Science, Space and Technology News 2024
Researchers have seen how cells move and attach to each other during the early development of a quail embryo. Credit: University of Queensland
Dr. Melanie White and Dr. Yanina Alvarez from UQ’s Institute for Molecular Bioscience used quail eggs to understand how cells begin to form tissues such as the heart, brain, and spinal cord. “Until now, most of our knowledge of post-implantation development came from studies on static slides, at fixed points in time.”The IMB researchers have generated quails with a fluorescent protein to reveal the structure, called the actin cytoskeleton, which gives cells shape and facilitates movement.
The researchers also imaged the open edges of the neural tube and it being ‘zipped up’ to begin to form the brain and spinal cord.
United Kingdom Latest News, United Kingdom Headlines
Similar News:You can also read news stories similar to this one that we have collected from other news sources.
 Scientists spot hidden companions of bright starsPhotographing faint objects close to bright stars is incredibly difficult. Yet, by combining data from ESA's Gaia space telescope with ESO's GRAVITY instrument on the ground, scientists managed just that. They took the first pictures of so far unseen dim companions of eight luminous stars.
Scientists spot hidden companions of bright starsPhotographing faint objects close to bright stars is incredibly difficult. Yet, by combining data from ESA's Gaia space telescope with ESO's GRAVITY instrument on the ground, scientists managed just that. They took the first pictures of so far unseen dim companions of eight luminous stars.
Read more »
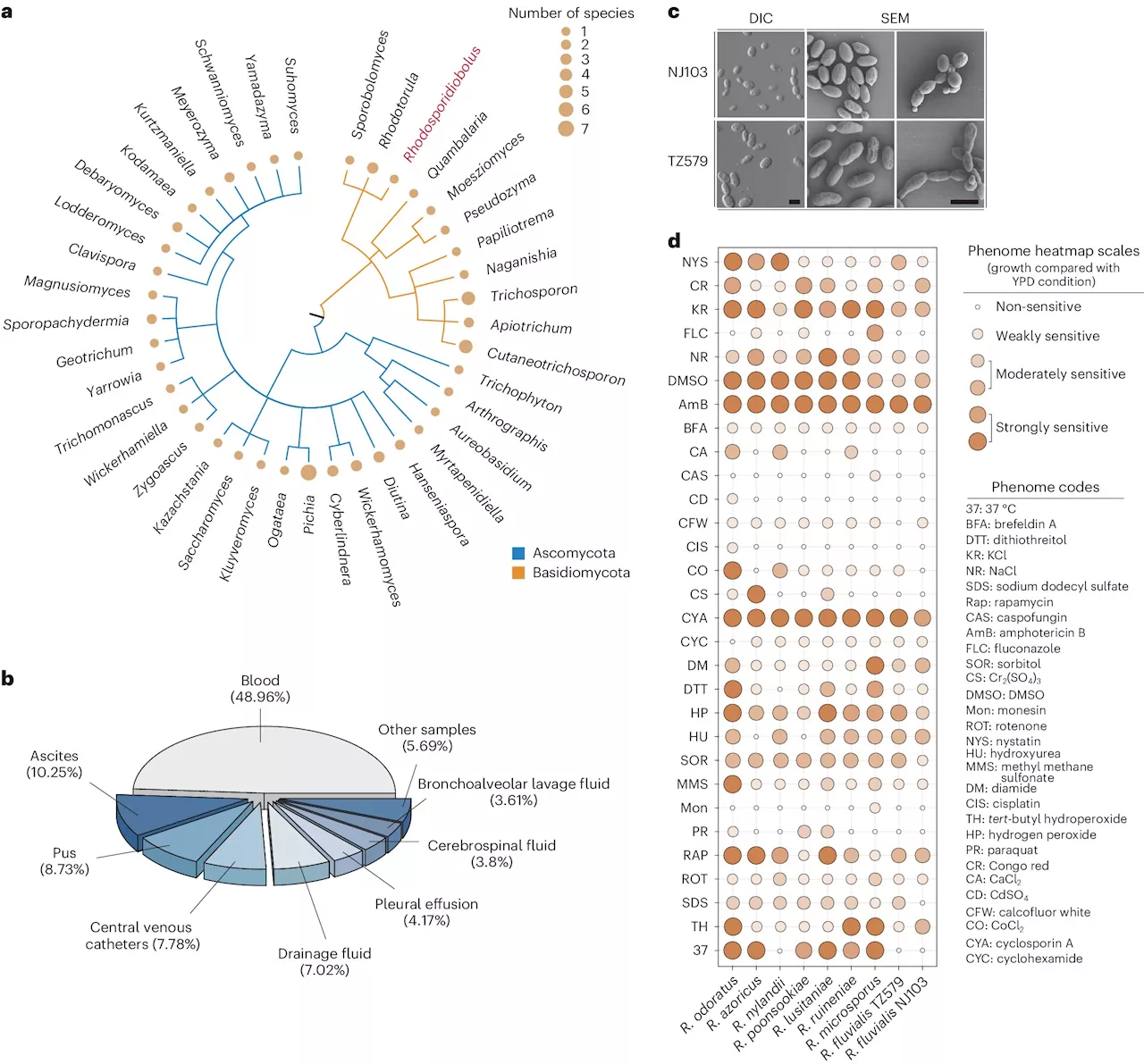 Scientists find further evidence that climate change could make fungi more dangerousA team of medical researchers and infectious disease specialists affiliated with multiple institutions in China, working with a pair of colleagues, one from Singapore, the other from Canada, has found evidence bolstering theories that suggest as the planet warms, fungi could become more dangerous to humans.
Scientists find further evidence that climate change could make fungi more dangerousA team of medical researchers and infectious disease specialists affiliated with multiple institutions in China, working with a pair of colleagues, one from Singapore, the other from Canada, has found evidence bolstering theories that suggest as the planet warms, fungi could become more dangerous to humans.
Read more »
 Mexico's Highest-Ever Temperature Recorded by ScientistsMexico had the hottest day in its history last week, scientists claim, after the Sonoran Desert recorded temperatures at a high of 125 degrees.
Mexico's Highest-Ever Temperature Recorded by ScientistsMexico had the hottest day in its history last week, scientists claim, after the Sonoran Desert recorded temperatures at a high of 125 degrees.
Read more »
 Attractive People More Likely to Have Drinking Problems, Scientists Say'Young people who are perceived to have the most pleasing appearance generally drink more,' one researcher said.
Attractive People More Likely to Have Drinking Problems, Scientists Say'Young people who are perceived to have the most pleasing appearance generally drink more,' one researcher said.
Read more »
 Citizen scientists gather eDNA in water samples for global biodiversity censusKara Andres, a postdoctoral fellow with the Living Earth Collaborative at Washington University in St. Louis, collected samples of water from Simpson Lake, in Valley Park, Mo., as part of a coordinated global effort to use environmental DNA—genetic material shed by organisms into the environment—to document the current state of biodiversity.
Citizen scientists gather eDNA in water samples for global biodiversity censusKara Andres, a postdoctoral fellow with the Living Earth Collaborative at Washington University in St. Louis, collected samples of water from Simpson Lake, in Valley Park, Mo., as part of a coordinated global effort to use environmental DNA—genetic material shed by organisms into the environment—to document the current state of biodiversity.
Read more »
 Hypersexual ‘zombie’ cicadas infected with parasitic fungus being collected by scientistsScientists are continuing to study the fungus Massospora cicadina on specimen of infected cicadas as the insects emerge across the country this summer.
Hypersexual ‘zombie’ cicadas infected with parasitic fungus being collected by scientistsScientists are continuing to study the fungus Massospora cicadina on specimen of infected cicadas as the insects emerge across the country this summer.
Read more »
