A recent Cell journal review explores key immunological assumptions to enhance our understanding of vaccine design, autoimmune responses, and immune system pathology, aiming to refine intervention strategies and theoretical frameworks in immunology.
By Vijay Kumar MalesuApr 28 2024Reviewed by Susha Cheriyedath, M.Sc. In a recent review published in the journal Cell , a group of authors explored existing immunological assumptions to better understand unresolved phenomena and improve vaccine design, autoimmune response management, and immune system pathology.The immune system, crucial for defending against pathogens, consists of innate and adaptive components.
Exploring the complexities of immune memory Immune memory, crucial for adaptive immunity, involves storing long-term information about pathogens, focusing on what is stored, how, and for how long. Traditional views highlight antigen-specificity, where memory cells retain details about antigen identity and infection characteristics. The concept extends to associative and reinforcement learning, where the immune system adjusts based on the success or failure of responses.
Protective immunity Protective immunity is characterized not just by its intensity or the types of effector mechanisms it involves but by its ultimate success in safeguarding the host against the adverse outcomes of infections, including morbidity and mortality. This form of immunity might not always require the complete elimination of pathogens; in some cases, coexistence proves less harmful than the effects of an aggressive immune response aimed at total pathogen clearance.
Vaccine Antibodies Antigen Cell Eukaryotes Immune Response Immunity Immunology Pathogen Pathology Prokaryotes Research Respiratory SARS SARS-Cov-2
United Kingdom Latest News, United Kingdom Headlines
Similar News:You can also read news stories similar to this one that we have collected from other news sources.
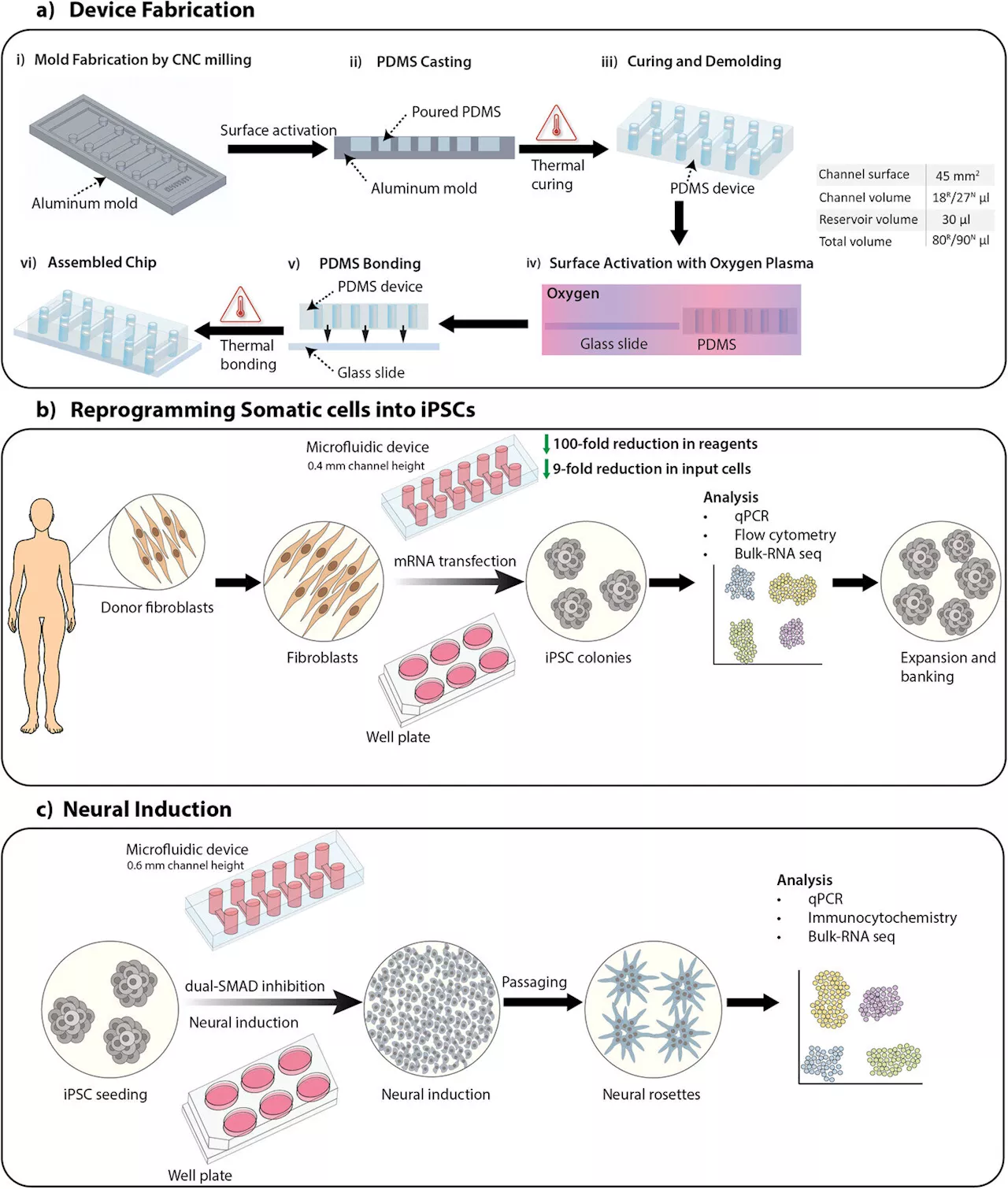 New device improves stem cell generation and chance for accessible Alzheimer's cell therapyResearchers in Sweden say they have improved on a technique for converting regular skin cells into neural stem cells—an advance that they say helps close the gap for accessible personalized cell-based therapies for Alzheimer's and Parkinson's.
New device improves stem cell generation and chance for accessible Alzheimer's cell therapyResearchers in Sweden say they have improved on a technique for converting regular skin cells into neural stem cells—an advance that they say helps close the gap for accessible personalized cell-based therapies for Alzheimer's and Parkinson's.
Read more »
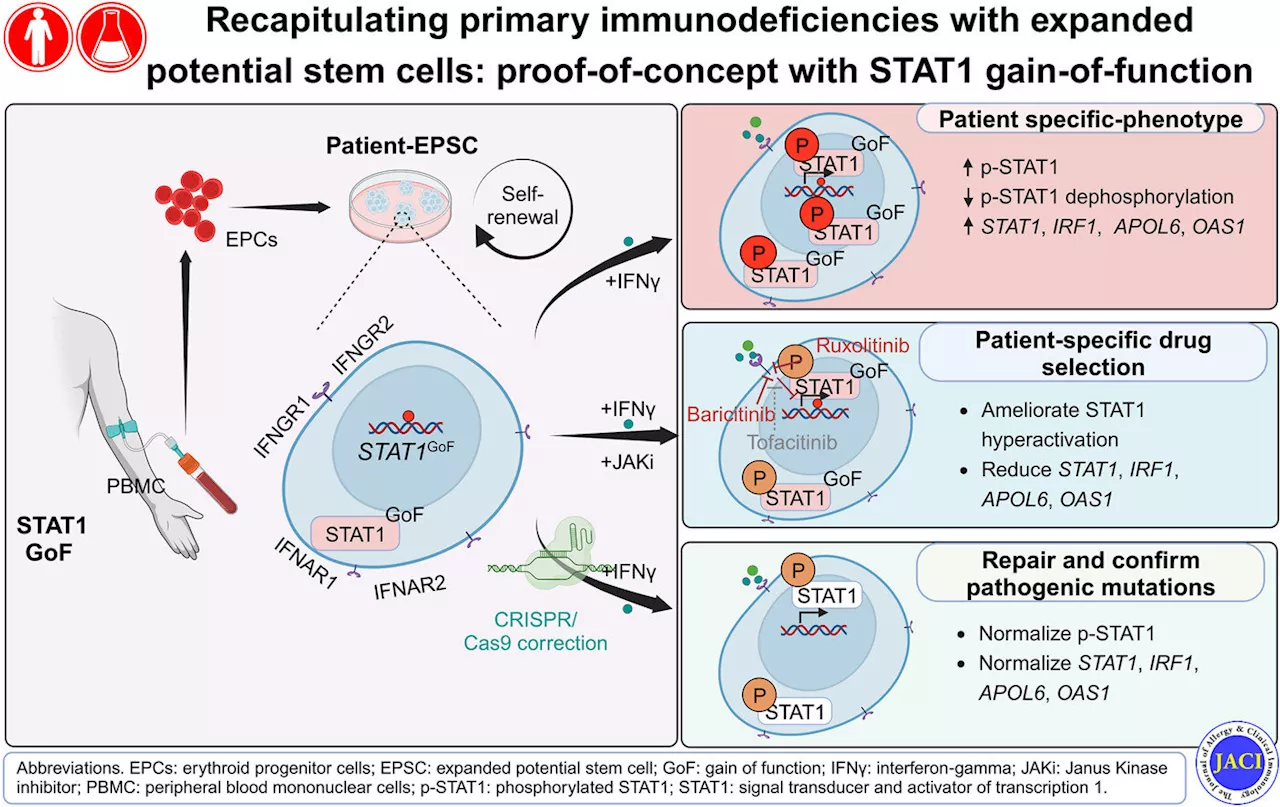 New stem cell model can help personalize stem cell treatment for immunodeficiency patientsA collaborative research team has pioneered a new stem cell model to help personalize treatment for patients suffering from rare forms of immunodeficiency. The research findings were published in the Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology.
New stem cell model can help personalize stem cell treatment for immunodeficiency patientsA collaborative research team has pioneered a new stem cell model to help personalize treatment for patients suffering from rare forms of immunodeficiency. The research findings were published in the Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology.
Read more »
 CD7 CAR T-cell therapy, stem-cell transplant beneficial for CD7-positive tumorsFor patients with relapsed or refractory CD7-positive leukemia or lymphoma, sequential CD7 chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T-cell therapy followed by haploidentical hematopoietic stem-cell transplantation (HSCT) is safe and effective, with remission seen for most patients, according to a study published in the New England Journal of Medicine.
CD7 CAR T-cell therapy, stem-cell transplant beneficial for CD7-positive tumorsFor patients with relapsed or refractory CD7-positive leukemia or lymphoma, sequential CD7 chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T-cell therapy followed by haploidentical hematopoietic stem-cell transplantation (HSCT) is safe and effective, with remission seen for most patients, according to a study published in the New England Journal of Medicine.
Read more »
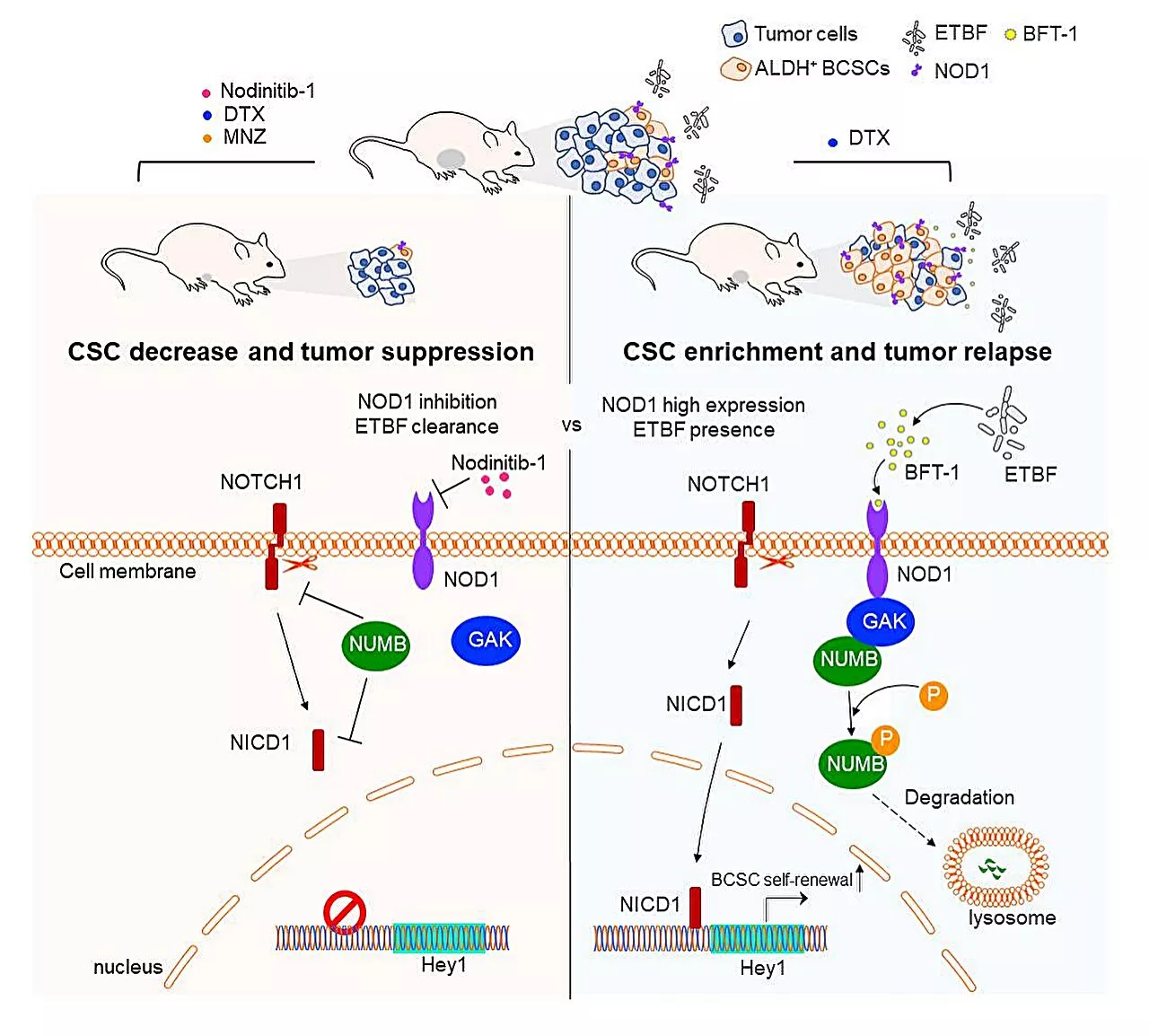 Microbiota B. fragilis-secreted BFT-1 promotes breast cancer cell stemness and chemoresistance: StudyTumor-resident microbiota in breast cancer promotes both the initiation and progression of cancer. However, the potential of targeting microbiota to enhance the efficacy of breast cancer treatment has not been comprehensively explored.
Microbiota B. fragilis-secreted BFT-1 promotes breast cancer cell stemness and chemoresistance: StudyTumor-resident microbiota in breast cancer promotes both the initiation and progression of cancer. However, the potential of targeting microbiota to enhance the efficacy of breast cancer treatment has not been comprehensively explored.
Read more »
 Study finds lower relapse risk in triple-negative breast cancer with high immune cell levelsWomen with triple-negative breast cancer, and high levels of immune cells in the tumors, have a lower relapse risk after surgery, even without chemotherapy, according to a recent study published in JAMA.
Study finds lower relapse risk in triple-negative breast cancer with high immune cell levelsWomen with triple-negative breast cancer, and high levels of immune cells in the tumors, have a lower relapse risk after surgery, even without chemotherapy, according to a recent study published in JAMA.
Read more »
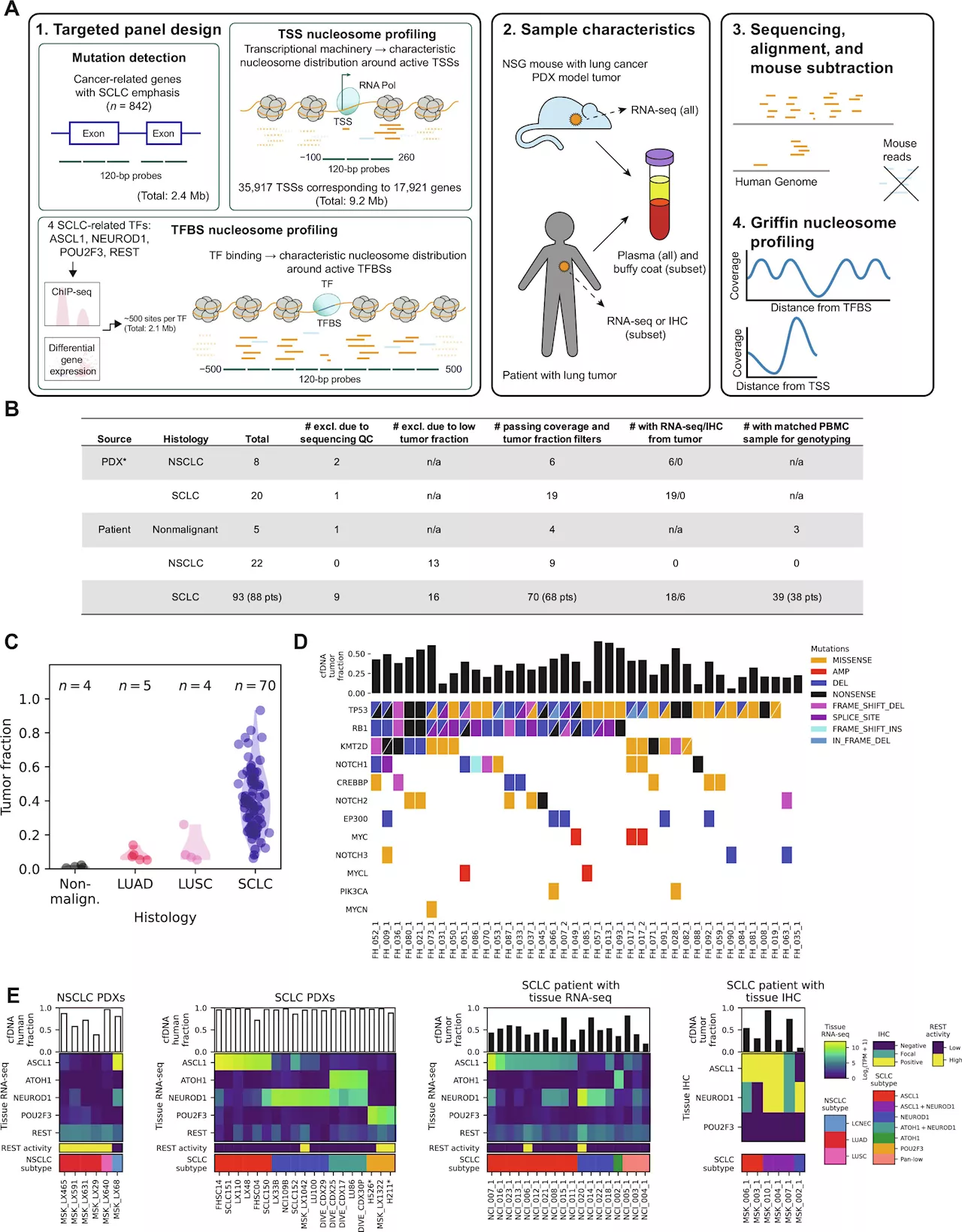 Study suggests liquid biopsy could detect and monitor aggressive small-cell lung cancerA new lab assay developed by researchers at Fred Hutch Cancer Center could make diagnosis and treatment of small-cell lung cancer and non-small cell lung cancer easier. The work is published in the journal Science Advances.
Study suggests liquid biopsy could detect and monitor aggressive small-cell lung cancerA new lab assay developed by researchers at Fred Hutch Cancer Center could make diagnosis and treatment of small-cell lung cancer and non-small cell lung cancer easier. The work is published in the journal Science Advances.
Read more »