SARS-CoV-2, the virus responsible for COVID-19, is widespread among wildlife species, according to Virginia Tech research published Monday (July 29, 2024) in Nature Communications.
Virginia TechJul 29 2024 SARS -CoV-2, the virus responsible for COVID-19, is widespread among wildlife species, according to Virginia Tech research published Monday in Nature Communications. The virus was detected in six common backyard species, and antibodies indicating prior exposure to the virus were found in five species, with rates of exposure ranging from 40 to 60 percent depending on the species.
The findings highlight the identification of novel mutations in SARS-CoV-2 in wildlife and the need for broad surveillance, researchers say. These mutations could be more harmful and transmissible, creating challenges for vaccine development. "The virus can jump from humans to wildlife when we are in contact with them, like a hitchhiker switching rides to a new, more suitable host," said Carla Finkielstein, professor of biological sciences at the Fralin Biomedical Research Institute at VTC and one of the paper's corresponding authors. "The goal of the virus is to spread in order to survive. The virus aims to infect more humans, but vaccinations protect many humans.
Joseph Hoyt, assistant professor of Biological Sciences in Virginia Tech's College of Science and corresponding author on the paper Researchers are not certain about the means of transmission from humans to animals. One possibility is wastewater, but the Virginia Tech scientists believe trash receptacles and discarded food are more likely sources.
"The virus is indifferent to whether its host walks on two legs or four. Its primary objective is survival. Mutations that do not confer a survival or replication advantage to the virus will not persist and will eventually disappear," said Finkielstein, who is also director of the Virginia Tech Molecular Diagnostics Lab. The Roanoke lab was established in April 2020 to expand COVID-19 testing.
Virus Antibodies Genetic Immune Response Research SARS SARS-Cov-2
United Kingdom Latest News, United Kingdom Headlines
Similar News:You can also read news stories similar to this one that we have collected from other news sources.
 Exploring PRM-A as a novel glycan-targeted therapy for SARS-CoV-2 inhibitionHIV, Ebola and most recently, COVID-19 viruses have had an enormous impact on our societies world-wide.
Exploring PRM-A as a novel glycan-targeted therapy for SARS-CoV-2 inhibitionHIV, Ebola and most recently, COVID-19 viruses have had an enormous impact on our societies world-wide.
Read more »
 How does SARS-CoV-2 cause lymphopenia when T cells barely express ACE-2 receptors?Researchers reveal both direct and indirect mechanisms of SARS-CoV-2-induced lymphopenia, highlighting the role of CD147 and alternative viral entry routes into T cells.
How does SARS-CoV-2 cause lymphopenia when T cells barely express ACE-2 receptors?Researchers reveal both direct and indirect mechanisms of SARS-CoV-2-induced lymphopenia, highlighting the role of CD147 and alternative viral entry routes into T cells.
Read more »
 Preclinical data suggest antioxidant strategy to address mitochondrial dysfunction caused by SARS-CoV-2 virusBuilding upon groundbreaking research demonstrating how the SARS-CoV-2 virus disrupts mitochondrial function in multiple organs, researchers from Children's Hospital of Philadelphia (CHOP) demonstrated that mitochondrially-targeted antioxidants could reduce the effects of the virus while avoiding viral gene mutation resistance, a strategy that may...
Preclinical data suggest antioxidant strategy to address mitochondrial dysfunction caused by SARS-CoV-2 virusBuilding upon groundbreaking research demonstrating how the SARS-CoV-2 virus disrupts mitochondrial function in multiple organs, researchers from Children's Hospital of Philadelphia (CHOP) demonstrated that mitochondrially-targeted antioxidants could reduce the effects of the virus while avoiding viral gene mutation resistance, a strategy that may...
Read more »
 Study finds hospital-onset SARS-CoV-2 infection during omicron linked to morbidityDuring the omicron era, hospital-onset severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) infection remained associated with increased morbidity and mortality, according to a study published online July 16 in the Annals of Internal Medicine.
Study finds hospital-onset SARS-CoV-2 infection during omicron linked to morbidityDuring the omicron era, hospital-onset severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) infection remained associated with increased morbidity and mortality, according to a study published online July 16 in the Annals of Internal Medicine.
Read more »
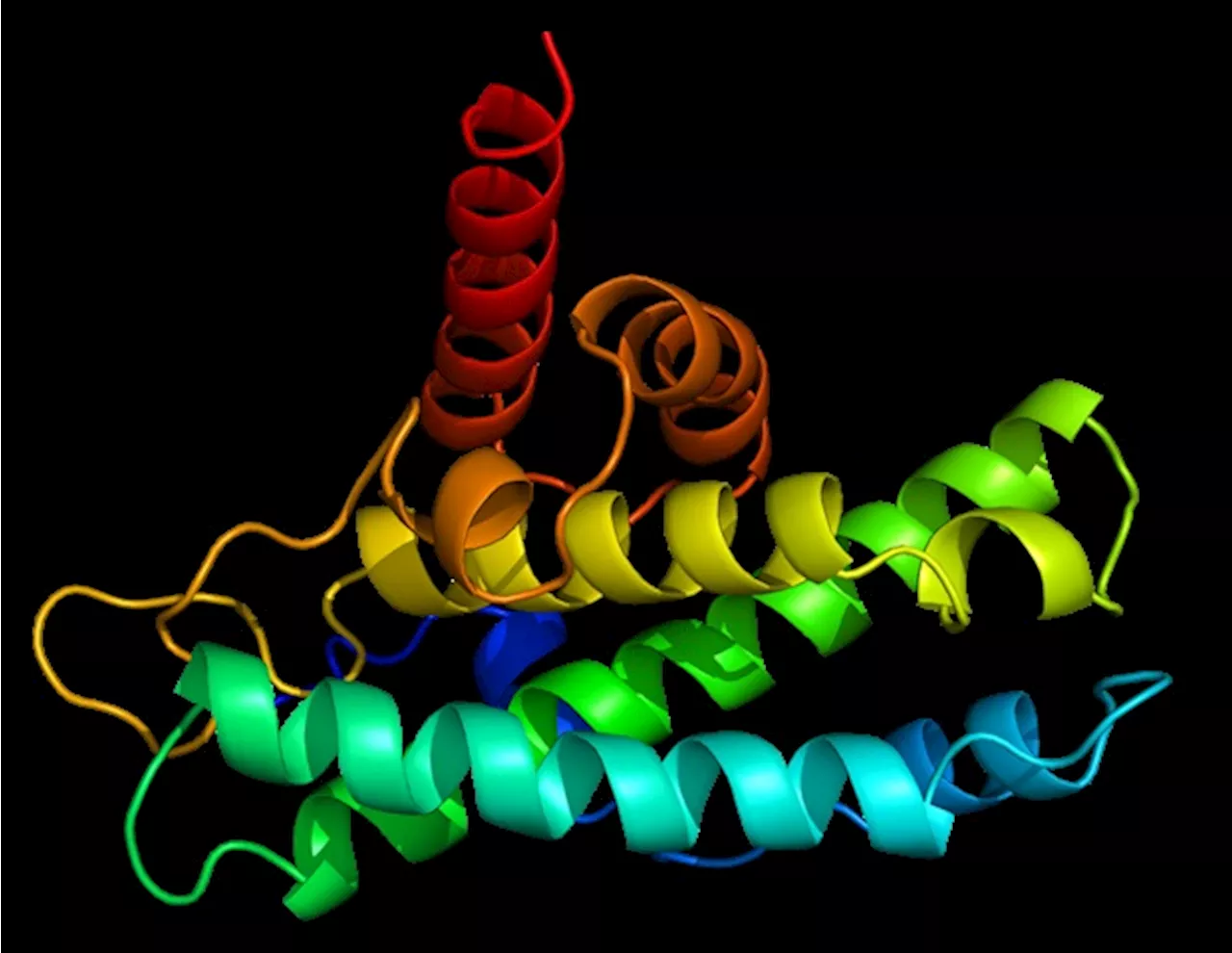 Researchers identify ORF6 protein as key to SARS-CoV-2 immune evasionAn article published in the journal Cell describes a study that enabled a group of researchers to discover how SARS-CoV-2 evades the cytotoxic immune response by identifying a protein called ORF6 that is a key factor in this mechanism.
Researchers identify ORF6 protein as key to SARS-CoV-2 immune evasionAn article published in the journal Cell describes a study that enabled a group of researchers to discover how SARS-CoV-2 evades the cytotoxic immune response by identifying a protein called ORF6 that is a key factor in this mechanism.
Read more »
 Research shows spike gene mutations do not correlate with increased SARS-CoV-2 variant severityNew research from UNC Charlotte's Center for Computational Intelligence to Predict Health and Environmental Risks (CIPHER) has found that the two recent and prevalent strains of the virus that cause COVID-19, SARS-CoV-2 variants BA.2.86 and JN.
Research shows spike gene mutations do not correlate with increased SARS-CoV-2 variant severityNew research from UNC Charlotte's Center for Computational Intelligence to Predict Health and Environmental Risks (CIPHER) has found that the two recent and prevalent strains of the virus that cause COVID-19, SARS-CoV-2 variants BA.2.86 and JN.
Read more »
