Cytotoxic T cells are an important component of the immune system. Once activated, they differentiate into either short-lived effector cells or long-lived memory cells.
Researchers identify key differences in inner workings of immune cells retrieved 6 June 2024 from https://medicalxpress.com/news/2024-06-key-differences-immune-cells.html
This document is subject to copyright. Apart from any fair dealing for the purpose of private study or research, no part may be reproduced without the written permission. The content is provided for information purposes only.Doctors develop minimally invasive procedure to avoid drilling a 'burr hole' in the skull to treat clot on the brain1 hour agoUse this form if you have come across a typo, inaccuracy or would like to send an edit request for the content on this page.
Your feedback is important to us. However, we do not guarantee individual replies due to the high volume of messages.to let the recipient know who sent the email. Neither your address nor the recipient's address will be used for any other purpose. The information you enter will appear in your e-mail message and is not retained by Medical Xpress in any form.Get weekly and/or daily updates delivered to your inbox.
Medicine Research Health Research News Health Research Health Science Medicine Science
United Kingdom Latest News, United Kingdom Headlines
Similar News:You can also read news stories similar to this one that we have collected from other news sources.
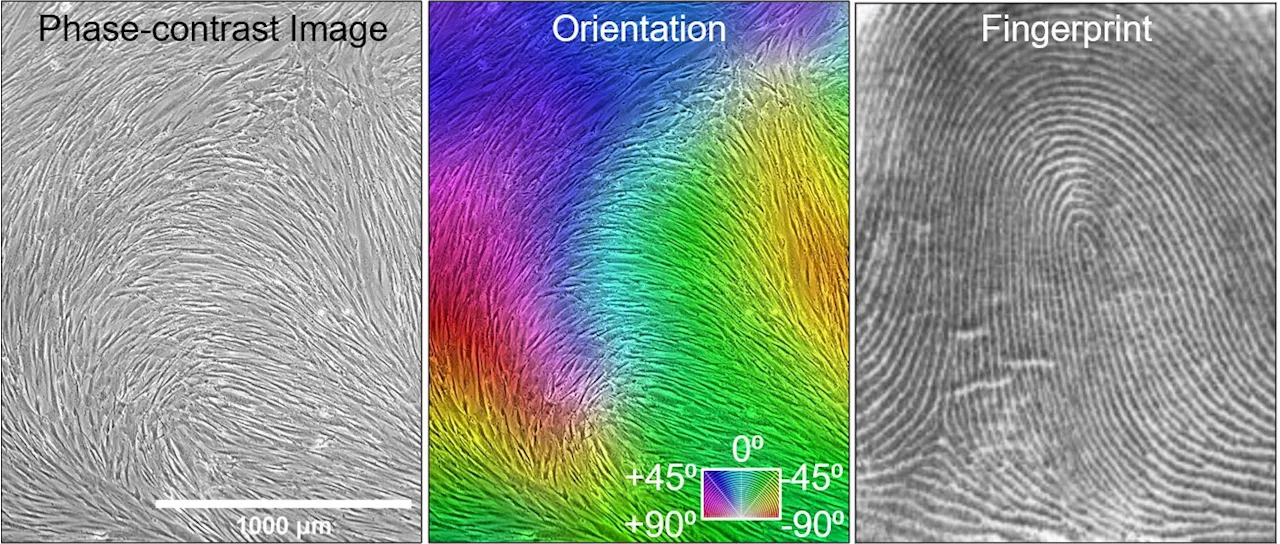 Researchers discover novel method to predict effectiveness of mesenchymal stromal cells for cartilage repairResearchers have discovered a more efficient method for evaluating the ability of mesenchymal stromal cells (MSCs) to regenerate cartilage. Their novel method is also the first to utilize topological defects in the self-assembly of MSCs to forecast their cartilage regeneration potential.
Researchers discover novel method to predict effectiveness of mesenchymal stromal cells for cartilage repairResearchers have discovered a more efficient method for evaluating the ability of mesenchymal stromal cells (MSCs) to regenerate cartilage. Their novel method is also the first to utilize topological defects in the self-assembly of MSCs to forecast their cartilage regeneration potential.
Read more »
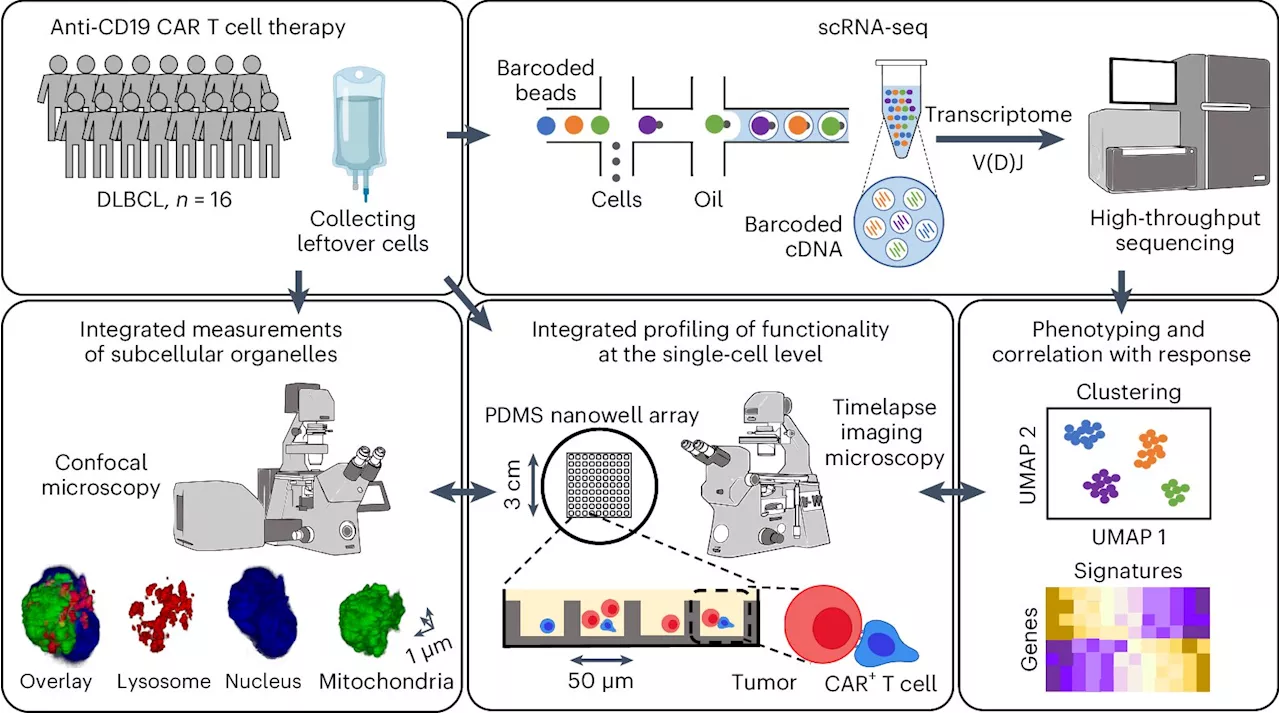 Cancer researchers discover optimal cancer-killing T cellsA team of cancer researchers, led by the University of Houston, has discovered a new subset of T cells that may improve the outcome for patients treated with T-cell therapies.
Cancer researchers discover optimal cancer-killing T cellsA team of cancer researchers, led by the University of Houston, has discovered a new subset of T cells that may improve the outcome for patients treated with T-cell therapies.
Read more »
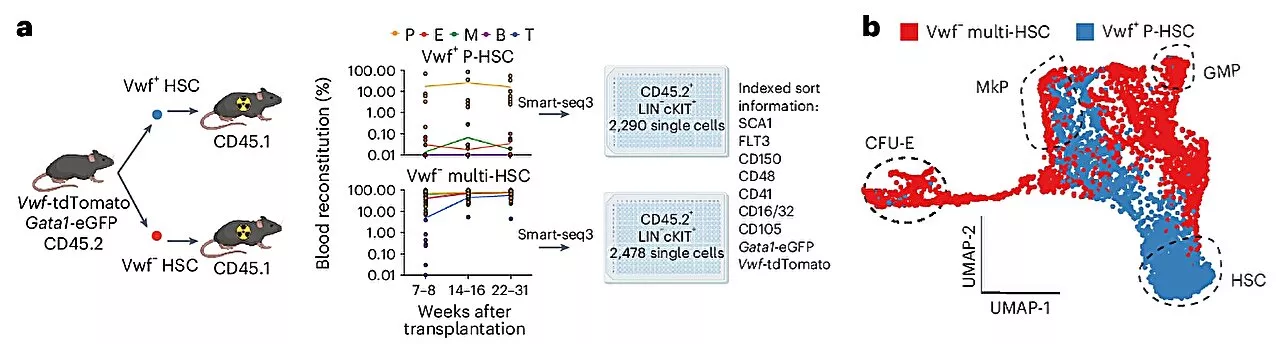 Q&A: Researchers determine that a subclass of stem cells replenish platelets more rapidlyTogether with researchers from University of Oxford, researchers at Karolinska Institutet have demonstrated that a subclass of stem cells that are dedicated to the production of platelets replenish those platelets through a distinct and shorter pathway than other stem cells.
Q&A: Researchers determine that a subclass of stem cells replenish platelets more rapidlyTogether with researchers from University of Oxford, researchers at Karolinska Institutet have demonstrated that a subclass of stem cells that are dedicated to the production of platelets replenish those platelets through a distinct and shorter pathway than other stem cells.
Read more »
Researchers reveal secrets of aging beta cells and their ability to secrete insulinA new study reveals that aging human pancreatic beta cells display features of senescence while maintaining elevated levels of genes crucial for their function. Despite their aging status, these cells therefore exhibit an ability to release insulin in response to glucose, aiding in blood sugar regulation.
Read more »
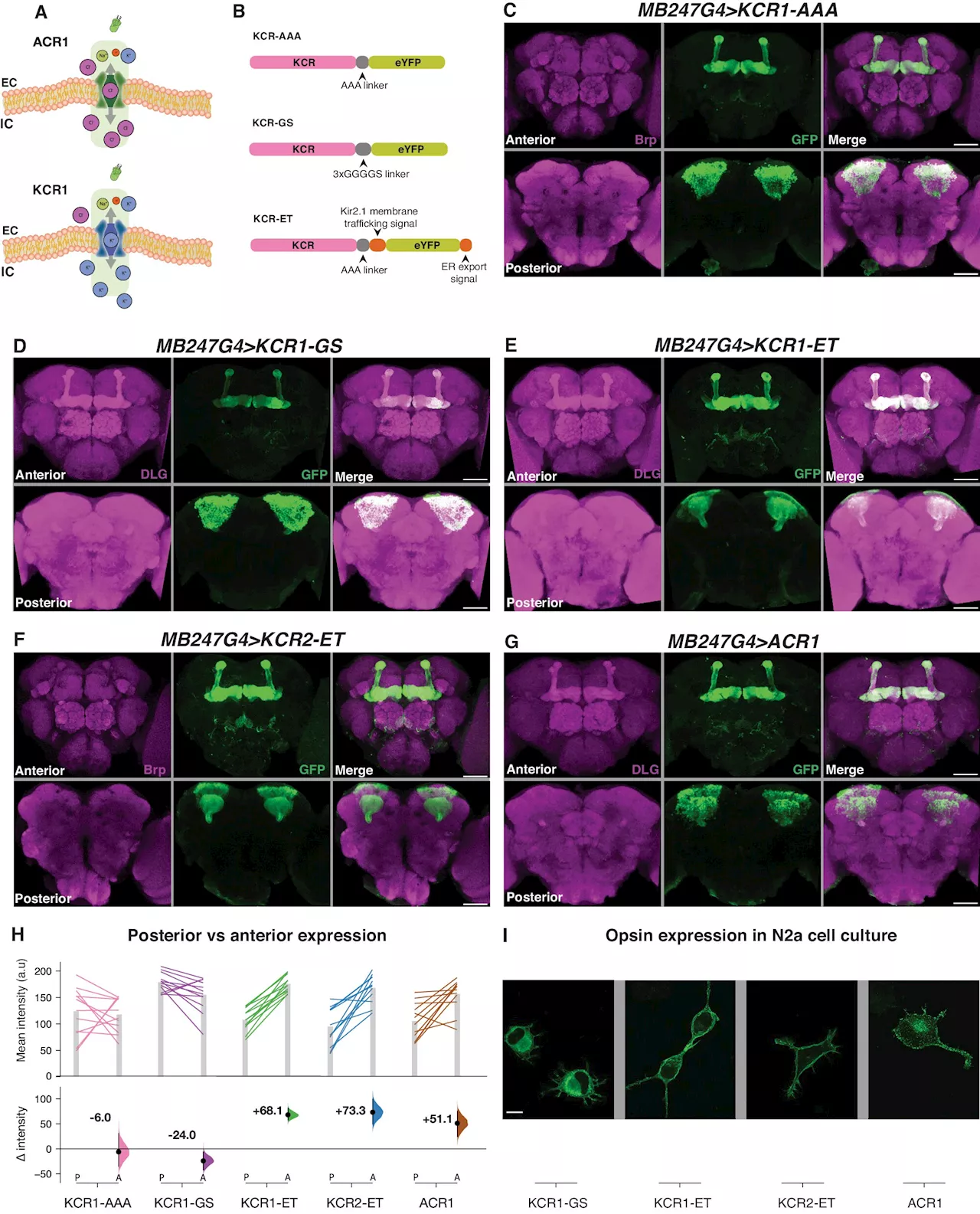 Researchers develop new light-controlled 'off switch' for brain cellsResearchers from Duke-NUS Medical School have found that a new class of light-sensitive proteins are capable of turning off brain cells with light, offering scientists an unprecedentedly effective tool to investigate brain function.
Researchers develop new light-controlled 'off switch' for brain cellsResearchers from Duke-NUS Medical School have found that a new class of light-sensitive proteins are capable of turning off brain cells with light, offering scientists an unprecedentedly effective tool to investigate brain function.
Read more »
 Researchers decipher how immune cells spot cancer's turbocharged metabolismWhen cells become tumor cells, their metabolism changes fundamentally. Researchers at the University of Basel and the University Hospital Basel have now demonstrated that this change leaves traces that could provide targets for cancer immunotherapies.
Researchers decipher how immune cells spot cancer's turbocharged metabolismWhen cells become tumor cells, their metabolism changes fundamentally. Researchers at the University of Basel and the University Hospital Basel have now demonstrated that this change leaves traces that could provide targets for cancer immunotherapies.
Read more »
