Scientists have generated a comprehensive map of the gene targets regulated by the transcription factors HNF4A and HNF1A in human pancreatic beta cells and liver cells.
Agency for Science, Technology and Research , SingaporeJun 26 2024 Published in the journal Nature Communications, the study revealed common and tissue-specific molecular pathways regulated by HNF4A and HNF1A, two proteins that possess important functions governing the development and function of the pancreas and liver.
The research team, led by Dr Adrian Teo, Senior Principal Investigator at A*STAR's Institute of Molecular and Cell Biology , used the cutting-edge technique of chromatin immunoprecipitation sequencing to map the genomic binding sites of HNF4A and HNF1A in stem cell-derived models of human pancreatic and liver cells, and in primary human islets.
Zooming in on the pancreatic beta cell targets, the scientists shortlisted several high-confidence genes directly bound and regulated by HNF4A, including HAAO and USH1C, which have not been previously characterized in beta cells. They showed that loss of HAAO or USH1C led to impaired glucose-stimulated insulin secretion in human beta cells, indicating that these genes regulate beta cell function.
Gene Transcription Transcription Factors Cell Cell Biology CHIP Chromatin Genes Genetic Immunoprecipitation Insulin Liver Pancreas Research Technology Type 2 Diabetes
United Kingdom Latest News, United Kingdom Headlines
Similar News:You can also read news stories similar to this one that we have collected from other news sources.
 Diabetes 'cure' discovered by scientists for the first time in brand new studyResearchers say they have 'cured' a man of type 2 diabetes through successful cell transplantation, with more tests planned going forward.
Diabetes 'cure' discovered by scientists for the first time in brand new studyResearchers say they have 'cured' a man of type 2 diabetes through successful cell transplantation, with more tests planned going forward.
Read more »
 Study may facilitate the development of new personalized treatments for schizophrenia An International Study Publi...An international study led by the Hospital del Mar Medical Research Institute, in collaboration with researchers from the Neuropsychopharmacology Group at the University of the Basque Country (UPV/EHU) and researchers from the CIBER of Mental Health (CIBERSAM), and published in Nature Communications, may facilitate the creation of new personalized...
Study may facilitate the development of new personalized treatments for schizophrenia An International Study Publi...An international study led by the Hospital del Mar Medical Research Institute, in collaboration with researchers from the Neuropsychopharmacology Group at the University of the Basque Country (UPV/EHU) and researchers from the CIBER of Mental Health (CIBERSAM), and published in Nature Communications, may facilitate the creation of new personalized...
Read more »
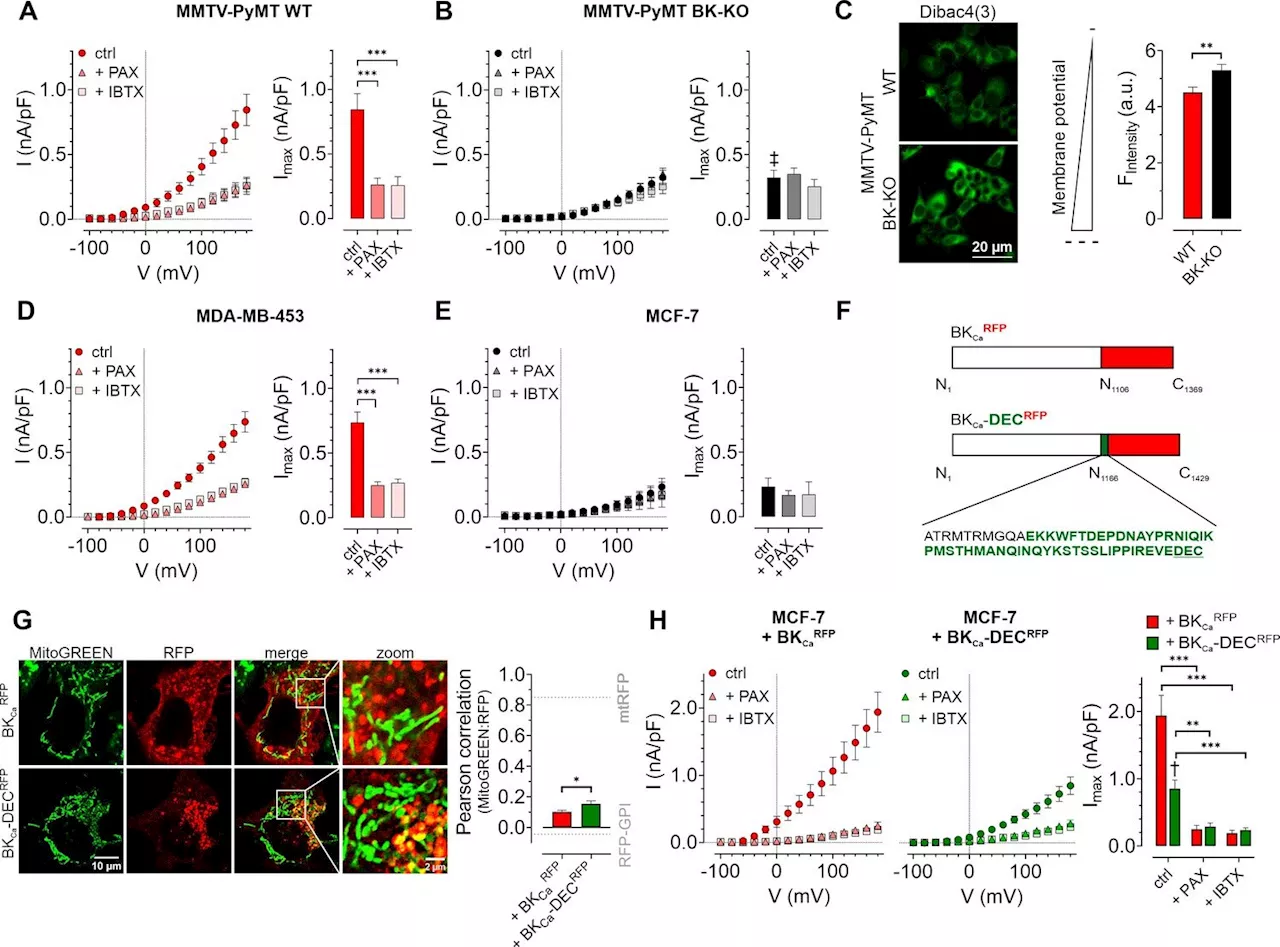 Scientists reveal how a potassium ion channel reprograms energy production in cancer cellsResearchers have revealed how a channel that controls cellular potassium levels causes metabolic rewiring in breast cancer cells, promoting tumor growth.
Scientists reveal how a potassium ion channel reprograms energy production in cancer cellsResearchers have revealed how a channel that controls cellular potassium levels causes metabolic rewiring in breast cancer cells, promoting tumor growth.
Read more »
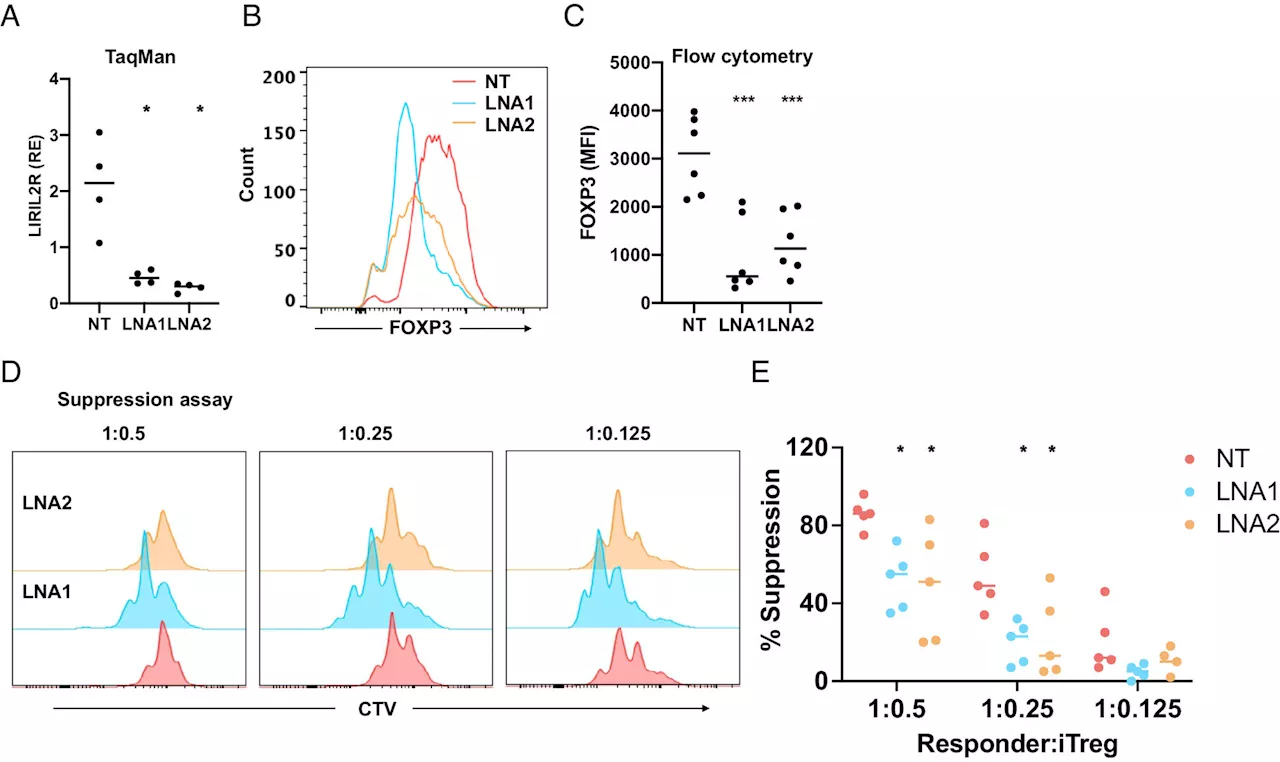 Scientists discover a novel modulator of human regulatory T cellsThe research group of Professor Riitta Lahesmaa have discovered a novel modulator for human regulatory T cells. This novel regulator can strengthen or dampen immune response and provides a new basis for therapeutic approaches for immune mediated diseases.
Scientists discover a novel modulator of human regulatory T cellsThe research group of Professor Riitta Lahesmaa have discovered a novel modulator for human regulatory T cells. This novel regulator can strengthen or dampen immune response and provides a new basis for therapeutic approaches for immune mediated diseases.
Read more »
 Scientists discover how the physics of colon cancer cells contributes to metastasisA study led by the Institute for Bioengineering of Catalonia (IBEC) has investigated how the mechanical properties of different types of colorectal cancer cells influence the process of metastasis.
Scientists discover how the physics of colon cancer cells contributes to metastasisA study led by the Institute for Bioengineering of Catalonia (IBEC) has investigated how the mechanical properties of different types of colorectal cancer cells influence the process of metastasis.
Read more »
 Heart failure triggers multimorbidity by altering stem cells, study revealsResearchers identified that heart failure (HF) promotes multimorbidity by altering hematopoietic stem cells (HSCs) to produce pro-inflammatory macrophages, increasing vulnerability in multiple organs. The study highlights the role of suppressed TGF-β signaling in these alterations, contributing to chronic inflammation and subsequent health issues.
Heart failure triggers multimorbidity by altering stem cells, study revealsResearchers identified that heart failure (HF) promotes multimorbidity by altering hematopoietic stem cells (HSCs) to produce pro-inflammatory macrophages, increasing vulnerability in multiple organs. The study highlights the role of suppressed TGF-β signaling in these alterations, contributing to chronic inflammation and subsequent health issues.
Read more »