Study found that MPXV DNA on pets in mpox-affected households was likely due to human contamination, not true infection, as no live virus or antibodies were detected.
By Vijay Kumar MalesuReviewed by Susha Cheriyedath, M.Sc.Sep 12 2024 Despite detecting mpox virus DNA on dogs and cats in infected households, researchers conclude the viral traces are likely from human contamination, not actual pet infections.In a recent study published in the journal Emerging Infectious Diseases , a group of researchers investigated the potential susceptibility of common companion animals to Mpox virus infection in households with confirmed human mpox cases.
The study was conducted between July 2022 and March 2023 in the District of Columbia, Minnesota, Virginia, and Tennessee. Follow-up sampling occurred 3-4 months later to assess immune responses. Study results The study sampled 34 companion animals from 21 households, including 24 dogs, 9 cats, and 1 rabbit. The animals' ages ranged from 4 months to 16 years, and they were evenly divided between male and female. Most households had a single human mpox case, while one household had two. A total of 191 animal swabs and 56 animal-associated environmental specimens were collected. Skin lesions were observed in 6 dogs and 1 cat during the examination.
Antibodies Blood Contamination Infectious Diseases Mpox Public Health Virus
United Kingdom Latest News, United Kingdom Headlines
Similar News:You can also read news stories similar to this one that we have collected from other news sources.
 Researchers discover DNA mechanism that regulates how disease-causing mutations are inheritedUniversity of Queensland researchers have discovered a mechanism in DNA that regulates how disease-causing mutations are inherited. The research paper has been published in Cell Metabolism.
Researchers discover DNA mechanism that regulates how disease-causing mutations are inheritedUniversity of Queensland researchers have discovered a mechanism in DNA that regulates how disease-causing mutations are inherited. The research paper has been published in Cell Metabolism.
Read more »
 Researchers study gambling-harm-minimization tools and their impact on gambling behaviorLike driving a car, gamblers should always prepare for a rocky ride—even if they believe they don't have a problem, Flinders University experts say.
Researchers study gambling-harm-minimization tools and their impact on gambling behaviorLike driving a car, gamblers should always prepare for a rocky ride—even if they believe they don't have a problem, Flinders University experts say.
Read more »
 UofL researchers receive $3.6 million to study the role of arsenic exposure in causing health problemsUniversity of Louisville researchers have received $3.6 million in new grant funding to study the role of arsenic exposure in causing cancer and other major health concerns.
UofL researchers receive $3.6 million to study the role of arsenic exposure in causing health problemsUniversity of Louisville researchers have received $3.6 million in new grant funding to study the role of arsenic exposure in causing cancer and other major health concerns.
Read more »
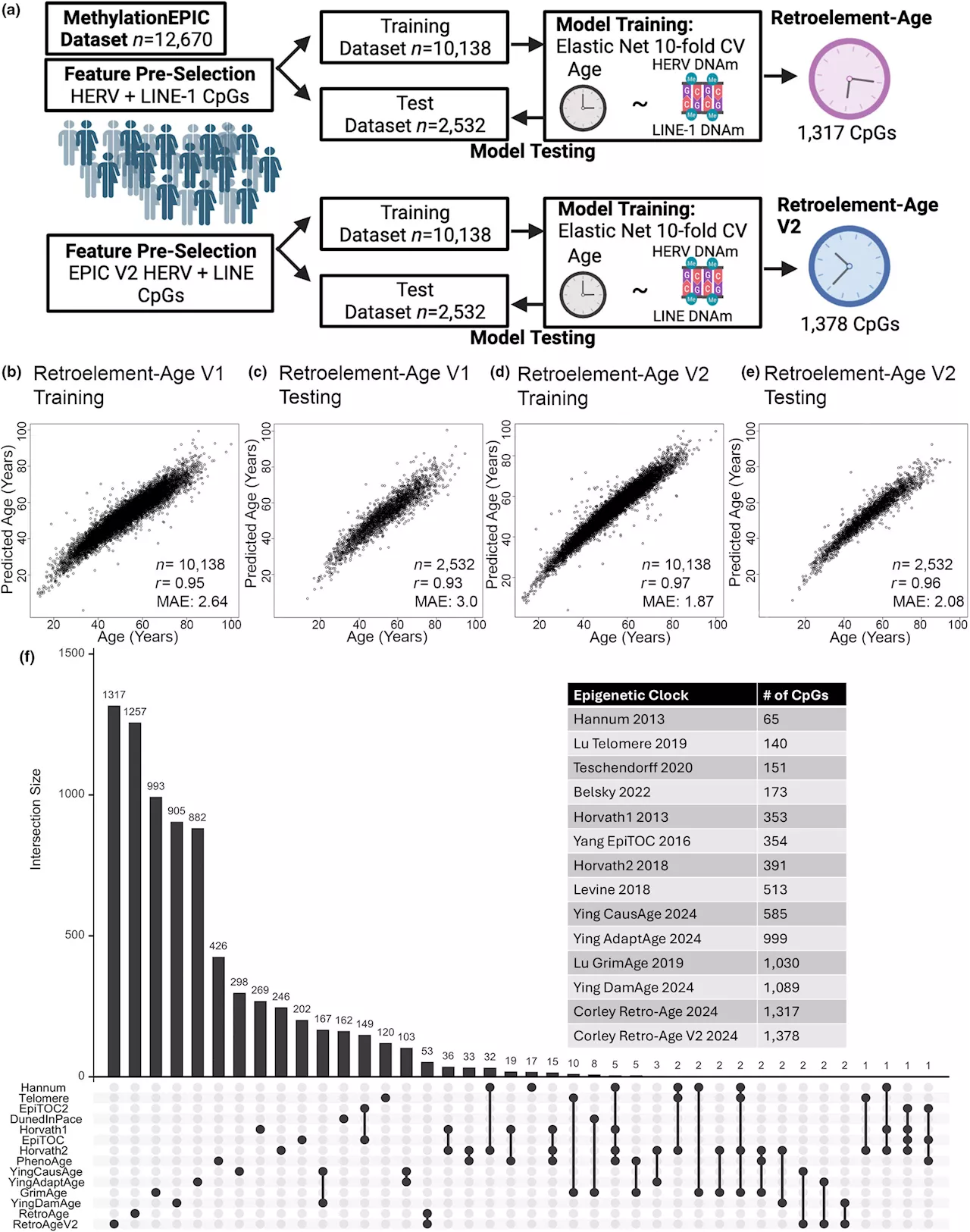 Study finds potential link between DNA markers and aging processResearchers at Weill Cornell Medicine and the epigenetics company TruDiagnostic have uncovered DNA markers associated with retroelements, remnants of ancient viral genetic material in our genes that act as highly accurate epigenetic clocks predicting chronological age.
Study finds potential link between DNA markers and aging processResearchers at Weill Cornell Medicine and the epigenetics company TruDiagnostic have uncovered DNA markers associated with retroelements, remnants of ancient viral genetic material in our genes that act as highly accurate epigenetic clocks predicting chronological age.
Read more »
 Study shows frequent mitochondrial DNA insertion in the brain cellsAs direct descendants of ancient bacteria, mitochondria have always been a little alien.
Study shows frequent mitochondrial DNA insertion in the brain cellsAs direct descendants of ancient bacteria, mitochondria have always been a little alien.
Read more »
 Study illuminates CDCA7's role in DNA methylationDNA methylation, a process by which methyl groups are added to DNA molecules, is essential for the maintenance of DNA and the overall health of an organism.
Study illuminates CDCA7's role in DNA methylationDNA methylation, a process by which methyl groups are added to DNA molecules, is essential for the maintenance of DNA and the overall health of an organism.
Read more »
