The researchers say 3D visualization of hurricanes and storm surges allows them to understand how flooding will impact coastal communities by allowing them to vividly see how each building and road might be impacted by a given flood.
Beginning annually on June 1, hurricane season poses a major threat to Texas coastal communities, causing both physical and financial damage to the areas they hit. This damage can be staggering; when Hurricane Harvey hit in 2017, it cost Galveston $132.73 billion in damages. Texas A&M University researchers have collaborated to understand the impacts of storm surge floods before they occur to potentially reduce the level of damage.
An advantage of 3D visualization over other damage modeling methods is that it allows researchers to model specific buildings, accounting for basements, back entrances, and windows. By identifying a residential building's first-floor elevation level, researchers can predict the physical and financial damage that a hurricane will cause to the specific building.
"Having used Galveston as an example, the next step would be to expand that to other coastal communities in Texas," Ye noted."In this study, we mainly used residential houses, but we can expand it to other business properties as well." Duffield adds that this project shows how the work at the intersection between geospatial data science and visualization can raise awareness for individuals, communities and government on the consequences of extreme weather and make informed planning decisions for responses.
Floods Hurricanes And Cyclones Weather Disaster Plan Urbanization STEM Education Ocean Policy
United Kingdom Latest News, United Kingdom Headlines
Similar News:You can also read news stories similar to this one that we have collected from other news sources.
 Researchers develop technology that may allow stroke patients to undergo rehab at homeFor survivors of strokes, regaining fine motor skills is critical for recovering independence and quality of life. But getting intensive, frequent rehabilitation therapy can be challenging and expensive.
Researchers develop technology that may allow stroke patients to undergo rehab at homeFor survivors of strokes, regaining fine motor skills is critical for recovering independence and quality of life. But getting intensive, frequent rehabilitation therapy can be challenging and expensive.
Read more »
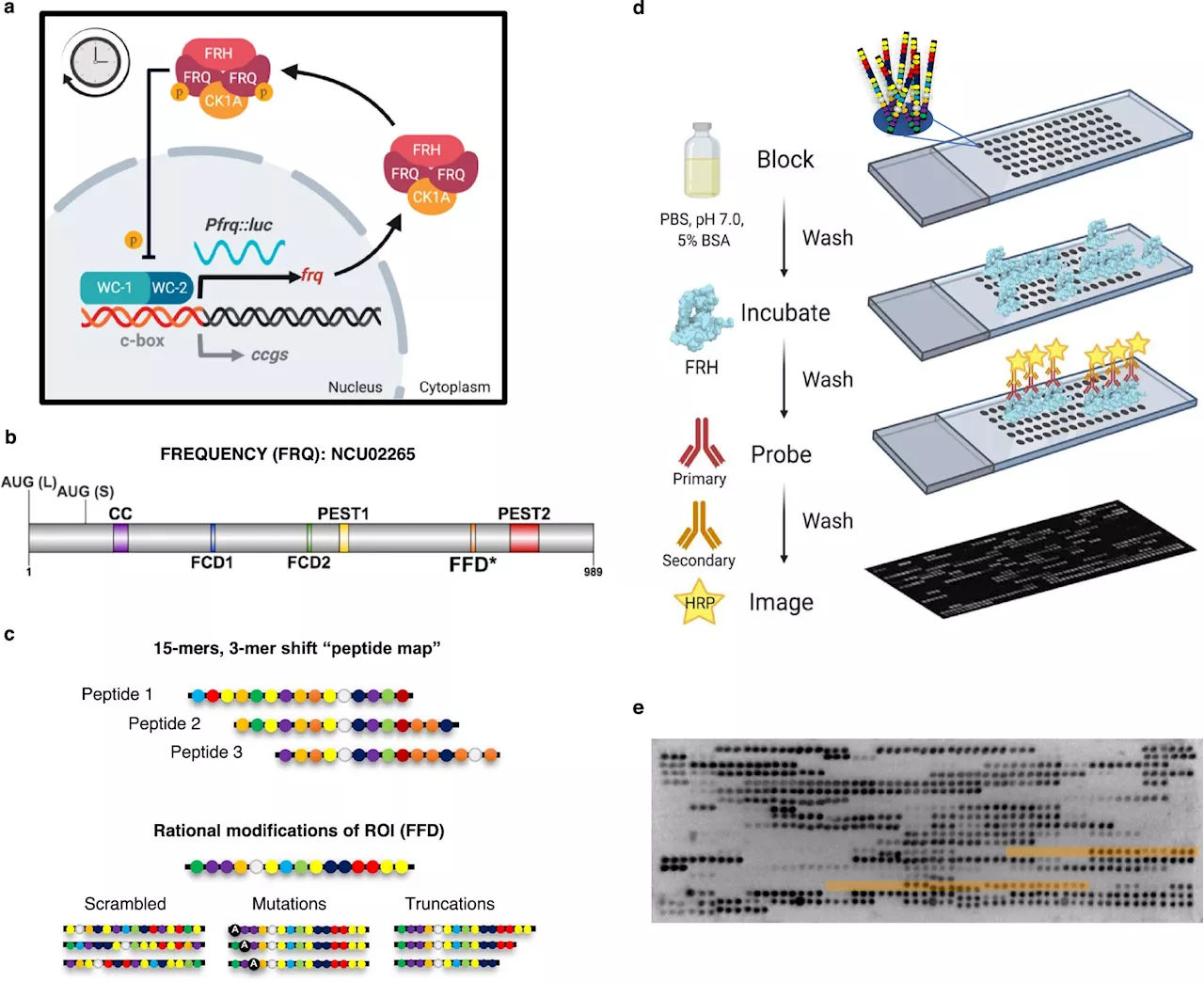 Researchers discover disordered clock protein that sheds new light on circadian rhythmsCircadian clocks, which drive circadian rhythms, are entwined with many essential systems in living things including plants, fungi, insects, and even humans. Because of this, disruptions to our circadian clocks are linked to higher disease rates in humans, including certain cancers and autoimmune diseases.
Researchers discover disordered clock protein that sheds new light on circadian rhythmsCircadian clocks, which drive circadian rhythms, are entwined with many essential systems in living things including plants, fungi, insects, and even humans. Because of this, disruptions to our circadian clocks are linked to higher disease rates in humans, including certain cancers and autoimmune diseases.
Read more »
 New method for safe and efficient cell transfection developed by researchersTransfection is the process of deliberately introducing nucleic acids into cells. Cell transfection is crucial in the fields of T cell and stem cell therapy. However, the existing transfection technology still faces challenges in achieving high efficiency and maintaining optimal cell viability.
New method for safe and efficient cell transfection developed by researchersTransfection is the process of deliberately introducing nucleic acids into cells. Cell transfection is crucial in the fields of T cell and stem cell therapy. However, the existing transfection technology still faces challenges in achieving high efficiency and maintaining optimal cell viability.
Read more »
 2 Common Dietary Habits Are Causing Colon Cancer in Young People, Researchers SayDigital destination for sophisticated men & women. Live your best life with expert tips and news on health, food, sex, relationships, fashion and lifestyle.
2 Common Dietary Habits Are Causing Colon Cancer in Young People, Researchers SayDigital destination for sophisticated men & women. Live your best life with expert tips and news on health, food, sex, relationships, fashion and lifestyle.
Read more »
 Researchers use tin to toughen bioimplant titanium alloys through the cocktail effectBeta(β)-type titanium (Ti) alloys are renowned for their strength, formability and resistance to harsh environments. This, along with their excellent biocompatibility, has made them adequately suited for implants and prosthetics, from joint replacement to stents.
Researchers use tin to toughen bioimplant titanium alloys through the cocktail effectBeta(β)-type titanium (Ti) alloys are renowned for their strength, formability and resistance to harsh environments. This, along with their excellent biocompatibility, has made them adequately suited for implants and prosthetics, from joint replacement to stents.
Read more »
 Human activity contributed to woolly rhinoceros' extinction, suggest researchersResearchers have discovered sustained hunting by humans prevented the woolly rhinoceros from accessing favorable habitats as Earth warmed following the Last Ice Age.
Human activity contributed to woolly rhinoceros' extinction, suggest researchersResearchers have discovered sustained hunting by humans prevented the woolly rhinoceros from accessing favorable habitats as Earth warmed following the Last Ice Age.
Read more »
