A mother's contribution to the makeup of a newborn baby's microbiota has been well documented. Now a new article shows the important contributions that fathers make to the composition of microorganisms colonizing a baby's gut as well.
Study shows role of fathers in seeding the microbiota of newborns and confirms benefits of maternal fecal microbiota transplants." ScienceDaily. ScienceDaily, 12 June 2024. <www.sciencedaily.comCell Press. . Study shows role of fathers in seeding the microbiota of newborns and confirms benefits of maternal fecal microbiota transplants.Cell Press."Study shows role of fathers in seeding the microbiota of newborns and confirms benefits of maternal fecal microbiota transplants.
Do cesarean-born babies miss out on essential microbes? New evidence suggests that the answer may be 'no.' Researchers report that mothers are able to transfer microbes to their babies via ... A research group has developed a new method for studying the functionality of microbiota through metaproteomics. The new method poses broad potential for the study of microbiota on a new, functional ...
Birth by Cesarean section is detrimental to normal gut microbiota development. Researchers demonstrated that the intestinal microbiota development can be restored by postnatal, orally-delivered ... Babies born vaginally have different gut bacteria -- their microbiome -- than those delivered by caesarean, research has shown. Scientists discovered that whereas vaginally born babies got most of ...People Feel More Connected to 'Tweezer-Like' Bionic Tools That Don't Resemble Human Hands
Pregnancy And Childbirth Breastfeeding Down Syndrome Microbes And More Mice Biology Microbiology
United Kingdom Latest News, United Kingdom Headlines
Similar News:You can also read news stories similar to this one that we have collected from other news sources.
 Study shows magnesium oxide undergoes dynamic transition when it comes to super-Earth exoplanetsResearchers from Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) and Johns Hopkins University have unlocked new secrets about the interiors of super-Earth exoplanets, potentially revolutionizing our understanding of these distant worlds.
Study shows magnesium oxide undergoes dynamic transition when it comes to super-Earth exoplanetsResearchers from Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) and Johns Hopkins University have unlocked new secrets about the interiors of super-Earth exoplanets, potentially revolutionizing our understanding of these distant worlds.
Read more »
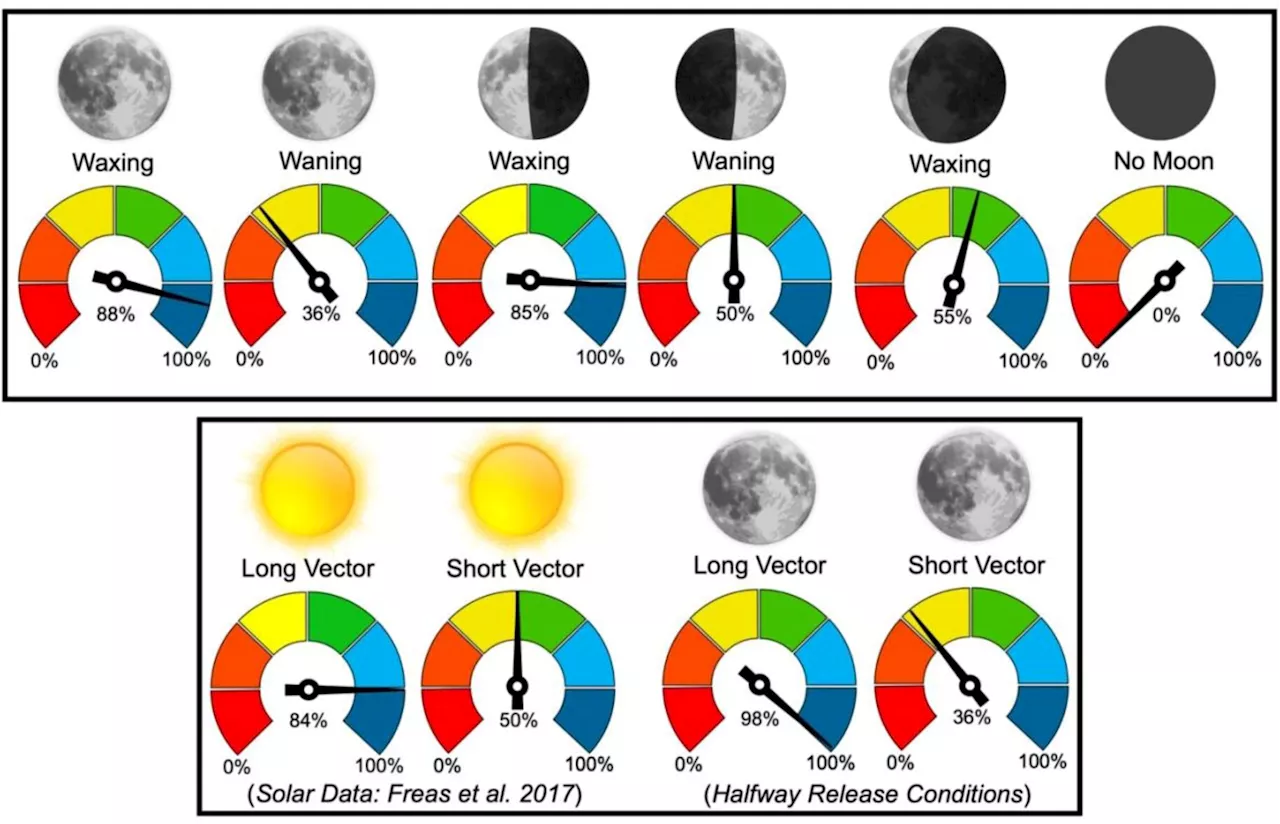 Ants detect and monitor low levels of moonlight to navigate at night, new study showsNocturnal bull ants can use low-level moonlight to navigate at night, according to new research.
Ants detect and monitor low levels of moonlight to navigate at night, new study showsNocturnal bull ants can use low-level moonlight to navigate at night, according to new research.
Read more »
 Fruit fly study shows that reproductive cells can renew chromosome-linking proteinsA Dartmouth study conducted on fruit flies reports the first evidence in any organism that oocytes—the cells that become eggs—regularly rejuvenate the critical protein linkages that bind chromosomes together.
Fruit fly study shows that reproductive cells can renew chromosome-linking proteinsA Dartmouth study conducted on fruit flies reports the first evidence in any organism that oocytes—the cells that become eggs—regularly rejuvenate the critical protein linkages that bind chromosomes together.
Read more »
 Cocaine trafficking threatens critical bird habitats, new study showsIn addition to its human consequences, cocaine trafficking harms the environment and threatens habitats important to dozens of species of migratory birds, according to a new study.
Cocaine trafficking threatens critical bird habitats, new study showsIn addition to its human consequences, cocaine trafficking harms the environment and threatens habitats important to dozens of species of migratory birds, according to a new study.
Read more »
 African elephants call each other by unique names, new study showsElephants responded more energetically to recordings that contained their names, and sometimes entirely ignored vocalizations addressed to others.
African elephants call each other by unique names, new study showsElephants responded more energetically to recordings that contained their names, and sometimes entirely ignored vocalizations addressed to others.
Read more »
 Texas is 10th-worst state for vehicle thefts, new study showsTexas is still the Wild West — at least when it comes to vehicle thefts.
Texas is 10th-worst state for vehicle thefts, new study showsTexas is still the Wild West — at least when it comes to vehicle thefts.
Read more »
