Researchers develop skyrmion-based microelectronic device for sustainable, high-performance AI computing with energy-efficient technology.
Researchers from the Agency for Space, Technology, and Research and the National University of Singapore have unveiled a remarkable microelectronic device. This device can function as a sustainable, high-performance “bit-switch”.
Imagine a little ball of magnetized material, but instead of the north and south poles pointing up and down like a regular magnet, they curl around in twisty circles on the surface of the ball. These are kind of what magnetic skyrmions are.AI and cloud computing uncover battery with 70% less lithium in record time technologies, such as ChatGPT has accelerated the need for sustainable computing solutions. These systems require vast amounts of data to be processed at lightning speeds.
This approach shifts data processing onto individual devices, alleviating strain on centralized data centers. However, the potential of edge computing is constrained by limited computing capacity and power constraints. The team identifies the need for innovative microelectronic platforms.At the heart of this research are skyrmions— minuscule magnetic whirls that exhibit remarkable stability and efficiency.
Remarkably, the team observed that switching between states in skyrmions takes 1,000 times less power than conventional commercial devices. They also found that more than two states could be achieved on a single device, implying enhanced performance without needing to scale the device down.
United Kingdom Latest News, United Kingdom Headlines
Similar News:You can also read news stories similar to this one that we have collected from other news sources.
 Men Forget About Female Researchers, Says Study On Gender Citation GapA gender bias expert, Kim Elsesser, Ph.D., is the author of Sex and the Office, and she taught classes on gender at UCLA for eight years. She is a senior contributor for Forbes and has published in the New York Times and Los Angeles Times.
Men Forget About Female Researchers, Says Study On Gender Citation GapA gender bias expert, Kim Elsesser, Ph.D., is the author of Sex and the Office, and she taught classes on gender at UCLA for eight years. She is a senior contributor for Forbes and has published in the New York Times and Los Angeles Times.
Read more »
 Automated method helps researchers quantify uncertainty in their predictionsA new technique can help researchers who use Bayesian inference achieve more accurate results more quickly, without a lot of additional work.
Automated method helps researchers quantify uncertainty in their predictionsA new technique can help researchers who use Bayesian inference achieve more accurate results more quickly, without a lot of additional work.
Read more »
 NASA and Google Earth team up with researchers to help save tigersAndrew Paul is Popular Science‘s staff writer covering tech news. Previously, he was a regular contributor to The A.V. Club and Input, and has had recent work featured by Rolling Stone, Fangoria, GQ, Slate, NBC, as well as McSweeney’s Internet Tendency. He lives outside Indianapolis.
NASA and Google Earth team up with researchers to help save tigersAndrew Paul is Popular Science‘s staff writer covering tech news. Previously, he was a regular contributor to The A.V. Club and Input, and has had recent work featured by Rolling Stone, Fangoria, GQ, Slate, NBC, as well as McSweeney’s Internet Tendency. He lives outside Indianapolis.
Read more »
 Researchers develop molecules for a new class of antibiotics that can overcome drug resistant bacteriaAbout a decade ago, researchers began to observe a recurring challenge in their research: Some of the compounds they were developing to harness energy from bacteria were instead killing the microbes. Not good if the objective of the project was to harness the metabolism of living bacteria to produce electricity.
Researchers develop molecules for a new class of antibiotics that can overcome drug resistant bacteriaAbout a decade ago, researchers began to observe a recurring challenge in their research: Some of the compounds they were developing to harness energy from bacteria were instead killing the microbes. Not good if the objective of the project was to harness the metabolism of living bacteria to produce electricity.
Read more »
 Researchers deploy supercomputer Hawk to feed on solar cell flawsScientists always try to make things to perfection. But imperfection will now help make solar cells more efficient.
Researchers deploy supercomputer Hawk to feed on solar cell flawsScientists always try to make things to perfection. But imperfection will now help make solar cells more efficient.
Read more »
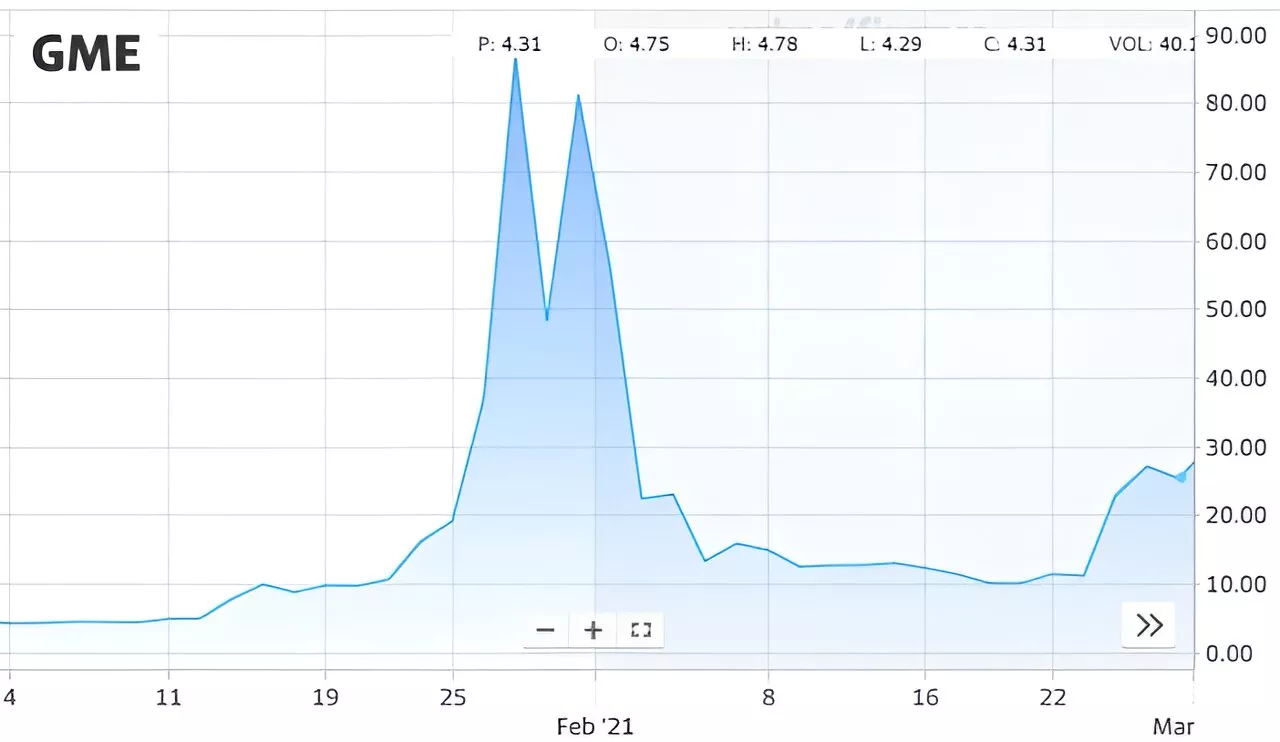 Researchers show Reddit users caused the famous GameStop 'short squeeze'Three years ago, the stock price of the company GameStop soared over 1,625% in just a week.
Researchers show Reddit users caused the famous GameStop 'short squeeze'Three years ago, the stock price of the company GameStop soared over 1,625% in just a week.
Read more »
