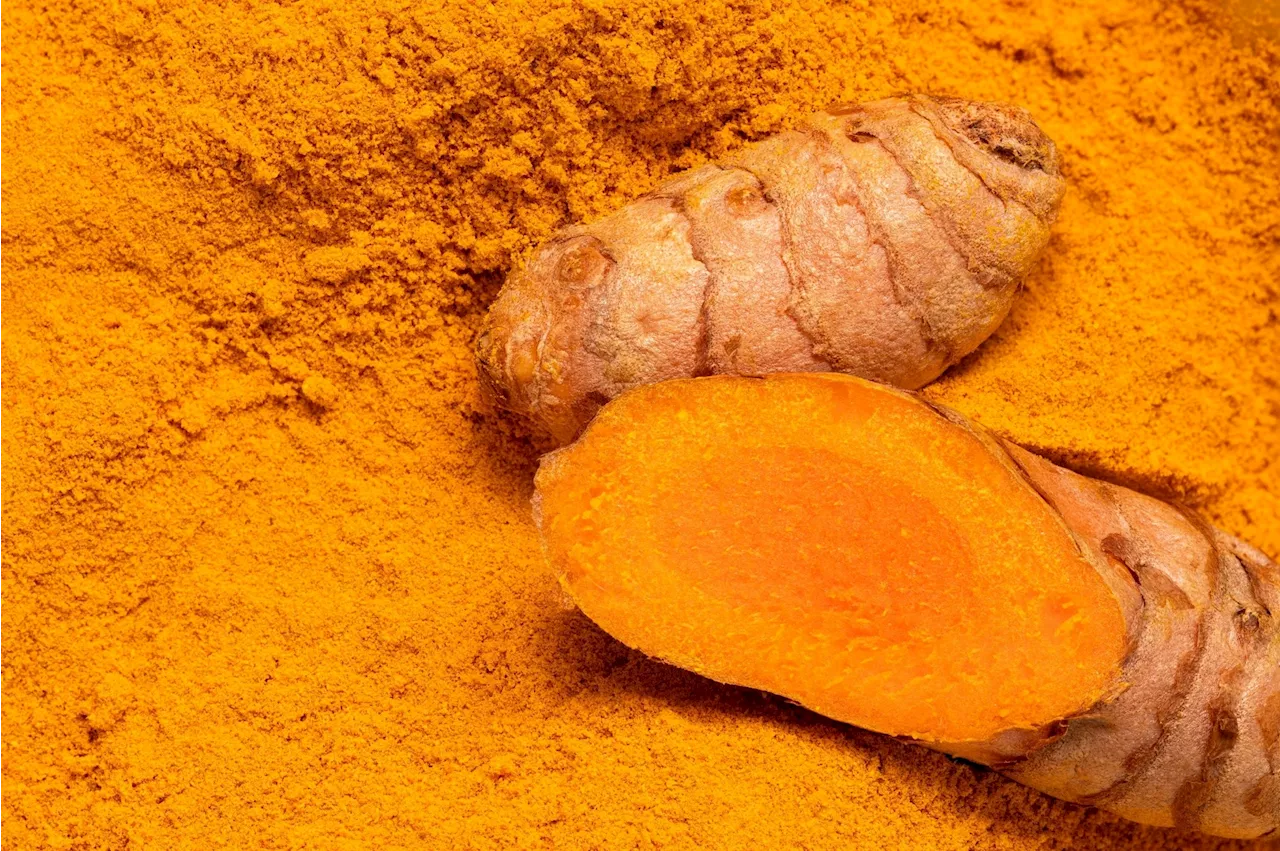
A randomized clinical trial (RCT) to investigate the effectiveness of curcumin in lowering depression among obese individuals with diabetes mellitus type 2 (T2DM).
By Pooja Toshniwal PahariaReviewed by Lily Ramsey, LLMJul 30 2024 In a recent study published in Nutrients , researchers performed a randomized clinical trial to investigate the effectiveness of curcumin in lowering depression among obese individuals with diabetes mellitus type 2 .
T2DM and depression coexist in a bidirectional manner, with those afflicted facing disability-related job loss, noncompliance with medical treatment, and increased mortality risks. The study excluded individuals with type 1 diabetes, metabolic syndrome, glucose tolerance impairment, maturity-onset diabetes of the young , dyslipidemia, gestational diabetes, severe hypertension, and those taking insulin injections or antidiabetic medicines apart from metformin.
The researchers assessed depression, the primary study outcome, using the Patient Health Questionnaire-9 . They withdrew participant blood to measure biomarkers at baseline and three months, six months, nine months, and one year.The researchers performed enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays to evaluate serum serotonin levels and Homeostatic Model Assessment of Insulin Resistance to assess insulin resistance.
RANSEL, RANSOD, and TAS were enhanced among curcumin consumers, whereas the placebo group showed higher MDA .
Curcumin Diabetes Type 2 Diabetes Anti-Inflammatory Antioxidant Anxiety Biomarker Blood Cardiometabolic Cell Chronic Clinical Trial Creatinine Depression Depressive Disorder Diabetes Mellitus Diet Disability Exercise Fasting Glucose Hba1c Insulin Insulin Resistance Major Depressive Disorder Mortality Nutrients Oxidative Stress Placebo Public Health Serotonin Stress Turmeric
United Kingdom Latest News, United Kingdom Headlines
Similar News:You can also read news stories similar to this one that we have collected from other news sources.
 Link between type 2 diabetes mellitus and spinal degenerative disorder may be method-dependentThe association between type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) and spinal degenerative disorders (SDDs) may be method-dependent, according to a study published online July 3 in The Journal of Bone & Joint Surgery.
Link between type 2 diabetes mellitus and spinal degenerative disorder may be method-dependentThe association between type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) and spinal degenerative disorders (SDDs) may be method-dependent, according to a study published online July 3 in The Journal of Bone & Joint Surgery.
Read more »
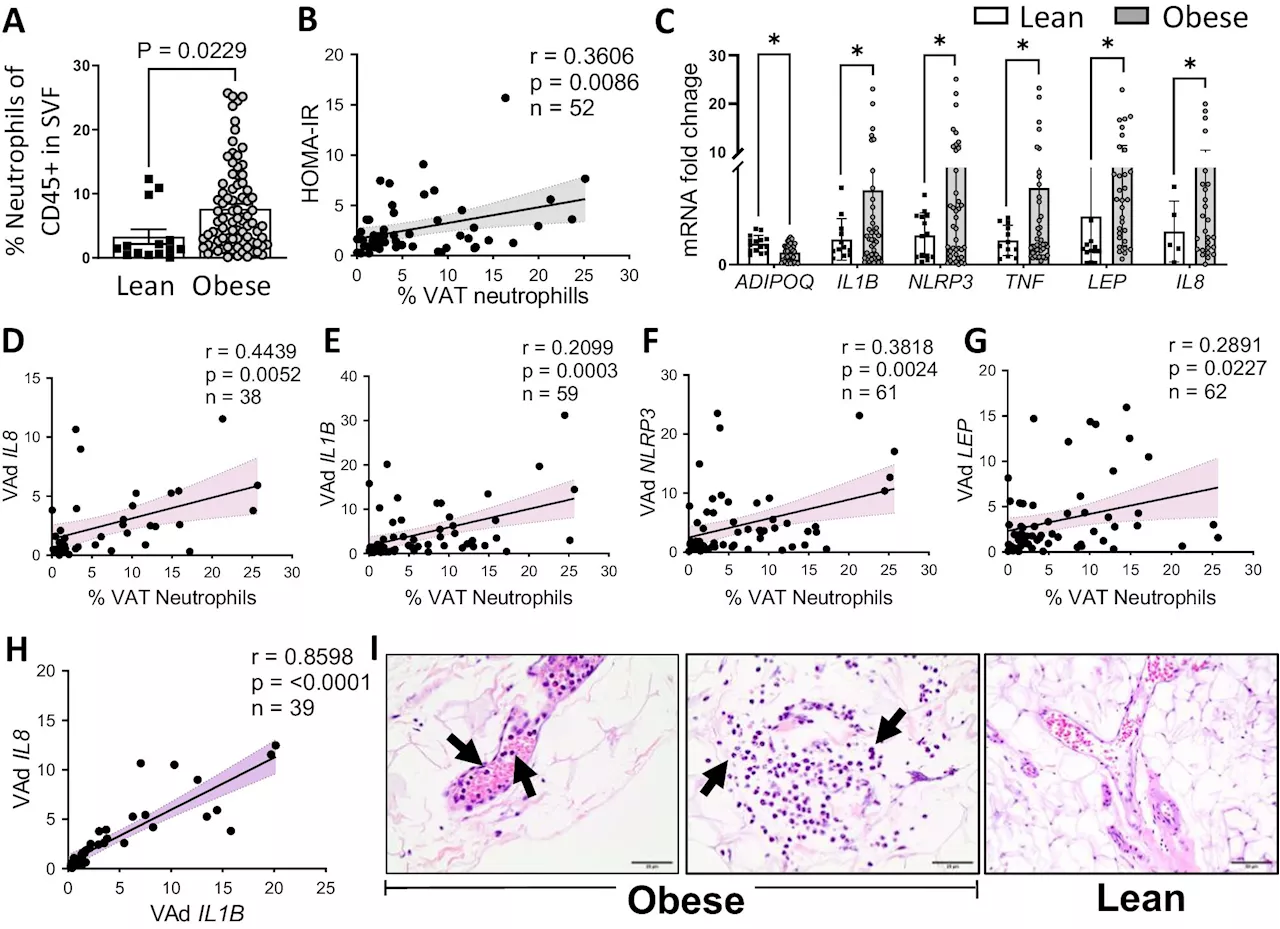 Study finds obese patients have more neutrophils than those who are not obeseObesity is an epidemic within the United States, with more than 70% of the adult population being overweight or obese.
Study finds obese patients have more neutrophils than those who are not obeseObesity is an epidemic within the United States, with more than 70% of the adult population being overweight or obese.
Read more »
 Weight loss reduces risky decisions and boosts mood in highly obese individuals, study findsResearchers examine how significant weight loss in highly obese individuals influences their metabolism, psychological state, and decision-making processes.
Weight loss reduces risky decisions and boosts mood in highly obese individuals, study findsResearchers examine how significant weight loss in highly obese individuals influences their metabolism, psychological state, and decision-making processes.
Read more »
 Gut microbiota essential for PAHSAs' metabolic benefits in obese mice, study findsDietary lipids play an essential role in regulating the function of the gut microbiota and gastrointestinal tract, and these luminal interactions contribute to mediating host metabolism.
Gut microbiota essential for PAHSAs' metabolic benefits in obese mice, study findsDietary lipids play an essential role in regulating the function of the gut microbiota and gastrointestinal tract, and these luminal interactions contribute to mediating host metabolism.
Read more »
 Study reveals laboratory predictors of periprosthetic joint infection in morbidly obese patientsFor patients with severe obesity undergoing knee or hip replacement, commonly obtained laboratory values – including markers of anemia and inflammation – are independent predictors of the risk of periprosthetic joint infection (PJI), reports a study in The Journal of Bone & Joint Surgery.
Study reveals laboratory predictors of periprosthetic joint infection in morbidly obese patientsFor patients with severe obesity undergoing knee or hip replacement, commonly obtained laboratory values – including markers of anemia and inflammation – are independent predictors of the risk of periprosthetic joint infection (PJI), reports a study in The Journal of Bone & Joint Surgery.
Read more »
