Supplementation with resistant starch leads to weight loss and improved insulin sensitivity by altering the gut microbiome and increasing secondary bile acids, according to a recent study in Nature Metabolism.
By Dr. Chinta SidharthanFeb 27 2024Reviewed by Susha Cheriyedath, M.Sc. In a recent study published in the journal Nature Metabolism, a team of scientists investigated whether modulation of the gut microbiome using dietary fiber supplementation in the form of resistant starch could help with insulin resistance and weight loss and offer a potential treatment avenue for metabolic disorders.
Increasing evidence indicates that the gut microbiome plays a pivotal role in the regulation of human physiology and development of various diseases. Gut microbiome composition and diversity are intricately linked to the metabolism of glucose and fat and inflammation. Furthermore, they studied antibiotic-treated mice that had received gut microbiomes from human donors that had already been modified through resistant starch supplementation to understand how gut microbiomes modified through supplementation with resistant starch influence glucose metabolism and adiposity. The metabolomic advantages offered by the gut microbiome modified through resistant starch supplements were also explored.
The starch was provided in sachets in powdered form, and all the participants in the treatment and control groups consumed one packet of the appropriate starch twice a day before a balanced, isoenergetic meal that was provided thrice a day. Since this was a crossover clinical trial, all the participants underwent two eight-week-long interventions, one for the resistant starch treatment and the other for the control treatment.
The gut microbiota impacts the host physiology through signaling metabolites, of which bile acids play a significant role. Secondary bile acids, such as glycodesoxycholic acid, deoxycholic acid, glycocholic acid, and taurodeoxycholic acid, are important in improving insulin sensitivity and ameliorating hepatic steatosis. The enzyme bile salt hydrolase carries out the deconjugation of secondary bile acids.
United Kingdom Latest News, United Kingdom Headlines
Similar News:You can also read news stories similar to this one that we have collected from other news sources.
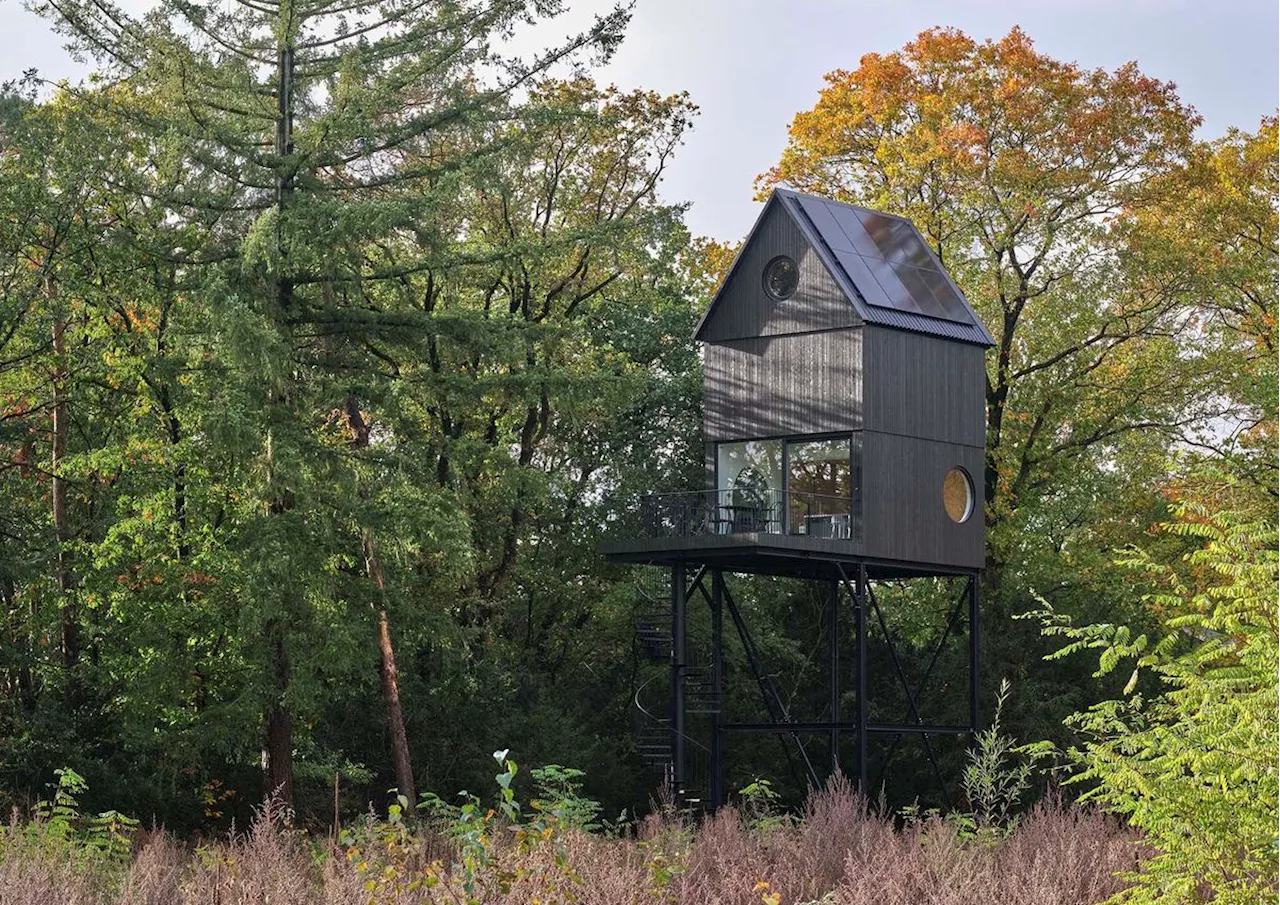 A nest house in the Netherlands immerses residents in natureEllie Stathaki is the Architecture Editor at Wallpaper*. She trained as an architect at the Aristotle University of Thessaloniki in Greece and studied architectural history at the Bartlett in London.
A nest house in the Netherlands immerses residents in natureEllie Stathaki is the Architecture Editor at Wallpaper*. She trained as an architect at the Aristotle University of Thessaloniki in Greece and studied architectural history at the Bartlett in London.
Read more »
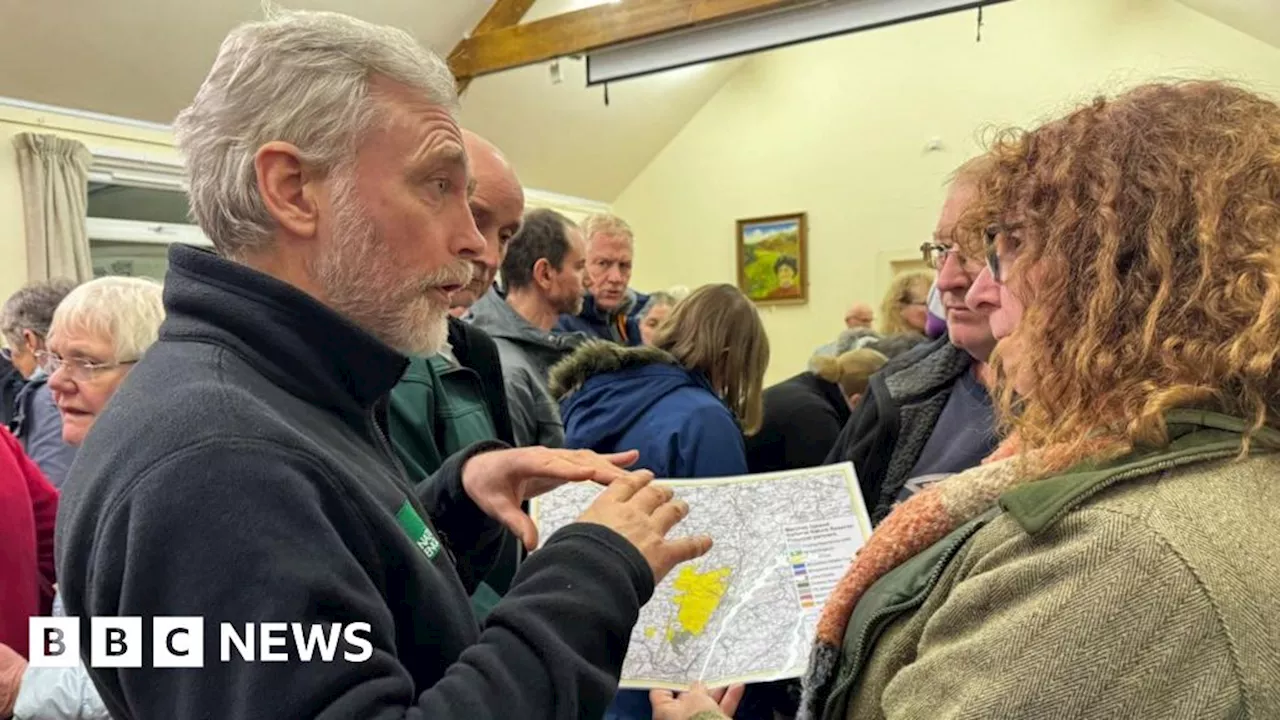
 £2m grant boosts plans for new nature reserve in SuffolkThe Suffolk Wildlife Trust has received a £2m grant from the National Lottery Heritage Fund to establish Worlingham Marshes as a new nature reserve. The 381-acre site in Suffolk will become a 'corridor of wildlife' and provide a haven for birds and other wildlife. The trust aims to reverse wildlife decline and support nature to adapt to climate change. This grant will help protect more of the beautiful Waveney Valley and allow more space for nature to thrive.
£2m grant boosts plans for new nature reserve in SuffolkThe Suffolk Wildlife Trust has received a £2m grant from the National Lottery Heritage Fund to establish Worlingham Marshes as a new nature reserve. The 381-acre site in Suffolk will become a 'corridor of wildlife' and provide a haven for birds and other wildlife. The trust aims to reverse wildlife decline and support nature to adapt to climate change. This grant will help protect more of the beautiful Waveney Valley and allow more space for nature to thrive.
Read more »
 Stiperstones: Mixed views on plan for super nature reservePeople living in the area have mixed views over how the scheme might impact their lives.
Stiperstones: Mixed views on plan for super nature reservePeople living in the area have mixed views over how the scheme might impact their lives.
Read more »
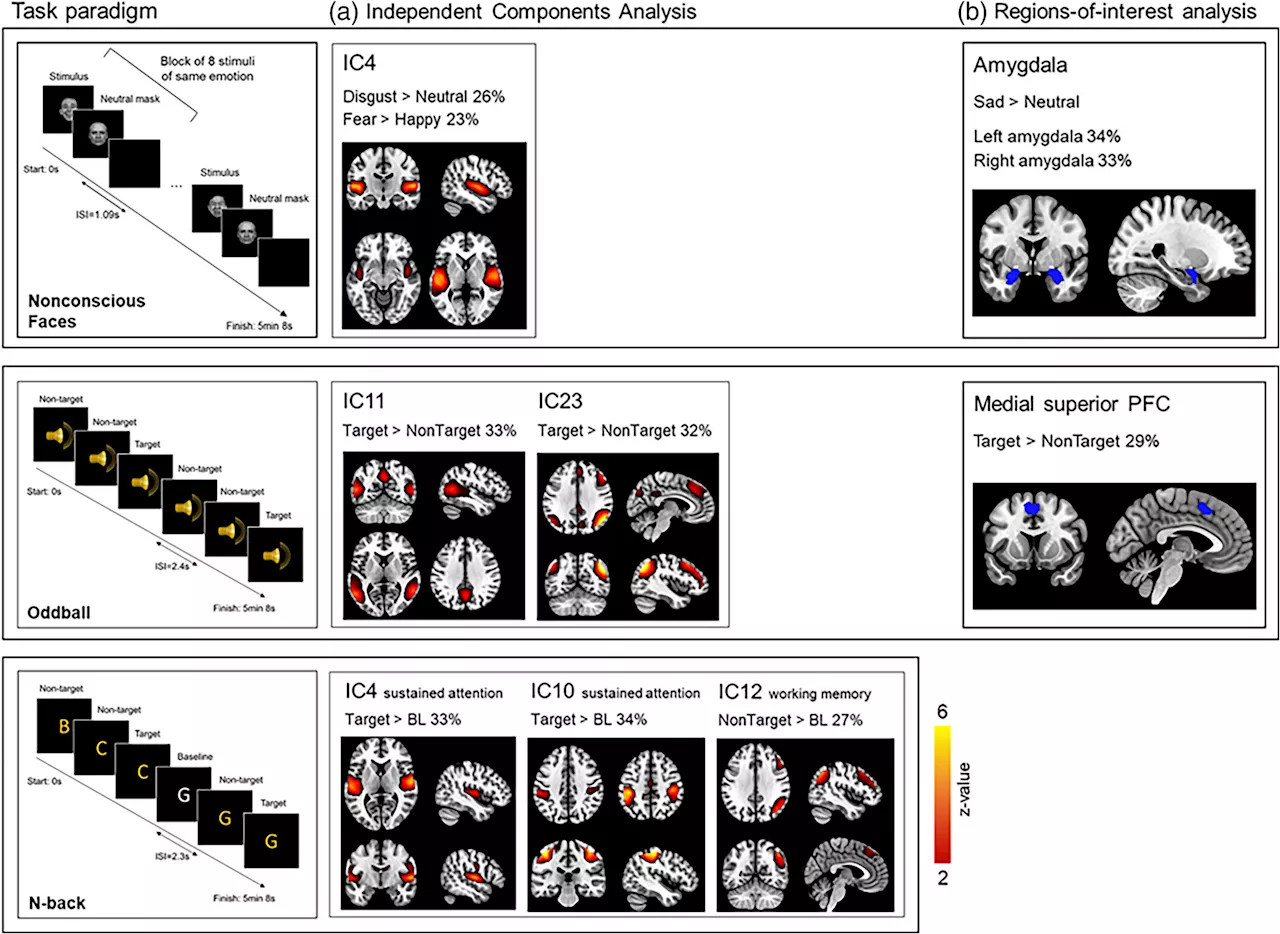 Nature vs nurture: Twin study sheds light on heritable brain activityThe way our brain processes different emotional and cognitive tasks may be underpinned by common factors, find scientists from UNSW and Neuroscience Research Australia (NeuRA).
Nature vs nurture: Twin study sheds light on heritable brain activityThe way our brain processes different emotional and cognitive tasks may be underpinned by common factors, find scientists from UNSW and Neuroscience Research Australia (NeuRA).
Read more »
 Bishop’s Castle nature projects receive £238k from National Lottery Heritage FundGoing Wild in Bishop’s Castle is celebrating an award of £238k from The National Lottery Heritage Fund to hire staff as coordinators to support the community to develop and implement local wildlife and nature projects.
Bishop’s Castle nature projects receive £238k from National Lottery Heritage FundGoing Wild in Bishop’s Castle is celebrating an award of £238k from The National Lottery Heritage Fund to hire staff as coordinators to support the community to develop and implement local wildlife and nature projects.
Read more »
 Telescope House is a viewing platform to enjoy seclusion and Arizona natureEllie Stathaki is the Architecture Editor at Wallpaper*. She trained as an architect at the Aristotle University of Thessaloniki in Greece and studied architectural history at the Bartlett in London.
Telescope House is a viewing platform to enjoy seclusion and Arizona natureEllie Stathaki is the Architecture Editor at Wallpaper*. She trained as an architect at the Aristotle University of Thessaloniki in Greece and studied architectural history at the Bartlett in London.
Read more »
