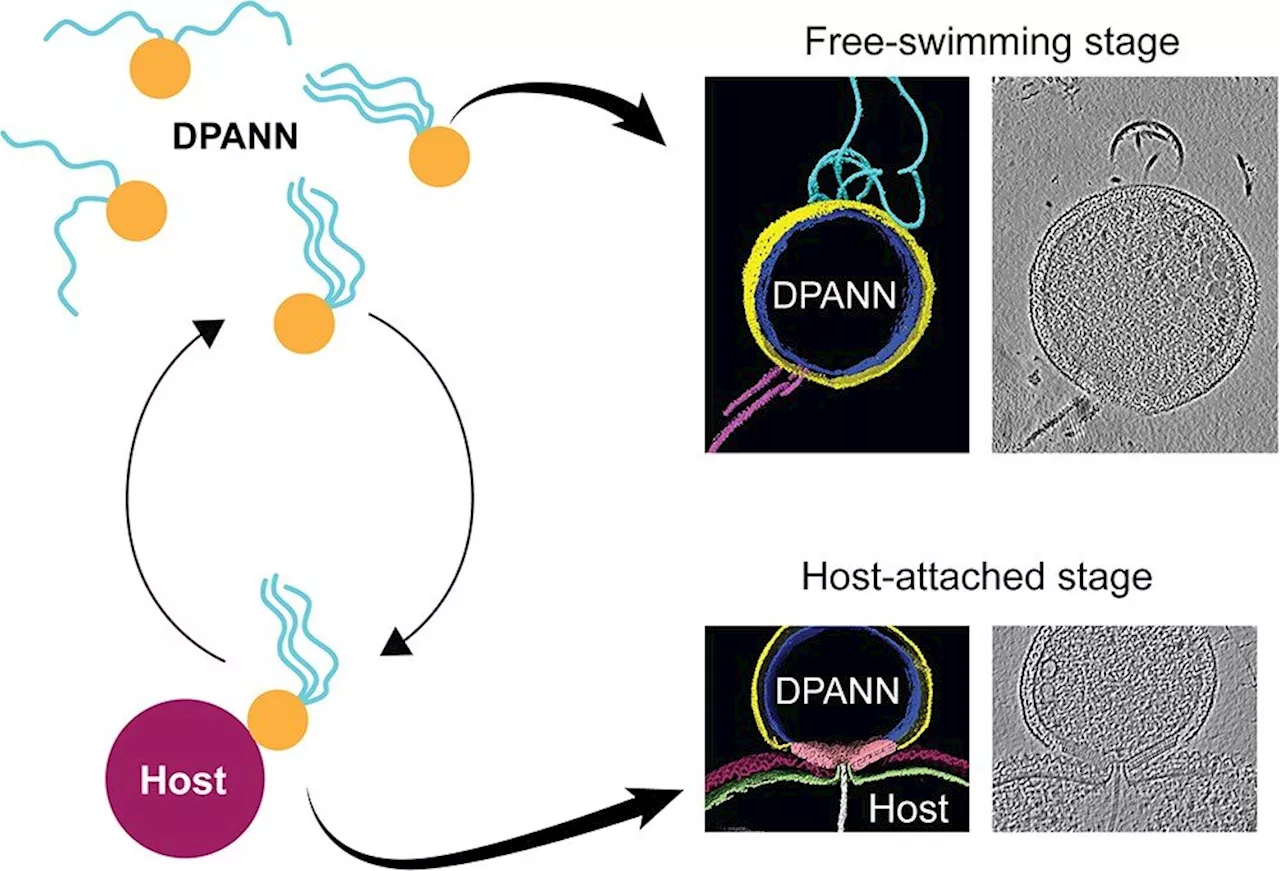
Archaea are ubiquitous microorganisms whose evolution shaped the biosphere of Earth. Their evolutionary paths are truly fascinating. A great example is an ectosymbiotic lifestyle which is found among DPANN archaea.
Researchers discover distinct life cycle stages of the ectosymbiotic DPANN archaeon Nanobdella aerobiophila retrieved 22 May 2024 from https://phys.org/news/2024-05-distinct-life-stages-ectosymbiotic-dpann.html
This document is subject to copyright. Apart from any fair dealing for the purpose of private study or research, no part may be reproduced without the written permission. The content is provided for information purposes only.Use this form if you have come across a typo, inaccuracy or would like to send an edit request for the content on this page. For general inquiries, please use ourThank you for taking time to provide your feedback to the editors.
Your feedback is important to us. However, we do not guarantee individual replies due to the high volume of messages.to let the recipient know who sent the email. Neither your address nor the recipient's address will be used for any other purpose. The information you enter will appear in your e-mail message and is not retained by Phys.org in any form.Get weekly and/or daily updates delivered to your inbox.
Physics News Science News Technology News Physics Materials Nanotech Technology Science
United Kingdom Latest News, United Kingdom Headlines
Similar News:You can also read news stories similar to this one that we have collected from other news sources.
 Archaea can be 'picky eaters': Study shows a group of parasitic microbes can change host metabolismA parasite that not only feeds off its host, but also makes the host change its own metabolism and thus biology: NIOZ microbiologists Su Ding and Joshua Hamm, Nicole Bale, Jaap Damsté and Anja Spang have shown this for the very first time in a specific group of parasitic microbes called DPANN archaea.
Archaea can be 'picky eaters': Study shows a group of parasitic microbes can change host metabolismA parasite that not only feeds off its host, but also makes the host change its own metabolism and thus biology: NIOZ microbiologists Su Ding and Joshua Hamm, Nicole Bale, Jaap Damsté and Anja Spang have shown this for the very first time in a specific group of parasitic microbes called DPANN archaea.
Read more »
 Archaea can be picky parasites | ScienceDailyA parasite that not only feeds of its host, but also makes the host change its own metabolism and thus biology. Microbiologists have shown this for the very first time in a specific group of parasitic microbes, so-called DPANN archea. Their study shows that these archaea are very 'picky eaters', which might drive their hosts to change the menu.
Archaea can be picky parasites | ScienceDailyA parasite that not only feeds of its host, but also makes the host change its own metabolism and thus biology. Microbiologists have shown this for the very first time in a specific group of parasitic microbes, so-called DPANN archea. Their study shows that these archaea are very 'picky eaters', which might drive their hosts to change the menu.
Read more »
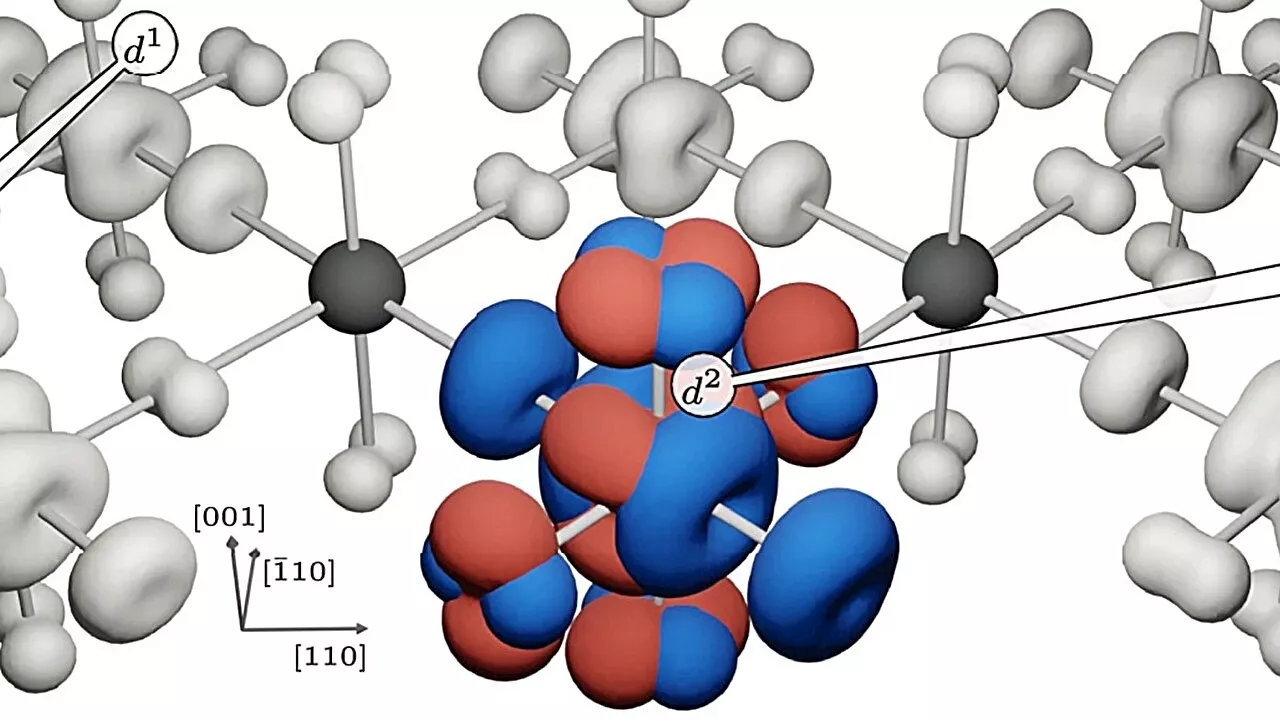 Researchers find unexpected roadblock to conductivity in Mott insulatorsIn the realm of condensed matter physics, few phenomena captivate physicists' curiosity as much as Mott insulators. According to traditional theory, this odd class of materials should be capable of conducting electricity, yet they behave mostly as insulators.
Researchers find unexpected roadblock to conductivity in Mott insulatorsIn the realm of condensed matter physics, few phenomena captivate physicists' curiosity as much as Mott insulators. According to traditional theory, this odd class of materials should be capable of conducting electricity, yet they behave mostly as insulators.
Read more »
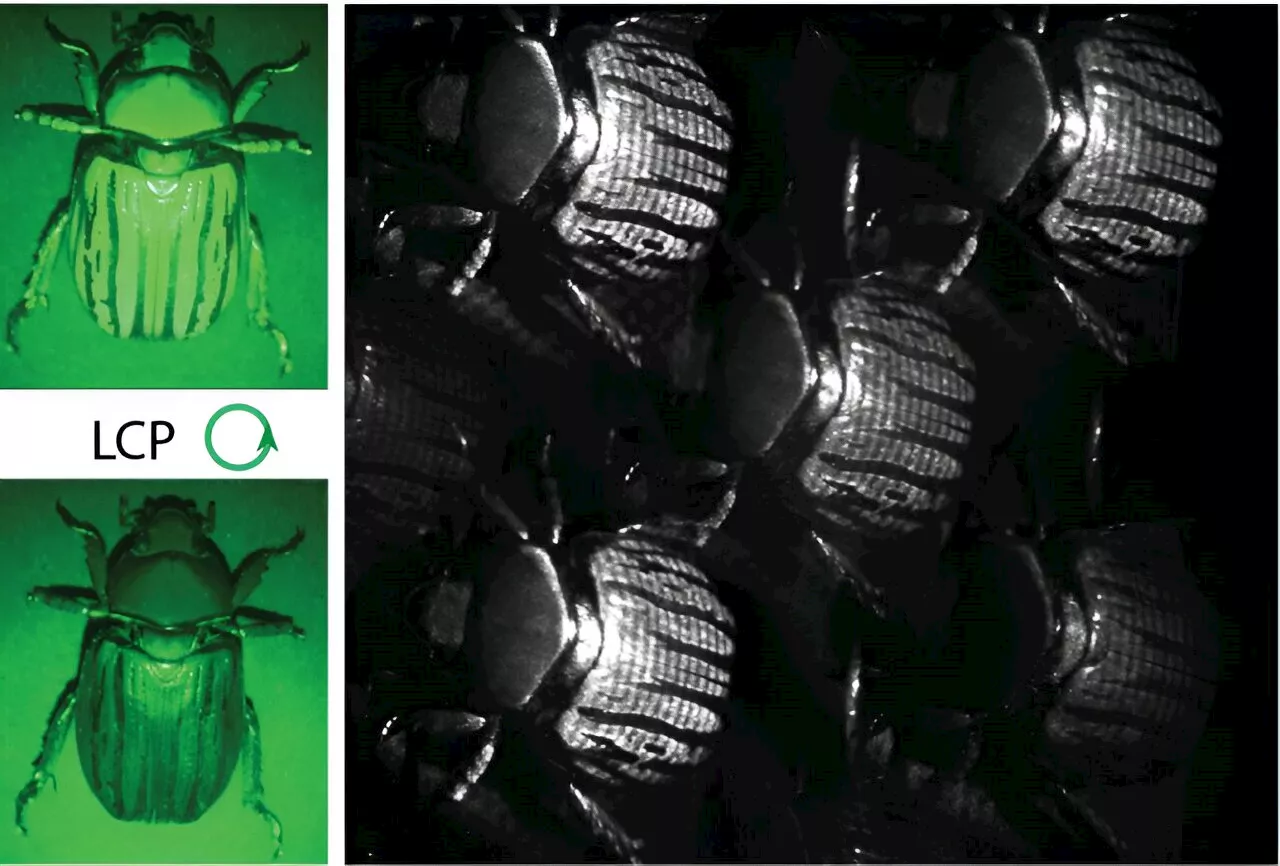 Researchers unveil single-shot and complete polarization imaging system using metasurfacesThink of all the information we get based on how an object interacts with wavelengths of light—aka color. Color can tell us if food is safe to eat or if a piece of metal is hot. Color is an important diagnostic tool in medicine, helping practitioners diagnose diseased tissue, inflammation, or problems in blood flow.
Researchers unveil single-shot and complete polarization imaging system using metasurfacesThink of all the information we get based on how an object interacts with wavelengths of light—aka color. Color can tell us if food is safe to eat or if a piece of metal is hot. Color is an important diagnostic tool in medicine, helping practitioners diagnose diseased tissue, inflammation, or problems in blood flow.
Read more »
 Researchers detect toxic chemicals in aquatic organisms with new AI methodSwedish researchers at Chalmers University of Technology and the University of Gothenburg have developed an AI method that improves the identification of toxic chemicals—based solely on knowledge of the molecular structure.
Researchers detect toxic chemicals in aquatic organisms with new AI methodSwedish researchers at Chalmers University of Technology and the University of Gothenburg have developed an AI method that improves the identification of toxic chemicals—based solely on knowledge of the molecular structure.
Read more »
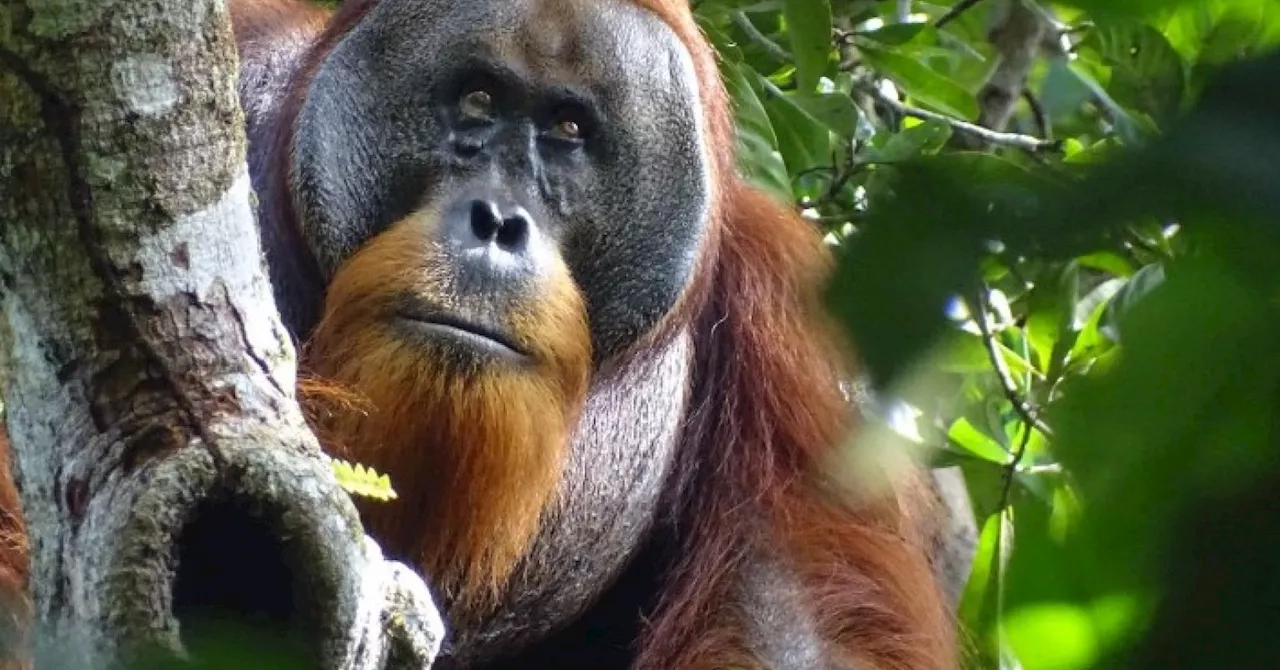 Researchers observed an orangutan applying chewed-up leaves to a facial wound.Scientists report the first observations of an animal using medicinal plants to treat a wound in the wild.
Researchers observed an orangutan applying chewed-up leaves to a facial wound.Scientists report the first observations of an animal using medicinal plants to treat a wound in the wild.
Read more »