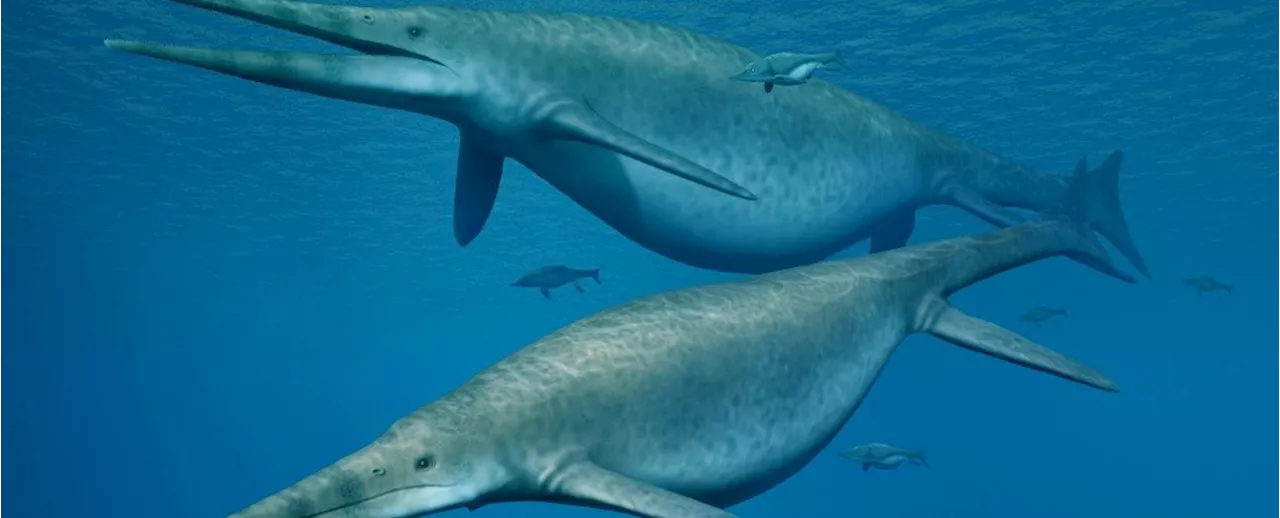
Scientists in Germany have discovered a way to identify the origin of mysterious fossilized bones, concluding that they belong to air-breathing, marine reptiles known as ichthyosaurs. By analyzing the microstructure of tissue in the fossilized jawbone, researchers were able to determine the animal group to which the bones belonged. This finding sheds light on the existence of these ancient giants and their size, ranging from a few feet to as long as a bus.
Mysterious fragments of fossilized bone proposed to be from a creature approaching the size of a blue whale could technically have been left by any one of a number of long-extinct giants.
Peering through a special microscope, paleontologists Marcello Perillo and Martin Sander, from the University of Bonn in Germany, have figured out a way to tell the difference. The microstructure of tissue in the fossilized jawbone, they say, is a dead giveaway."Osteohistology – the analysis of bone tissue – can thus be used to draw conclusions about the animal group from which the find originates.
Along with confirmed ichthyosaur bones, these 'mystery' jaws all showed long strands of fibrous collagen that were woven in a unique, shared pattern. This suggests they come from the same animal group.
Fossilized Bones Marine Reptiles Ichthyosaurs Microstructure Analysis Paleontology
United Kingdom Latest News, United Kingdom Headlines
Similar News:You can also read news stories similar to this one that we have collected from other news sources.
 Scientists discover fossilized remnants of earliest known forest“This was a pretty weird forest,” a Cambridge University researcher said of the 390-million-year-old fossils.
Scientists discover fossilized remnants of earliest known forest“This was a pretty weird forest,” a Cambridge University researcher said of the 390-million-year-old fossils.
Read more »
 Scientists Identify Speech Trait That Foreshadows Cognitive DeclineThe Best in Science News and Amazing Breakthroughs
Scientists Identify Speech Trait That Foreshadows Cognitive DeclineThe Best in Science News and Amazing Breakthroughs
Read more »
 Johns Hopkins Scientists Identify New Function of Learning Gene Common to All Mammalian Brain CellsScience, Space and Technology News 2024
Johns Hopkins Scientists Identify New Function of Learning Gene Common to All Mammalian Brain CellsScience, Space and Technology News 2024
Read more »
 Scientists Identify the Three Main Risk Factors for Brain AgingThe research opens the door to potential prevention strategies for dementia and other neurodegenerative diseases.
Scientists Identify the Three Main Risk Factors for Brain AgingThe research opens the door to potential prevention strategies for dementia and other neurodegenerative diseases.
Read more »
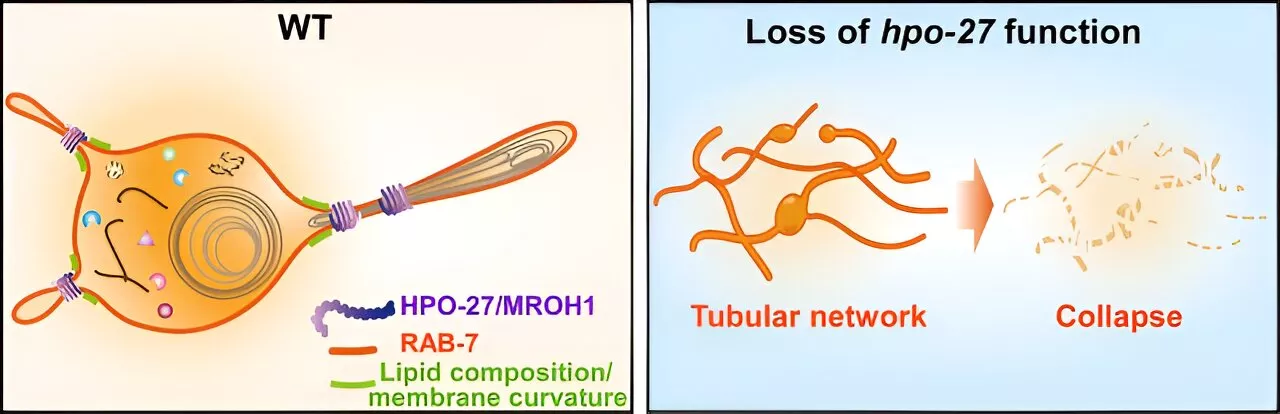 Scientists identify novel lysosome fission factorLysosomes are centers for degradation, recycling, and signaling of cellular materials that are crucial for maintaining cellular homeostasis, development, and aging. To meet various physiological demands, lysosomes continuously remodel their shape and function through fusion and fission processes.
Scientists identify novel lysosome fission factorLysosomes are centers for degradation, recycling, and signaling of cellular materials that are crucial for maintaining cellular homeostasis, development, and aging. To meet various physiological demands, lysosomes continuously remodel their shape and function through fusion and fission processes.
Read more »
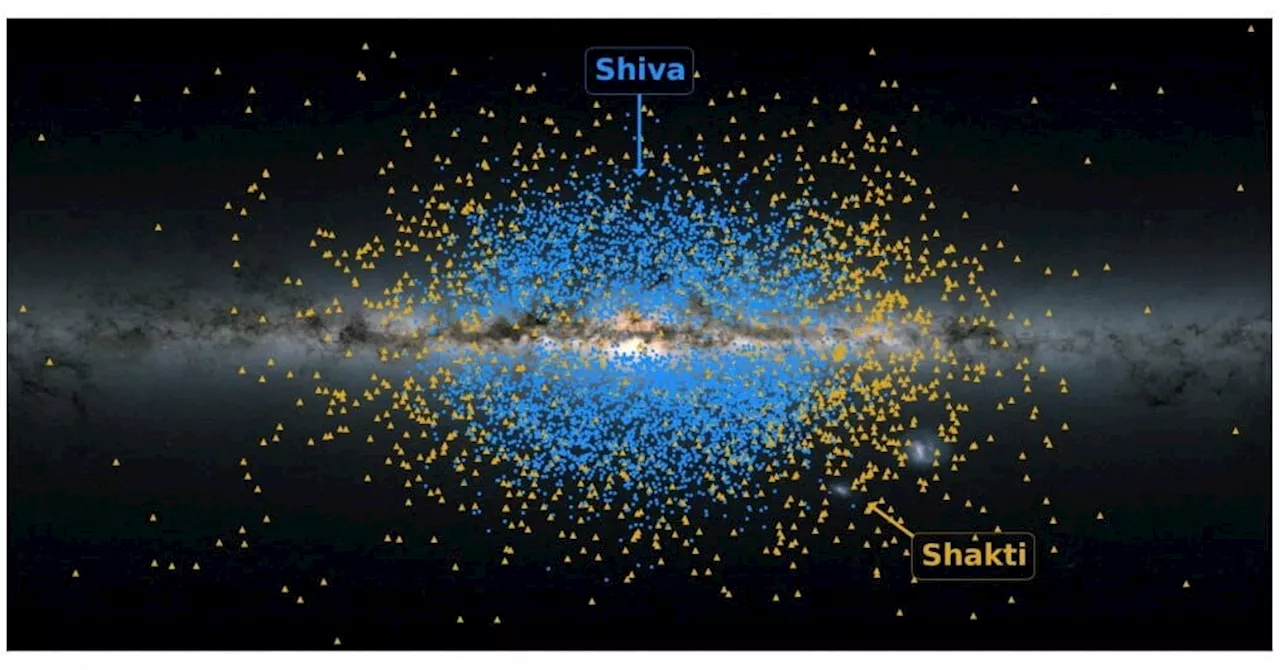 Scientists identify Milky Way's ancient building blocks Shakti and ShivaAstronomers have identified two ancient streams of stars - named after the Hindu deities Shakti and Shiva - that appear to be among the Milky Way's earliest building blocks, offering new insight into how our galaxy came together long ago.
Scientists identify Milky Way's ancient building blocks Shakti and ShivaAstronomers have identified two ancient streams of stars - named after the Hindu deities Shakti and Shiva - that appear to be among the Milky Way's earliest building blocks, offering new insight into how our galaxy came together long ago.
Read more »
