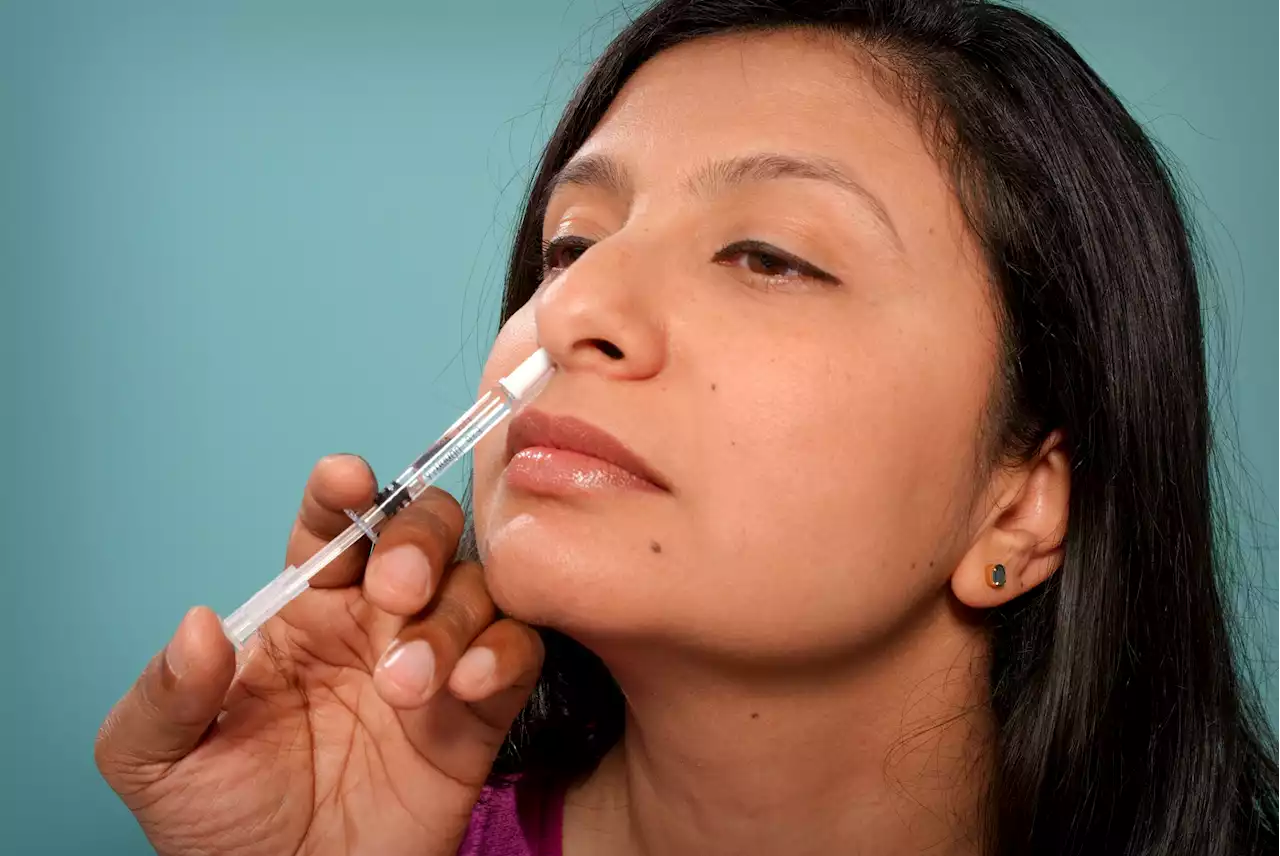
Alzheimer's is a debilitating neurodegenerative and neuroinflammatory disease that is difficult to treat. Most existing therapies target the buildup of amyloid beta (Aβ) plaques in the brain, which requires early intervention and intravenous therapy.
A team of researchers from Brigham and Women's Hospital, a founding member of the Mass General Brigham health care system, tested whether a therapy being tested in multiple sclerosis patients that dampens immune cell inflammation in thecould have a positive effect in Alzheimer's mouse models. They found that a nasal immunotherapy—anti-CD3—reduced inflammation and improved cognition independent of Aβ plaques.
In this study, mice were treated three times a week with an intranasal anti-CD3 for five months. The therapy effectively limited the activation of microglia—
United Kingdom Latest News, United Kingdom Headlines
Similar News:You can also read news stories similar to this one that we have collected from other news sources.
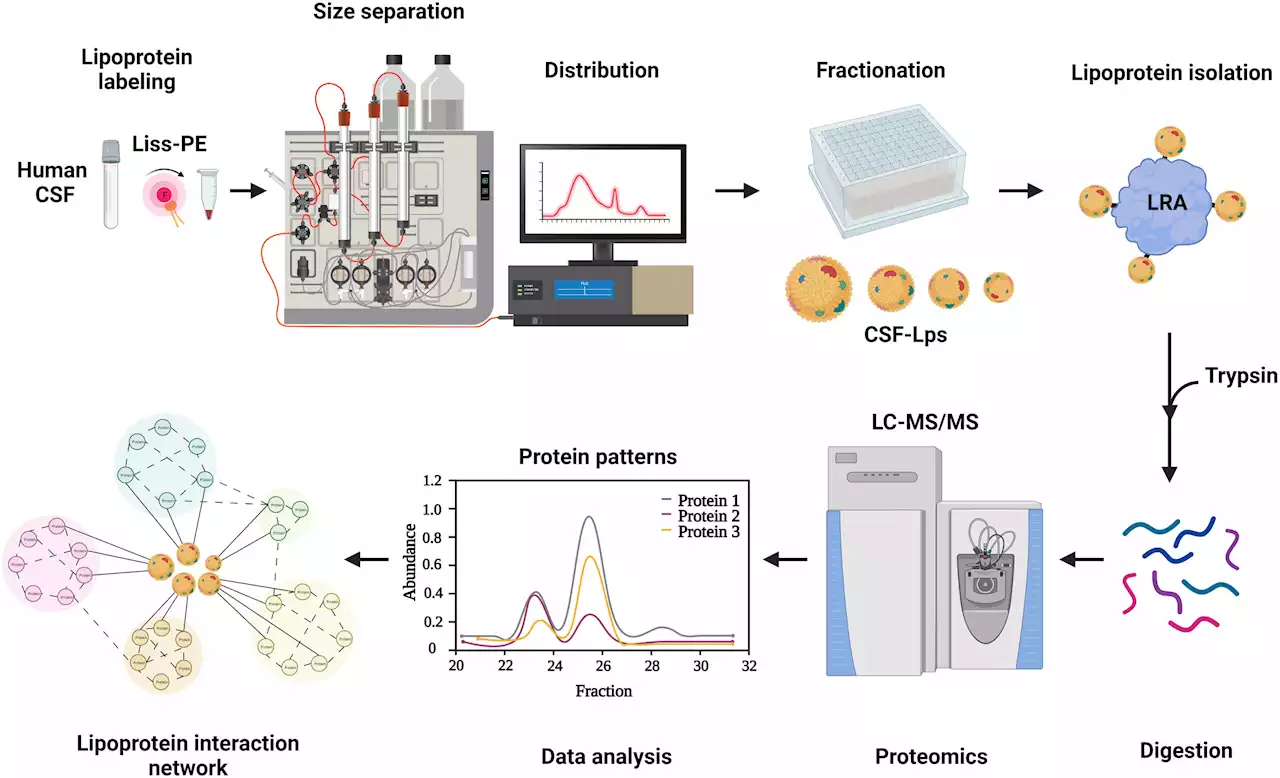 Researchers create a new window on leading genetic cause of Alzheimer'sScientists have created a method to detect key fat-filled particles known as lipoproteins in the central nervous system, opening a new view into the workings of the brain.
Researchers create a new window on leading genetic cause of Alzheimer'sScientists have created a method to detect key fat-filled particles known as lipoproteins in the central nervous system, opening a new view into the workings of the brain.
Read more »
 Researchers develop new protocol to study white matter injury in Alzheimer's diseaseA new editorial paper was published in Aging (listed by MEDLINE/PubMed as 'Aging (Albany NY)' and 'Aging-US' by Web of Science) Volume 15, Issue 16, entitled, 'Microvascular contributions to white matter injury in Alzheimer's disease.'
Researchers develop new protocol to study white matter injury in Alzheimer's diseaseA new editorial paper was published in Aging (listed by MEDLINE/PubMed as 'Aging (Albany NY)' and 'Aging-US' by Web of Science) Volume 15, Issue 16, entitled, 'Microvascular contributions to white matter injury in Alzheimer's disease.'
Read more »
 Using focused ultrasound to treat Alzheimer's and Parkinson'sThe Ultrasound and Elasticity Imaging Laboratory, led by Elisa Konofagou, Robert and Margaret Hariri Professor of Biomedical Engineering, develops novel, ultrasound-based techniques for both imaging and therapeutic applications.
Using focused ultrasound to treat Alzheimer's and Parkinson'sThe Ultrasound and Elasticity Imaging Laboratory, led by Elisa Konofagou, Robert and Margaret Hariri Professor of Biomedical Engineering, develops novel, ultrasound-based techniques for both imaging and therapeutic applications.
Read more »
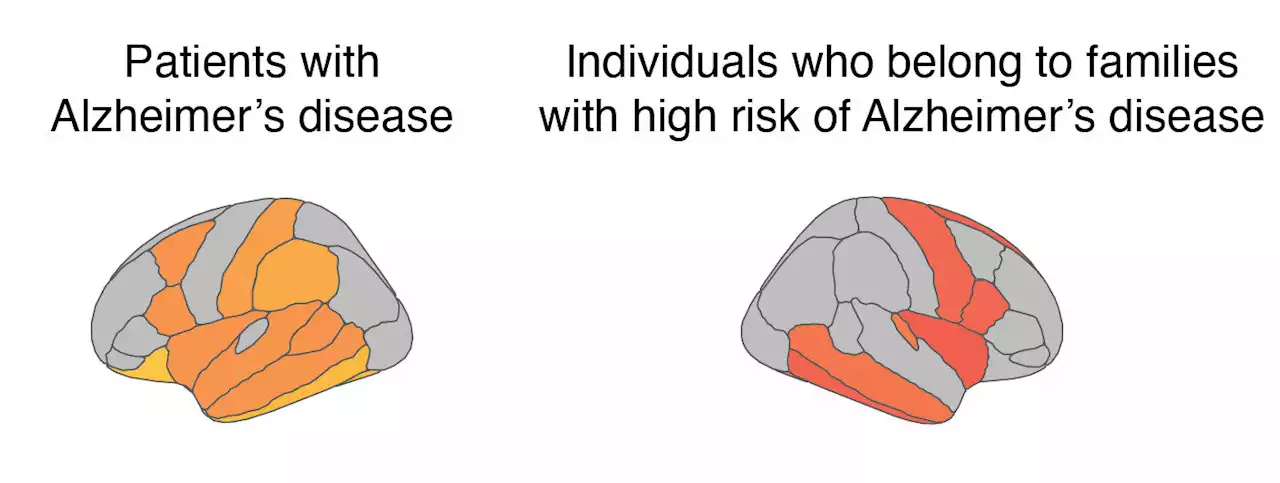 New link between increased astrocytes in the brain and blood in early Alzheimer's diseaseA new study shows that the activation of the brain's immune defense cells—astrocytes—in the early stages of Alzheimer's disease could be tracked early with a brain PET scanner and is linked to changes that can be detected in the blood later in the course of the disease. The study has now been published in Molecular Neurodegeneration.
New link between increased astrocytes in the brain and blood in early Alzheimer's diseaseA new study shows that the activation of the brain's immune defense cells—astrocytes—in the early stages of Alzheimer's disease could be tracked early with a brain PET scanner and is linked to changes that can be detected in the blood later in the course of the disease. The study has now been published in Molecular Neurodegeneration.
Read more »
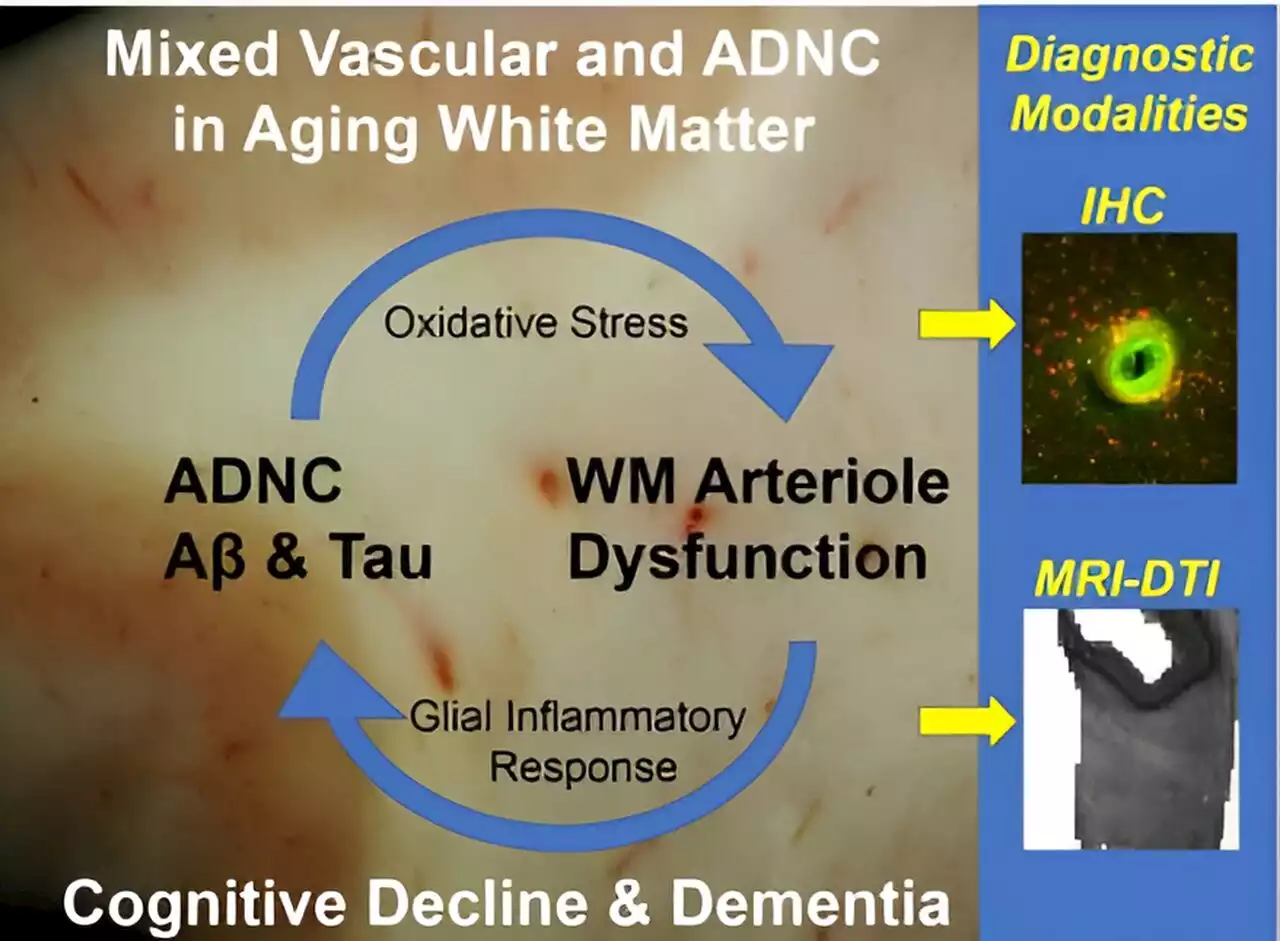 Study reports on contributions to white matter injury in Alzheimer's diseaseA new editorial paper titled 'Microvascular contributions to white matter injury in Alzheimer's disease' has been published in Aging.
Study reports on contributions to white matter injury in Alzheimer's diseaseA new editorial paper titled 'Microvascular contributions to white matter injury in Alzheimer's disease' has been published in Aging.
Read more »
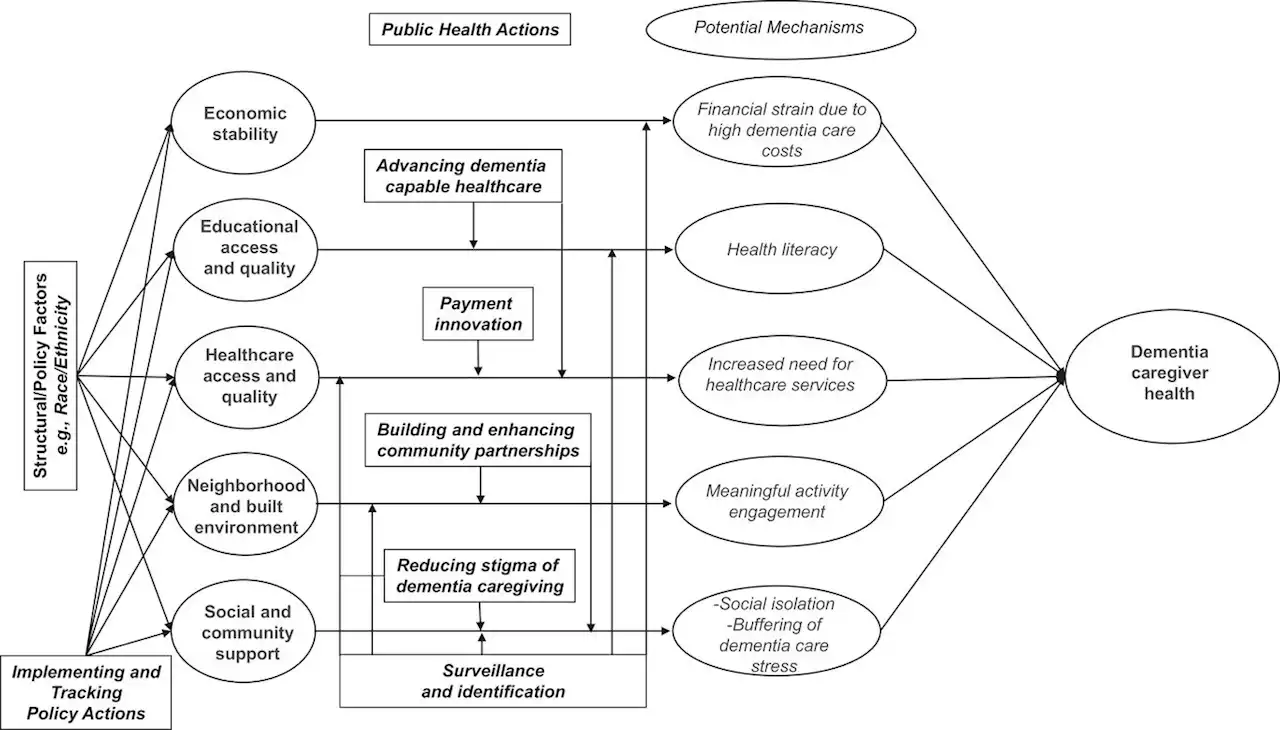 Public health initiatives can support caregivers of people with Alzheimer's and related dementiaUnlike many other long-term health conditions, most people with Alzheimer's disease and related dementia (ADRD) receive some or all of their care from an unpaid relative or friend—a situation that has spawned robust scientific literature on the potentially negative health implications of caring for a friend or family member over a sustained period of time.
Public health initiatives can support caregivers of people with Alzheimer's and related dementiaUnlike many other long-term health conditions, most people with Alzheimer's disease and related dementia (ADRD) receive some or all of their care from an unpaid relative or friend—a situation that has spawned robust scientific literature on the potentially negative health implications of caring for a friend or family member over a sustained period of time.
Read more »