Researchers have reported finding major differences between postmortem and living prefrontal cortex brain tissues as they relate to one of the most abundant RNA modifications in the brain, known as adenosine-to-inosine (A-to-I) editing.
Study reveals significant differences in RNA editing between postmortem and living human brain." ScienceDaily. ScienceDaily, 28 June 2024. <www.sciencedaily.comThe Mount Sinai Hospital / Mount Sinai School of Medicine. . Study reveals significant differences in RNA editing between postmortem and living human brain.The Mount Sinai Hospital / Mount Sinai School of Medicine."Study reveals significant differences in RNA editing between postmortem and living human brain.
Engineers have discovered that some brain cells age more rapidly than others, and they are disproportionately abundant in individuals afflicted with Alzheimer's disease. Additionally, researchers ... The brain registers what we see even if we are not consciously aware of it. We even react emotionally to the content. How is this possible? A new experiment reveals that, while various regions of the ...
Researchers have catalogued thousands of sites in the brain where RNA is modified throughout the human lifespan in a process known as adenosine-to-inosine editing, offering important new ... While the overall experience is stored in the hippocampus, the brain structure long considered the seat of memory, individual details are parsed and stored elsewhere, in the prefrontal cortex. This ...Research on the Visual Rabbit Illusion Takes a Leap Forward
Brain Injury Psychology Intelligence Neuroscience Disorders And Syndromes Autism Learning Disorders
United Kingdom Latest News, United Kingdom Headlines
Similar News:You can also read news stories similar to this one that we have collected from other news sources.
 Researchers develop RNA-targeting technology for precisely manipulating parts of human genesResearchers at the University of Toronto have harnessed a bacterial immune defense system, known as CRISPR, to efficiently and precisely control the process of RNA splicing.
Researchers develop RNA-targeting technology for precisely manipulating parts of human genesResearchers at the University of Toronto have harnessed a bacterial immune defense system, known as CRISPR, to efficiently and precisely control the process of RNA splicing.
Read more »
 Researchers develop RNA-targeting technology for precisely manipulating parts of human genesResearchers have harnessed a bacterial immune defense system, known as CRISPR, to efficiently and precisely control the process of RNA splicing. The technology opens the door to new applications, including systematically interrogating the functions of parts of genes and correcting splicing deficiencies that underlie numerous diseases and disorders.
Researchers develop RNA-targeting technology for precisely manipulating parts of human genesResearchers have harnessed a bacterial immune defense system, known as CRISPR, to efficiently and precisely control the process of RNA splicing. The technology opens the door to new applications, including systematically interrogating the functions of parts of genes and correcting splicing deficiencies that underlie numerous diseases and disorders.
Read more »
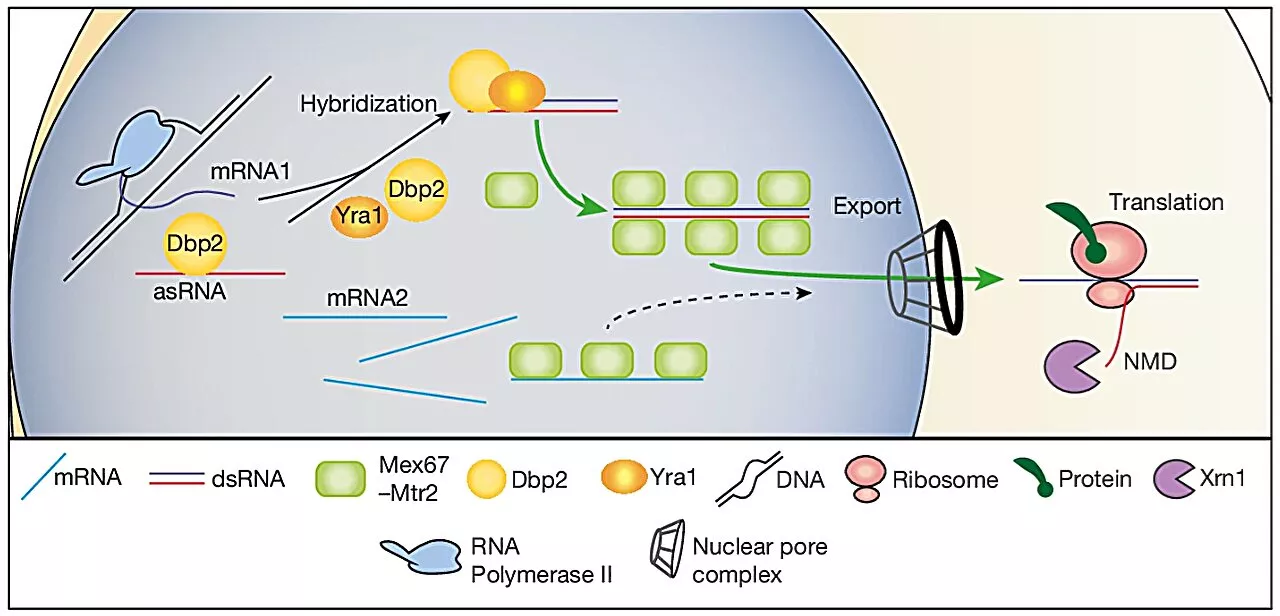 Non-coding RNA acts as 'superhighway' for gene expression, study findsThe function of non-coding RNA in the cell has long been a mystery to researchers. Unlike coding RNA, non-coding RNA does not produce proteins—yet it exists in large quantities.
Non-coding RNA acts as 'superhighway' for gene expression, study findsThe function of non-coding RNA in the cell has long been a mystery to researchers. Unlike coding RNA, non-coding RNA does not produce proteins—yet it exists in large quantities.
Read more »
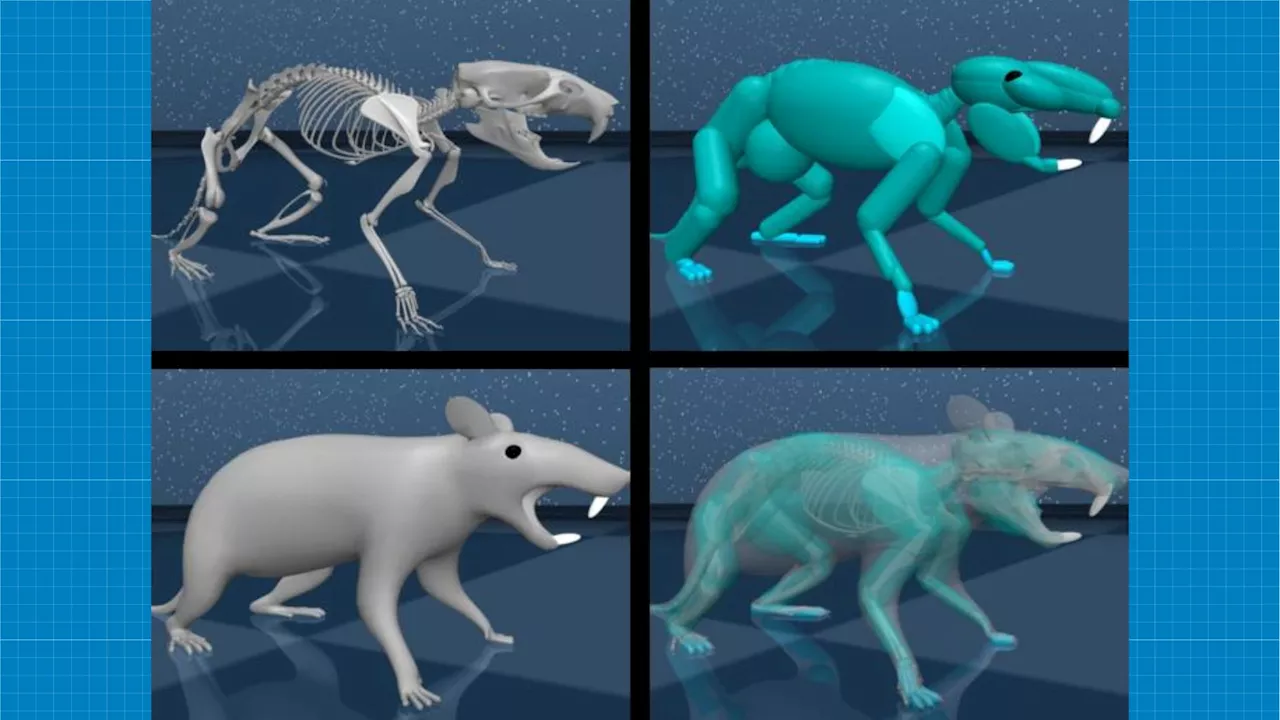 Harvard researchers create virtual rat model to study brain controlHarvard scientists, with Google's DeepMind AI lab, crafted a virtual rat model with an artificial brain mimicking natural movements.
Harvard researchers create virtual rat model to study brain controlHarvard scientists, with Google's DeepMind AI lab, crafted a virtual rat model with an artificial brain mimicking natural movements.
Read more »
 Protein study could help researchers develop new antibioticsA team has found a way to make the bacterial enzyme histidine kinase water-soluble, which could make it possible to rapidly screen potential antibiotics that might interfere with its functions.
Protein study could help researchers develop new antibioticsA team has found a way to make the bacterial enzyme histidine kinase water-soluble, which could make it possible to rapidly screen potential antibiotics that might interfere with its functions.
Read more »
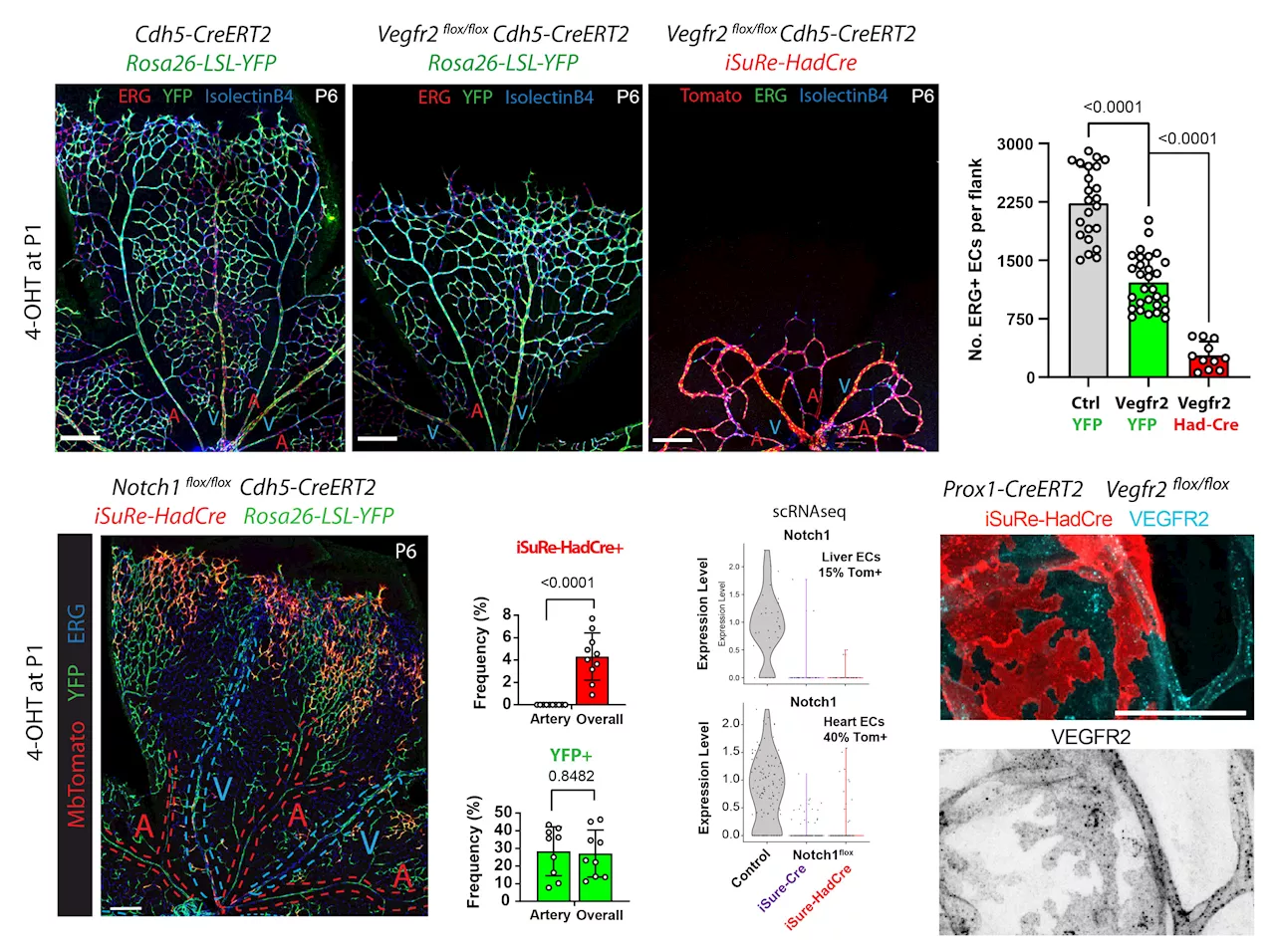 Researchers create an innovative tool for the reliable and efficient study of gene functionA team of scientists at the Centro Nacional de Investigaciones Cardiovasculares (CNIC) led by Rui Benedito has generated a novel genetic tool, called iSuRe-HadCre, that enables the induction of precise genetic alterations in whole tissues or in individual cells with high efficiency and reliability.
Researchers create an innovative tool for the reliable and efficient study of gene functionA team of scientists at the Centro Nacional de Investigaciones Cardiovasculares (CNIC) led by Rui Benedito has generated a novel genetic tool, called iSuRe-HadCre, that enables the induction of precise genetic alterations in whole tissues or in individual cells with high efficiency and reliability.
Read more »
