A team of US researchers have found that sleeping habits largely fit into four different categories, each carrying varying health risks.
Researchers identified four types of sleepers with varying disease risk. Insomniacs and nappers are at the highest risk of developing diseases. READ MORE:The way in which all Americans sleep can be divided into one of four categories, according to a major new study.
They were attempting to determine how people's sleep patterns changed as they aged, and how that might relate to developing chronic conditions. The final sleep category identified was nappers. These participants were pretty consistent nighttime sleepers, but reported taking frequent daytime naps. Nappers also had a 128 percent increased risk for diabetes, compared to good sleepers, and a 62 percent increased risk for frailty.Previous studies have found that getting too little sleep can increase the risk of developing dementia, having a stroke, heart attack and liver disease. One study found that about 83 percent of people with depression also have insomnia.
Another theory is that those who nap tend to have a higher BMI, and are therefore at higher risk of the condition, and another is that sleeping too much increases inflammation in the body.
United Kingdom Latest News, United Kingdom Headlines
Similar News:You can also read news stories similar to this one that we have collected from other news sources.
 Researchers identify the sleeping habit that could make you twice as likely to get diabetesA team of US researchers have found that sleeping habits largely fit into four different categories, each carrying varying health risks.
Researchers identify the sleeping habit that could make you twice as likely to get diabetesA team of US researchers have found that sleeping habits largely fit into four different categories, each carrying varying health risks.
Read more »
 New nasal spray may reduce severity of sleep apnea, researchers findAustralian researchers have discovered that a bedtime nasal spray has the potential to reduce the severity of sleep apnea in people and lower their blood pressure.
New nasal spray may reduce severity of sleep apnea, researchers findAustralian researchers have discovered that a bedtime nasal spray has the potential to reduce the severity of sleep apnea in people and lower their blood pressure.
Read more »
 Researchers forge new path to combat viruses and cancers with helicase inhibitorsHelicases are enzymes that unwind DNA and RNA. They're central to cellular life, implicated in a number of cancers and infections-;and, alas, extraordinarily difficult to target with drugs.
Researchers forge new path to combat viruses and cancers with helicase inhibitorsHelicases are enzymes that unwind DNA and RNA. They're central to cellular life, implicated in a number of cancers and infections-;and, alas, extraordinarily difficult to target with drugs.
Read more »
 Researchers develop precise drugs to target HIV's Nef proteinA team of University of Michigan researchers has successfully modified a naturally occurring chemical compound in the lab, resulting in advanced lead compounds with anti-HIV activity.
Researchers develop precise drugs to target HIV's Nef proteinA team of University of Michigan researchers has successfully modified a naturally occurring chemical compound in the lab, resulting in advanced lead compounds with anti-HIV activity.
Read more »
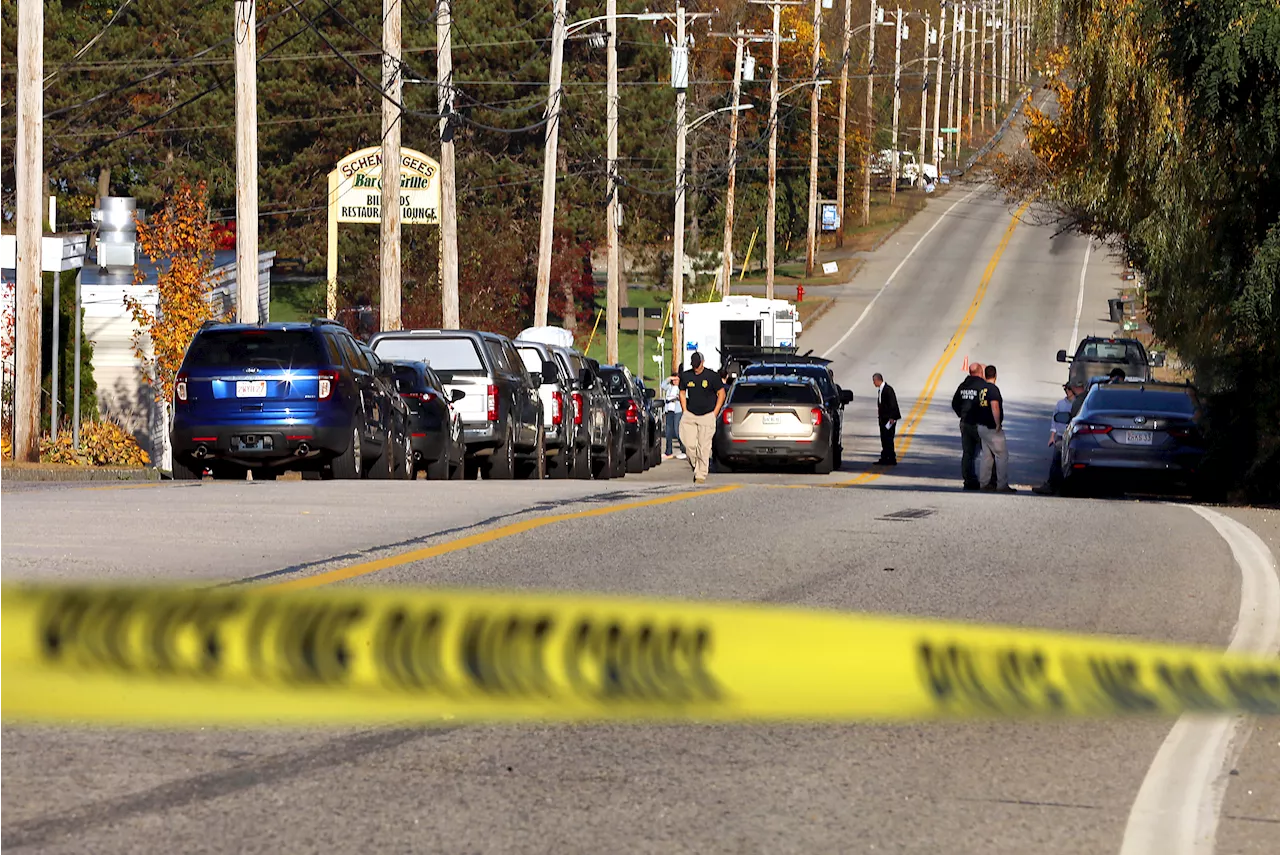 Brain of Lewiston gunman showed signs of traumatic injury, researchers sayThe brain of a gunman who killed 18 people and injured 13 others in Lewiston, Maine, showed signs of significant traumatic injury at the time of the mass…
Brain of Lewiston gunman showed signs of traumatic injury, researchers sayThe brain of a gunman who killed 18 people and injured 13 others in Lewiston, Maine, showed signs of significant traumatic injury at the time of the mass…
Read more »
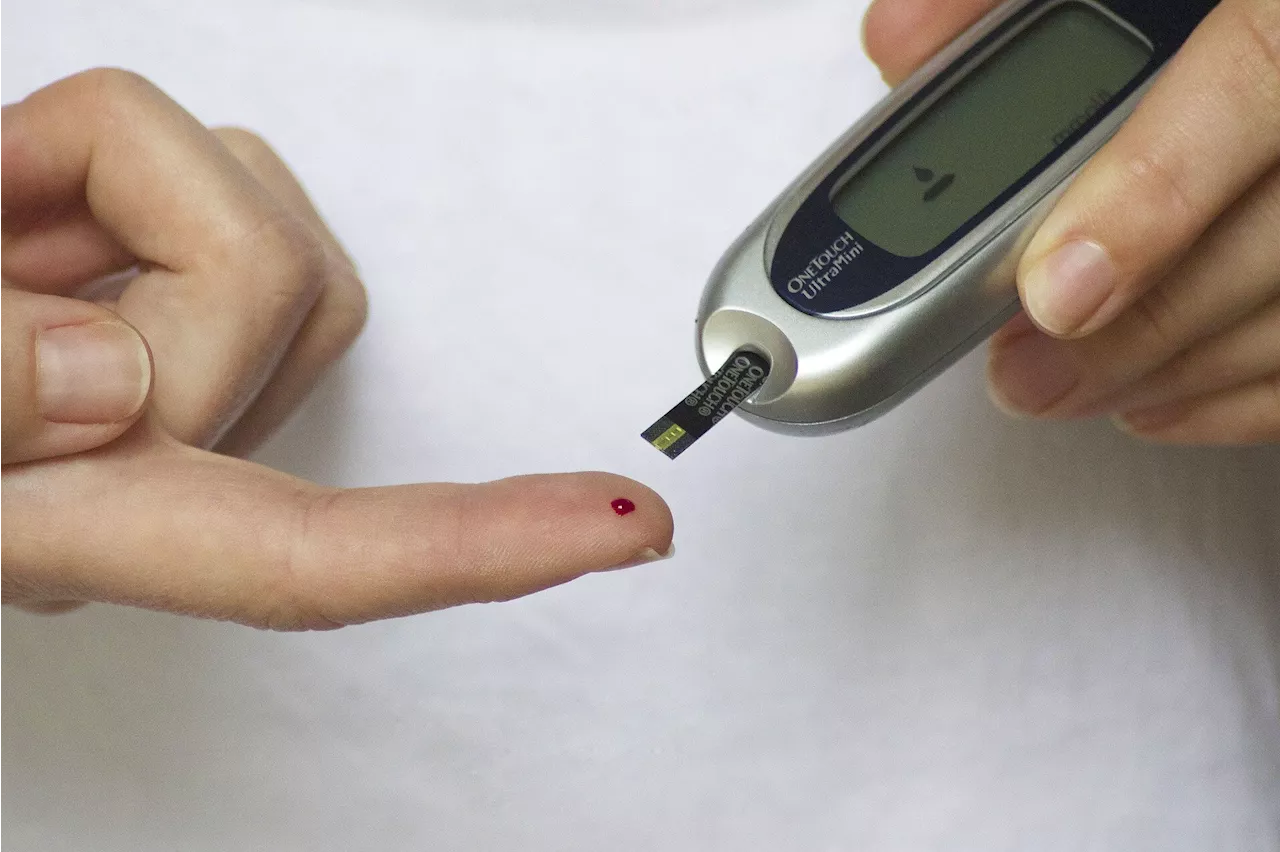 Many type 2 diabetes patients lack potentially lifesaving knowledge about their disease, researchers findThe body's inability to produce enough insulin or use it effectively often results in type 2 diabetes (T2D), a chronic disease affecting hundreds of millions of people around the globe. Disease management is crucial to avoid negative long-term outcomes, such as limb amputation or heart disease.
Many type 2 diabetes patients lack potentially lifesaving knowledge about their disease, researchers findThe body's inability to produce enough insulin or use it effectively often results in type 2 diabetes (T2D), a chronic disease affecting hundreds of millions of people around the globe. Disease management is crucial to avoid negative long-term outcomes, such as limb amputation or heart disease.
Read more »
