The Steamboat Willie version of Mickey Mouse is coming to Disney Speedstorm in the summer.
The new racer, simply named Steamboat Mickey, was announced by Disney’s official fan club D23, which tweeted artwork of the black-and-white character.Although the tweet doesn’t say so in the text, the accompanying image confirms that Steamboat Mickey will feature as part of the game’s second season of content.Disney Speedstorm launched on Tuesday and its first season is set to end on 5 June, meaning Season 2 will start in early June and last through the rest of the summer.
The game’s first season has a Monsters Inc theme, and adds a track based on the first movie as well as four characters from the series – Mike, Sulley, Celia and Randall.
United Kingdom Latest News, United Kingdom Headlines
Similar News:You can also read news stories similar to this one that we have collected from other news sources.
 Transfer of nuclear and ribosomal material from Sox10-lineage cells to neurons in the mouse brainMayrhofer et al. report that neurons in the mouse central nervous system receive nuclear and ribosomal material from Sox10-lineage cells. They identified nuclea
Transfer of nuclear and ribosomal material from Sox10-lineage cells to neurons in the mouse brainMayrhofer et al. report that neurons in the mouse central nervous system receive nuclear and ribosomal material from Sox10-lineage cells. They identified nuclea
Read more »
 Topographical mapping of catecholaminergic axon innervation in the flat-mounts of the mouse atria: a quantitative analysis - Scientific ReportsScientific Reports - Topographical mapping of catecholaminergic axon innervation in the flat-mounts of the mouse atria: a quantitative analysis
Topographical mapping of catecholaminergic axon innervation in the flat-mounts of the mouse atria: a quantitative analysis - Scientific ReportsScientific Reports - Topographical mapping of catecholaminergic axon innervation in the flat-mounts of the mouse atria: a quantitative analysis
Read more »
 Enriched binocular experience followed by sleep optimally restores binocular visual cortical responses in a mouse model of amblyopia - Communications BiologyIn a mouse model of amblyopia, binocular sight conditions (including time for sleep) lead to a better recovery of visual function.
Enriched binocular experience followed by sleep optimally restores binocular visual cortical responses in a mouse model of amblyopia - Communications BiologyIn a mouse model of amblyopia, binocular sight conditions (including time for sleep) lead to a better recovery of visual function.
Read more »
 MiR-3180 inhibits hepatocellular carcinoma growth and metastasis by targeting lipid synthesis and uptake - Cancer Cell InternationalPurpose Reprogrammed lipid metabolism is a hallmark of cancer that provides energy, materials, and signaling molecules for rapid cancer cell growth. Cancer cells acquire fatty acids primarily through de novo synthesis and uptake. Targeting altered lipid metabolic pathways is a promising anticancer strategy. However, their regulators have not been fully investigated, especially those targeting both synthesis and uptake. Methods Immunohistochemistry was performed on samples from patients with hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) to establish the correlation between miR-3180, stearoyl-CoA desaturase-1 (SCD1), and CD36 expression, quantified via qRT-PCR and western blotting. The correlation was analyzed using a luciferase reporter assay. Cell proliferation, migration, and invasion were analyzed using CCK-8, wound healing, and transwell assays, respectively. Oil Red O staining and flow cytometry were used to detect lipids. Triglycerides and cholesterol levels were analyzed using a reagent test kit. CY3-labeled oleic acid transport was analyzed using an oleic acid transport assay. Tumor growth and metastasis were detected in vivo in a xenograft mouse model. Results MiR-3180 suppressed de novo fatty acid synthesis and uptake by targeting the key lipid synthesis enzyme SCD1 and key lipid transporter CD36. MiR-3180 suppressed HCC cell proliferation, migration, and invasion in an SCD1- and CD36-dependent manner in vitro. The mouse model demonstrated that miR-3180 inhibits HCC tumor growth and metastasis by inhibiting SCD1- and CD36-mediated de novo fatty acid synthesis and uptake. MiR-3180 expression was downregulated in HCC tissues and negatively correlated with SCD1 and CD36 levels. Patients with high miR-3180 levels showed better prognosis than those with low levels. Conclusions Our investigation indicates that miR-3180 is a critical regulator involved in de novo fatty acid synthesis and uptake, which inhibits HCC tumor growth and metastasis by suppressing SCD1 and CD36. Therefo
MiR-3180 inhibits hepatocellular carcinoma growth and metastasis by targeting lipid synthesis and uptake - Cancer Cell InternationalPurpose Reprogrammed lipid metabolism is a hallmark of cancer that provides energy, materials, and signaling molecules for rapid cancer cell growth. Cancer cells acquire fatty acids primarily through de novo synthesis and uptake. Targeting altered lipid metabolic pathways is a promising anticancer strategy. However, their regulators have not been fully investigated, especially those targeting both synthesis and uptake. Methods Immunohistochemistry was performed on samples from patients with hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) to establish the correlation between miR-3180, stearoyl-CoA desaturase-1 (SCD1), and CD36 expression, quantified via qRT-PCR and western blotting. The correlation was analyzed using a luciferase reporter assay. Cell proliferation, migration, and invasion were analyzed using CCK-8, wound healing, and transwell assays, respectively. Oil Red O staining and flow cytometry were used to detect lipids. Triglycerides and cholesterol levels were analyzed using a reagent test kit. CY3-labeled oleic acid transport was analyzed using an oleic acid transport assay. Tumor growth and metastasis were detected in vivo in a xenograft mouse model. Results MiR-3180 suppressed de novo fatty acid synthesis and uptake by targeting the key lipid synthesis enzyme SCD1 and key lipid transporter CD36. MiR-3180 suppressed HCC cell proliferation, migration, and invasion in an SCD1- and CD36-dependent manner in vitro. The mouse model demonstrated that miR-3180 inhibits HCC tumor growth and metastasis by inhibiting SCD1- and CD36-mediated de novo fatty acid synthesis and uptake. MiR-3180 expression was downregulated in HCC tissues and negatively correlated with SCD1 and CD36 levels. Patients with high miR-3180 levels showed better prognosis than those with low levels. Conclusions Our investigation indicates that miR-3180 is a critical regulator involved in de novo fatty acid synthesis and uptake, which inhibits HCC tumor growth and metastasis by suppressing SCD1 and CD36. Therefo
Read more »
 The usherin mutation c.2299delG leads to its mislocalization and disrupts interactions with whirlin and VLGR1 - Nature CommunicationsThe c.2299delG mutation in usherin causes loss of hearing and vision. Here, the authors show in a mouse model of this disease that the expression of mutant usherin leads to retinitis pigmentosa and structural defects in the photoreceptor cilium associated with mislocalization of VLGR1 and WHRN.
The usherin mutation c.2299delG leads to its mislocalization and disrupts interactions with whirlin and VLGR1 - Nature CommunicationsThe c.2299delG mutation in usherin causes loss of hearing and vision. Here, the authors show in a mouse model of this disease that the expression of mutant usherin leads to retinitis pigmentosa and structural defects in the photoreceptor cilium associated with mislocalization of VLGR1 and WHRN.
Read more »
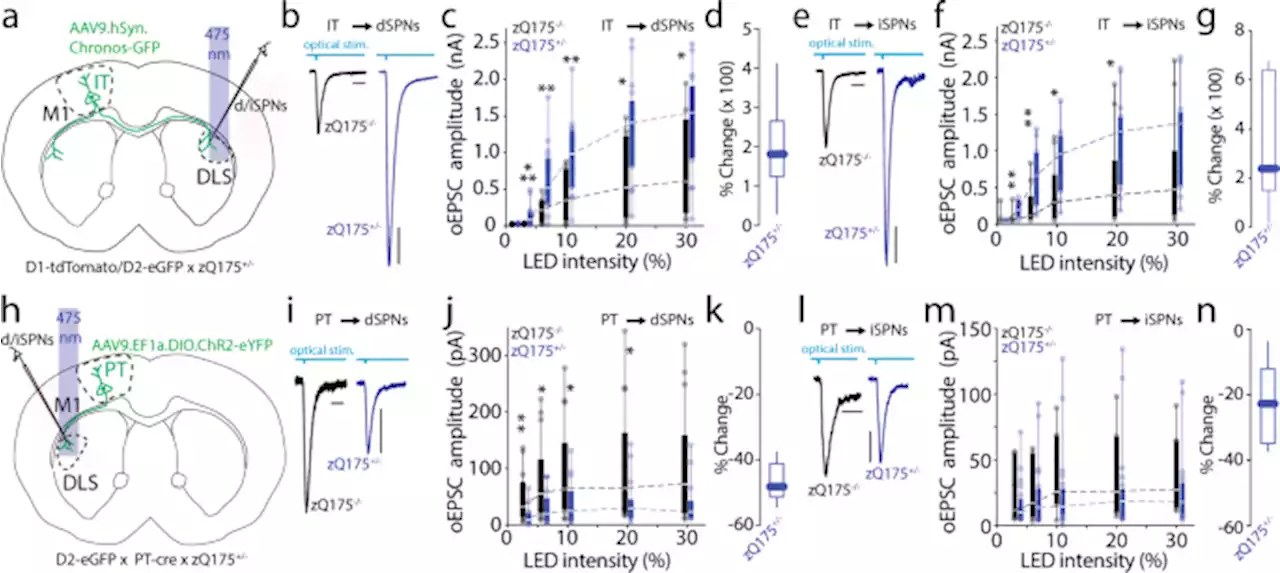 Cholinergic deficits selectively boost cortical intratelencephalic control of striatum in male Huntington’s disease model mice - Nature CommunicationsThe corticostriatal dysfunction underlying Huntington’s disease remains incompletely understood. Here, the authors find increased intratelencephalic connectivity resulting from deficient cholinergic transmission in a mouse model of Huntington’s disease.
Cholinergic deficits selectively boost cortical intratelencephalic control of striatum in male Huntington’s disease model mice - Nature CommunicationsThe corticostriatal dysfunction underlying Huntington’s disease remains incompletely understood. Here, the authors find increased intratelencephalic connectivity resulting from deficient cholinergic transmission in a mouse model of Huntington’s disease.
Read more »
